在使用传统的JDBC来编写代码时,很多时候需要去拼接SQL,这是一件很麻烦的事情,因为有些查询需要许多的条件,比如在查询用户时,需要根据用户名,年龄,性别或地址等信息进行查询,当不需要用户名查询时却依然使用用户名作为条件查询就不合适了,而如果使用大量的Java进行判断,那么代码的可读性比较差,又或者在拼接的时候,不注意哪里少了或多了个空格、符号,都会导致错误。而Mybatis提供了对SQL语句动态拼接的能力,可以让我们在 xml 映射文件内,以标签的形式编写动态 SQL,完成逻辑判断和动态拼接 SQL的功能。大量的判断都可以在Mybatis的映射xml文件里面配置,以达到许多需要大量代码才能实现的功能,从而大大减少了代码量。
Mybatis动态SQL语句是基于OGNL表达式的,主要有以下几类:
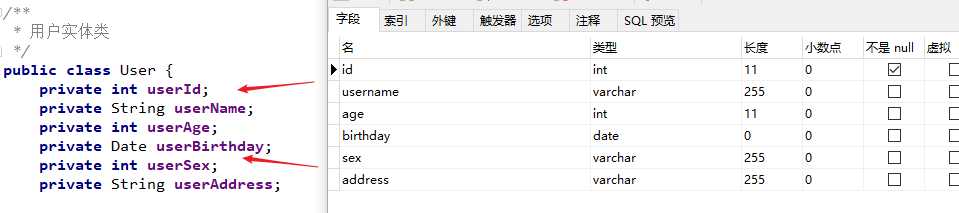
本章我们以 User 表为例来说明:
if 标签用来实现根据条件拼接sql语句,如果判断参数不为null,则拼接sql,否则不拼接。判断条件内容写在if标签的 test 属性中。示例如下:
<mapper namespace="com.thr.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="userMap" type="com.thr.pojo.User">
<id property="userId" column="id"/>
<result property="userName" column="username"/>
<result property="userAge" column="age"/>
<result property="userBirthday" column="birthday"/>
<result property="userSex" column="sex"/>
<result property="userAddress" column="address"/>
</resultMap>
<!--根据用户名和地址查询用户信息-->
<select id="selectUserByNameAndAddress" parameterType="user" resultMap="userMap">
select * from t_user where
<if test="userName!=null and userName!=‘‘">
username = #{userName}
</if>
<if test="userAddress!=null and userAddress!=‘‘">
and address = #{userAddress}
</if>
</select>
</mapper>上述代码当参数userName和userAddress都不为 null 时,拼接出的SQL语句为:select * from t_user where username = ? and address = ? 。但是如果上面的SQL语句中传入的参数 userName 为null,则拼接出的sql语句为:select * from t_user where and address = ? ,可以明显看到 where and 是错误的语法,导致报错,又或者是传入的两个参数都为null,那么拼接出的sql语句为:select * from t_user where ,这明显也是错误的语法,要解决这个问题,需要用到where标签。
<where>标签相当于SQL语句中的where关键字,而且where标签还有特殊的作用。作用如下:
上面的示例用where标签改写后示例如下:
<!--根据用户名和地址查询用户信息-->
<select id="selectUserByNameAndAddress" parameterType="user" resultMap="userMap">
select * from t_user
<where>
<if test="userName!=null and userName!=‘‘" >
and username = #{userName}
</if>
<if test="userAddress!=null and userAddress!=‘‘">
and address = #{userAddress}
</if>
</where>
</select>SQL语句等价于:select * from t_user where username = ? and address = ?
set标签的功能和 where 标签差不多,只是set 标签是用在更新操作的时候,作用如下:
使用set标签示例代码如下:
<!--修改用户名、年龄和地址-->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="user">
update t_user
<set>
<if test="userName!=null and userName!=‘‘">
username = #{userName},
</if>
<if test="userAge!=null and userAge!=‘‘">
age = #{userAge},
</if>
<if test="userAddress!=null and userAddress!=‘‘">
address = #{userAddress},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{userId}
</update>可以发现最后一个修改条件多了一个逗号(,),但set标签帮我们去掉了,SQL语句等价于:update t_user SET username = ?, age = ?, address = ? where id = ?
