一、集合
1.1、概念:是对象的容器,实现了对于对象常用的操作,可实现数组的功能
1.2、集合与数组的区别
1.3、概述
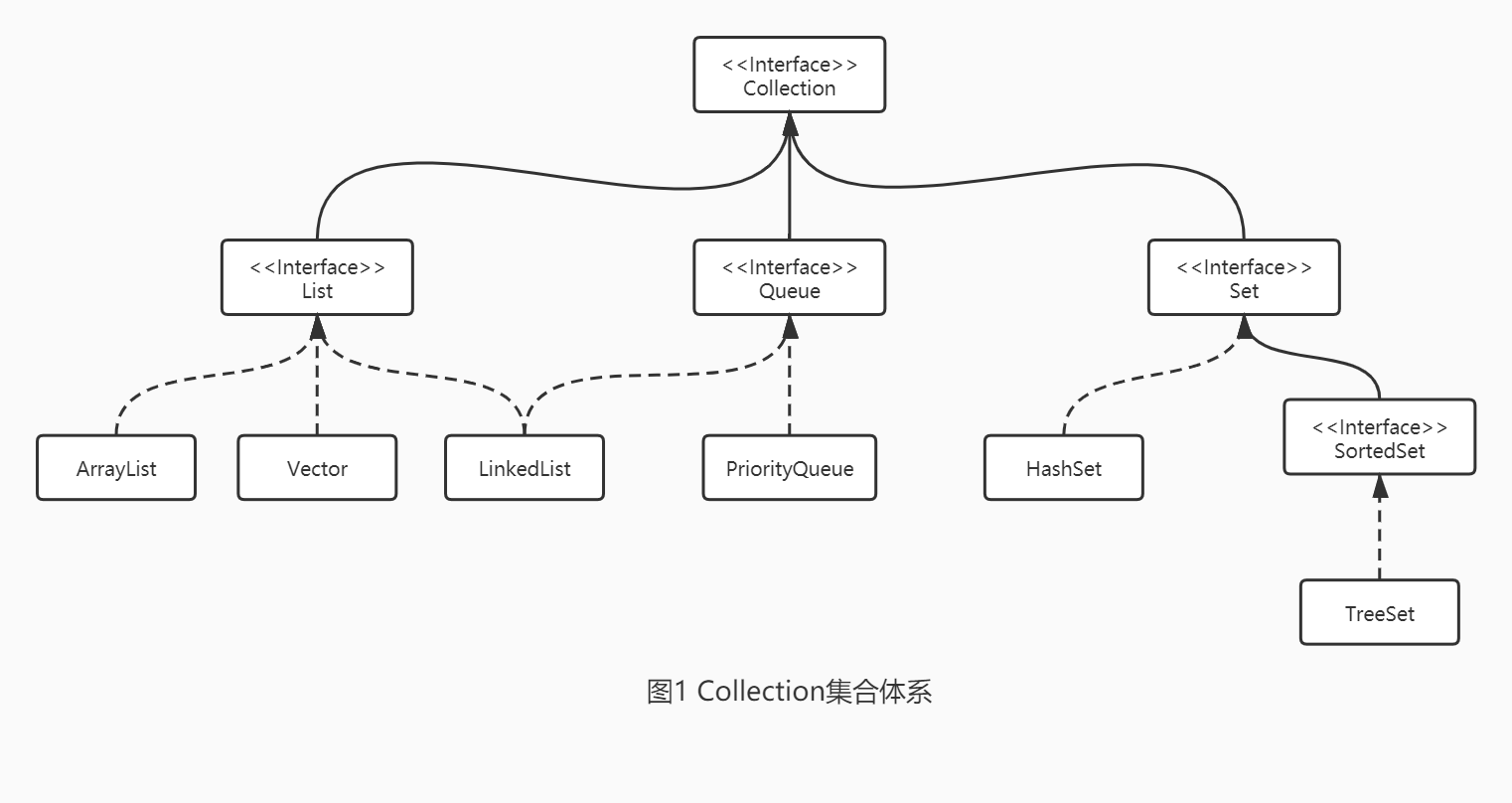
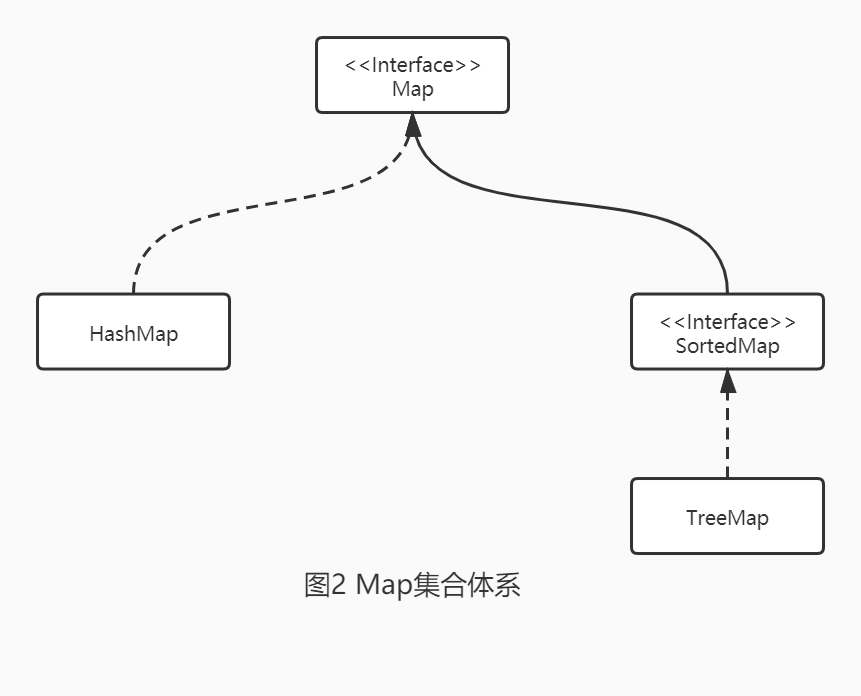
注:LinkedList既实现了List接口,也实现了Queue接口。不过Queue接口窄化了LinkedList的方法,即只能使用Queue接口中定义的方法,不可以使用其他方法
二、Collection集合
1、List接口
1.1、特点:有序、有下标、元素可以重复
1.2、常用操作方法:add(E e)、remove(int index)、get(int index)、iterator()
1.3、实现类特点:
| 数据结构 | 查询速度 | 增删速度 | 运行效率 | 线程安全 | |
| ArrayList | 数组 | 快 | 慢 | 高 | 否 |
| Vector | 数组 | 快 | 慢 | 低 | 是 |
| LinkedList | 双向链表 | 慢 | 快 | 高 | 否 |
1.4、ArrayList与LinkedList区别:
ArrayList是数组结构,需要开辟连续空间,查询比较快,增删比较慢;
LinkedList是双向链表结构,所以无需开辟连续空间,查询比较慢,增删比较快
2、Set集合
2.1、特点:无序、无下标、元素不可以重复,
2.2、常用操作方法:add(E e)、remove(Object o)、iterator()
2.3、实现类特点:
| 数据结构 | 是否排序 | 元素可否为null | 元素可否重复 | 线程安全 | 插入速度 | |
| HashSet | 哈希表 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 快 |
| TreeSet | 红黑树 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 慢 |
3.4、HashSet存储方式:
HashSet的存储结构是哈希表,当存入元素时,首先基于HashCode计算元素存放位置,如果此位置为空,则直接保存,如果不为空则会调用equals进行确认,如果结构为true,则认为重复,否则,形成链表。
3.5、TreeSet的排序方法:
1、对于系统定义的引用类型(如Integer、Double、String等)
public class Demo0 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合 TreeSet<Integer> treeset = new TreeSet<>(); //添加元素 treeset.add(4); treeset.add(5); treeset.add(51); treeset.add(15); treeset.add(26); for(Integer i:treeset) System.out.println(i); } }

可以看见,遍历的结果是有序的。
