最近想写点,细小的知识点,从这些细小的知识点入手看看我们常用的一些spring方法是怎么实现的
一 初始化Bean的流程
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { if (instanceWrapper == null) { // 创建 Bean 实例 instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);//1 } ... synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) { if (!mbd.postProcessed) { try { // 调用 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 回调(在这里完成相关方法的扫描及保存) applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName); } mbd.postProcessed = true; } } // 初始化 Bean 实例 Object exposedObject = bean; try { populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);//2 // 在这里进行 @PostConstruct 方法的调用 exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);//3 } ... return exposedObject; }
对一个bean进行初始化分为3步
1 实例化,说白了new出来先 createBeanInstance
2 填充字段,比如@Autowired注解就在这里完成的,下一篇就分析@Autowired, populateBean
3 执行用户指定的,或者配置的@PostConstruct initializeBean
protected void applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor bdp = (MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) bp; bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName); } } }
那么对于 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 它的实现类有哪些呢
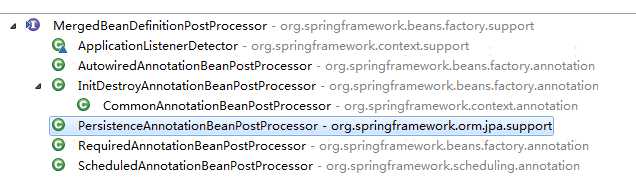
比如我们现在正在分析的@PostConstruct 对它进行处理的就是 InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor ,及其子类 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
@Override public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) { if (beanType != null) { LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(beanType); metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition); } }
private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) { if (this.lifecycleMetadataCache == null) { // Happens after deserialization, during destruction... return buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz); } // Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking. LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);//缓存这些东西不管,直接分析buildLifecycleMetadata if (metadata == null) { synchronized (this.lifecycleMetadataCache) { metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz); if (metadata == null) { metadata = buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz); this.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata); } return metadata; } } return metadata; }
private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) { final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled(); LinkedList<LifecycleElement> initMethods = new LinkedList<LifecycleElement>(); LinkedList<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new LinkedList<LifecycleElement>(); Class<?> targetClass = clazz; do { final LinkedList<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new LinkedList<LifecycleElement>(); final LinkedList<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new LinkedList<LifecycleElement>(); ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, new ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback() { @Override public void doWith(Method method) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException { if (initAnnotationType != null) { if (method.getAnnotation(initAnnotationType) != null) { LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method); currInitMethods.add(element); if (debug) { logger.debug("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method); } } }
initAnnotationType的值是什么呢?
在它的子类进行了赋值
public CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() { setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 3); setInitAnnotationType(PostConstruct.class); setDestroyAnnotationType(PreDestroy.class); ignoreResourceType("javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext"); }
重点看看,就是使用java反射得到全部的method,然后调用接口 MethodCallback的实现逻辑
public static void doWithLocalMethods(Class<?> clazz, MethodCallback mc) { Method[] methods = getDeclaredMethods(clazz); for (Method method : methods) { try { mc.doWith(method); } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Not allowed to access method ‘" + method.getName() + "‘: " + ex); } } }
判断某一个方法是否有注解 PostConstruct,有就先构造成LifecycleElement,并放入currInitMethods,缓存起来
if (initAnnotationType != null) { if (method.getAnnotation(initAnnotationType) != null) { LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method); currInitMethods.add(element);
最后把这些信息封装一下
return new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods);
还要进行一次缓存
private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) { if (this.lifecycleMetadataCache == null) { // Happens after deserialization, during destruction... return buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz); } // Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking. LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz); if (metadata == null) { synchronized (this.lifecycleMetadataCache) { metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz); if (metadata == null) { metadata = buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz); this.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata);//缓存起来 } return metadata; } } return metadata; }
数据准备部分就分析好了
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/juniorMa/p/13970718.html