trim 元素的主要功能是可以在自己包含的内容前加上某些前缀,也可以在其后加上某些后缀,与之对应的属性是 prefix 和 suffix;可以把包含内容的首部某些内容去除,也可以把尾部的某些内容去除,对应的属性是 prefixOverrides 和 suffixOverrides;正因为 trim 有这样的功能,它可以用来实现 where 和 set 一样的效果。
trim标签的属性:
将前面where 标签示例用trim 标签代替:
<!--根据用户名和地址查询用户信息-->
<select id="selectUserByNameAndAddress" parameterType="user" resultMap="userMap">
select * from t_user
<!--<where>
<if test="userName!=null and userName!=‘‘" >
and username = #{userName}
</if>
<if test="userAddress!=null and userAddress!=‘‘">
and address = #{userAddress}
</if>
</where>-->
<!-- 插入prefix属性中指定的内容,并且移除首部所有指定在prefixOverrides属性中的内容-->
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and | or">
<if test="userName!=null and userName!=‘‘" >
and username = #{userName}
</if>
<if test="userAddress!=null and userAddress!=‘‘">
and address = #{userAddress}
</if>
</trim>
</select>将前面set 标签示例用trim 标签代替:
<!--修改用户名、年龄和地址-->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="user">
update t_user
<!--<set>
<if test="userName!=null and userName!=‘‘">
username = #{userName},
</if>
<if test="userAge!=null and userAge!=‘‘">
age = #{userAge},
</if>
<if test="userAddress!=null and userAddress!=‘‘">
address = #{userAddress},
</if>
</set>-->
<!-- 插入prefix属性中指定的内容,并且移除尾部所有指定在suffixOverrides属性中的内容-->
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="userName!=null and userName!=‘‘">
username = #{userName},
</if>
<if test="userAge!=null and userAge!=‘‘">
age = #{userAge},
</if>
<if test="userAddress!=null and userAddress!=‘‘">
address = #{userAddress},
</if>
</trim>
where id = #{userId}
</update>choose、when、otherwise标签是按顺序判断其内部 when 标签中的 test 条件出否成立,如果有一个成立,则choose结束,执行条件成立的SQL。当 choose 中所有 when 的条件都不满足时,则执行 otherwise 中的SQL,类似于Java中的switch…case…default语句。
示例代码如下:
<select id="selectUserByChoose" resultType="user" parameterMap="userMap">
select * from t_user
<where>
<choose>
<when test="userName!= null and userName!=‘‘">
username=#{userName}
</when>
<when test="userAddress!= null and userAddress!=‘‘">
and address=#{userAddress}
</when>
<otherwise>
and age=#{userAge}
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select> 虽然这种场景有点不切实际,但是我们这里主要集中如何使用这三个标签来实现即可![]() 。
。
foreach 标签主要用于遍历集合。通常是用来构建 IN 条件语句,也可用于其他情况下动态拼接sql语句。
foreach标签有以下几个属性:
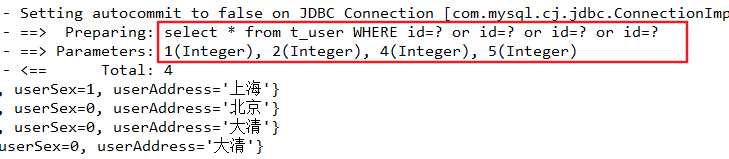
示例:如果现在有这样的需求:我们需要查询 t_user 表中 id 分别为1,2,4,5的用户。所对应的sql语句有这两条:select * from user where id=1 or id=2 or id=4 or id=5;和 select * from user where id in (1,2,4,5);。下面我们使用foreach标签来改写。
①、创建一个UserVo类,里面封装一个 List<Integer> ids 的属性,代码如下:
public class UserVo {
//封装多个id
private List<Integer> ids;
public List<Integer> getIds() {
return ids;
}
public void setIds(List<Integer> ids) {
this.ids = ids;
}
}②、foreach 来改写 select * from user where id=1 or id=2 or id=4 or id=5;代码如下:
<select id="selectUserByListId" parameterType="userVo" resultMap="userMap">
select * from t_user
<where>
<!--加个括号
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator="or">
id=#{id}
</foreach>-->
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="or">
id=#{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>测试代码如下:
@Test
public void testSelectUserByListId(){
UserVo userVo = new UserVo();
List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(1);
ids.add(2);
ids.add(4);
ids.add(5);
userVo.setIds(ids);
List<User> userList = mapper.selectUserByListId(userVo);
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}运行结果:
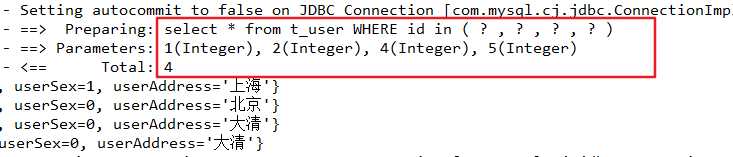
③、foreach 来改写 select * from user where id in (1,2,4,5);将上面的映射文件稍加修改:
<select id="selectUserByListId" parameterType="userVo" resultMap="userMap">
select * from t_user
<where>
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="id in (" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>运行结果:
bind 标签允许你在 OGNL 表达式以外创建一个变量,并将其绑定到当前的上下文(可定义多个)。示例代码如下:
<!-- 模糊查询,根据username字段查询用户-->
<select id="selectUserByName" parameterType="string" resultMap="userMap">
<bind name="pattern" value="‘%‘+_parameter+‘%‘"/>
select * from t_user where username like #{pattern}
</select>这里的”_parameter”代表的是传递进来的参数,它和通配符(%)连接后赋给了pattern,SQL语句等价于:select * from t_user where username like ?。这种方式无论是Mysql还是Oracle都可以使用这样的语句,提高了代码的可移植性。如果传递了多个参数,则可以定义多个bind 标签。
<select id="selectUserByNameAndAddress" parameterType="user" resultMap="userMap">
<bind name="pattern_username" value="‘%‘+userName+‘%‘"/>
<bind name="pattern_address" value="‘%‘+userAddress+‘%‘"/>
select * from t_user where username like #{pattern_username} and address like #{pattern_address}
</select>原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/tanghaorong/p/13960269.html