2、**对于储存的元素为自己定义的类
public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合 TreeSet<Person> treeset = new TreeSet<>(); //生成对象 Person p1 = new Person("Bce",10); Person p2 = new Person("Ace",12); Person p3 = new Person("Fce",8); Person p4 = new Person("Cce",6); //添加元素 treeset.add(p1); treeset.add(p2); treeset.add(p3); treeset.add(p4); System.out.println(treeset.toString()); } }
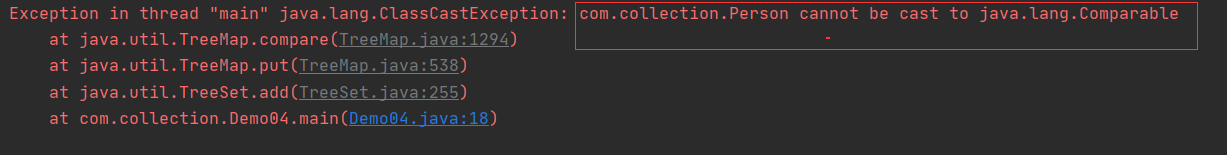
我们发现此时系统会抛出异常,大致意思是我们的Person类不可以进行比较,因为排序需要元素之间能比较大小才能进行,我们有两种解决方法:
(1)元素对象实现Comparable接口,重写其compareTo方法
public class Person implements Comparable<Person> { public String name; public int age; public Person(){}; public Person(String name, int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } //这里重写Comparable public int compareTo(Person p){ //这里我们简单的进行名字的比较 int n1 = this.name.compareTo(p.name); return n1; } @Override public String toString(){ return this.name+":"+(Integer)this.age; } }

可以看到运行结果按照我们定义的比较方法进行排序
(2)为TreeSet指定比较器进行排序
public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合 TreeSet<Person> treeset = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Person>(){ @Override public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) { int n = o1.name.compareTo(o2.name); return n; } }); //生成对象 Person p1 = new Person("Bce",10); Person p2 = new Person("Ace",12); Person p3 = new