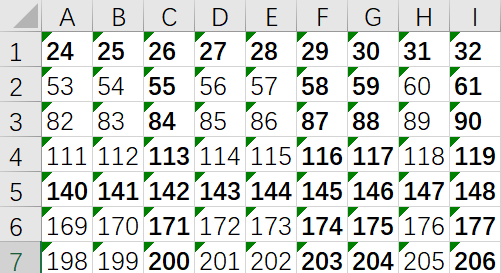
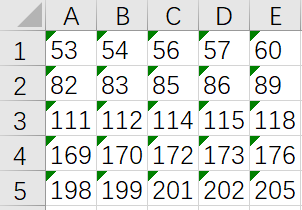
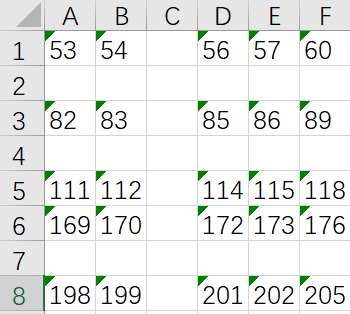
现在有个r行c列(1<=r,c<=50)的表格,行从上到下编号为1r,列从左到右编号为1c。如图a,如果先删除第1,5行,再删除3,6,7,9列,结果如图b所示。接下来在第2,3,5行前各插入一个空行,然后在第3列前插入一个空列,会得到如图c所示结果。共有5种操作,具体来说是:
EX r1 c1 r2 c2 为交换单元格(r1,c1),(r2,c2)
A x1 x2 ... xA 为插入或删除A行或列(DC-删除列,DR-删除行,IC-插入列,IR-插入行,1<=A<=10)
在插入/删除指令后,各个x值不相同,且顺序任意。
接下来是q个查询,每个查询格式为“r c”,表示查询原始表格的单元格(r,c)。对于每个查询,输出操作执行完后该单元格的新位置
输入保证在任意时候行列数均不会超过50。
输入有多个表格。输入结束为0 0
输出时,每个表格前要输出序号(从1开始),查询时如果能查到就输出新位置,如果这个单元格没了,就输出"GONE"。每2个表格之间要空行间隔开来。
7 9
5
DR 2 1 5
DC 4 3 6 7 9
IC 1 3
IR 2 2 4
EX 1 2 6 5
4
4 8
5 5
7 8
6 5
0 0
Spreadsheet #1
Cell data in (4,8) moved to (4,6)
Cell data in (5,5) GONE
Cell data in (7,8) moved to (7,6)
Cell data in (6,5) moved to (1,2)
最容易想到的就是模拟表格操作了,然后直接查询就好。
在代码中用了个小技巧。BIG=10000;ans数组用来表示初始的(r,c)的移动到了(ans[r][c]/BIG, ans[r][c]%BIG)。
Then show the code.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define BIG 10000
#define maxn 100
//r c表示当前行列
int r, c, n;
//d数组表示当前状态 d2数组临时用
//ans数组用来表示初始的(r,c)的移动到了(ans[r][c]/BIG, ans[r][c]%BIG)
int d[maxn][maxn], d2[maxn][maxn], ans[maxn][maxn], cols[maxn];
void copy(char type, int p, int q);
void del(char type);
void ins(char type);
int main(){
int kase = 0;
while(scanf("%d%d%d", &r, &c, &n) == 3 && r){
//给d数组的值刻上印记 以后无论这个值到了哪儿 他都明白他初始位置为 i, j (滑稽.jpg
memset(d, 0, sizeof(d));
for(int i=1; i<=r; i++)
for(int j=1; j<=c; j++)
d[i][j] = i*BIG+j;
//模拟操作
char cmd[10];
while(n--){
memset(cmd, 0, sizeof(cmd));
scanf("%s", cmd);
//交换操作
if(cmd[0] == ‘E‘){
int r1, c1, r2, c2, temp;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &r1, &c1, &r2, &c2);
temp = d[r1][c1]; d[r1][c1] = d[r2][c2]; d[r2][c2] = temp;
} //交换或删除操作
else{
int a, x;
//cols数组表示要操作的行或列
memset(cols, 0, sizeof(cols));
scanf("%d", &a);
while(a--){
scanf("%d", &x);
cols[x] = 1;
}
if(cmd[0] == ‘D‘) del(cmd[1]);
else ins(cmd[1]);
}
}
memset(ans, 0, sizeof(ans));
for(int i=1; i<=r; i++)
for(int j=1; j<=c; j++)
ans[d[i][j]/BIG][d[i][j]%BIG] = i*BIG+j;
int q, r1, c1;
scanf("%d", &q);
if(kase++) printf("\n");
printf("Spreadsheet #%d\n", kase);
while(q--){
scanf("%d%d", &r1, &c1);
printf("Cell data in (%d,%d) ", r1, c1);
if(ans[r1][c1])
printf("moved to (%d,%d)\n", ans[r1][c1]/BIG, ans[r1][c1]%BIG);
else
printf("GONE\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
//将d2的q行/列复制到d的p行/列
void copy(char type, int p, int q){
if(type == ‘R‘)
for(int i=1; i<=c; i++)
d[p][i] = d2[q][i];
else
for(int i=1; i<=r; i++)
d[i][p] = d2[i][q];
}
void del(char type){
memcpy(d2, d, sizeof(d));
int cnt1 = type == ‘R‘ ? r : c, cnt2 = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=cnt1; i++)
//如果需要操作这行/列 则不复制这行/列
if(!cols[i]) copy(type, ++cnt2, i);
type == ‘R‘ ? r = cnt2 : c = cnt2;
}
void ins(char type){
memcpy(d2, d, sizeof(d));
int cnt1 = type == ‘R‘ ? r : c, cnt2 = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=cnt1; i++){
//如果需要操作这行/列 则在前面加一个空行/列(用0表示空行)
if(cols[i]) copy(type, ++cnt2, 0);
copy(type, ++cnt2, i);
}
type == ‘R‘ ? r = cnt2 : c = cnt2;
}
UVa512 - Spreadsheet Tracking 题解(模拟)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/1v7w/p/13974527.html