Person("Fce",8); Person p4 = new Person("Cce",6); //添加元素 treeset.add(p1); treeset.add(p2); treeset.add(p3); treeset.add(p4); System.out.println("运行结果:"); for(Person p:treeset) System.out.println(p.toString()); } }

三、Map集合
1、特点:
2、常用方法:put(K key, V value)、get(Object key)、keySet()、remove(K key)、entrySet()等
3、实现类的特点:
| 数据结构 | 是否排序 | 运行效率 | Key可否为null | 线程安全 | |
| HashMap | 哈希表+红黑树 | 否 | 高 | 是 | 否 |
| TreeMap | 红黑树 | 是(对key排序) | 高 | 否 | 否 |
| HashTable | 哈希表 | 否 | 低 | 否 | 是 |
4、关于Map的遍历
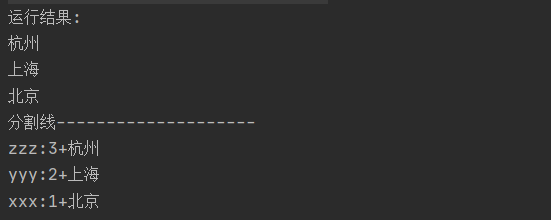
package com.collection; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; public class Demo06 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合 HashMap<Person,String> person = new HashMap<>(); //1.添加元素 Person p1 = new Person("xxx",1); Person p2 = new Person("yyy",2); Person p3 = new Person("zzz",3); person.put(p1,"北京"); person.put(p2,"上海"); person.put(p3,"杭州"); //System.out.println(person); //2.遍历 //2.1keySet方法 Set<Person> pkey = person.keySet(); for(Person p:pkey) System.out.println(person.get(p)); System.out.println("分割线--------------------"); //2.2entrySet方法 Set<Map.Entry<Person,String>> entry = person.entrySet(); for(Map.Entry<Person,String> mmp:entry){ System.out.println(mmp.getKey()+"+"+mmp.getValue()); } } }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/mikellee/p/14006963.html