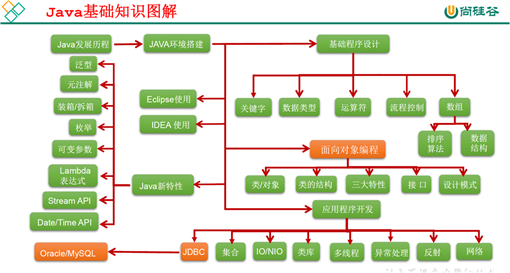
学习面向对象内容的三条主线:
java类及类的成员:属性、方法、构造器、代码块、内部类
面向对象的三大特征:继承、封装、多态、(抽象性)
其他关键字:this、super、static、final、abstract、interface、package、import等
面向对象: Object Oriented Programming
面向过程: Procedure Oriented Programming
二者都是一种思想,面向对象是相对于面向过程而言的。面向过程,强调的是功能行为,以函数为最小单位,考虑怎么做。面向对象,将功能封装进对象,强调具备了功能的对象,以类/对象为最小单位,考虑谁来做。
面向对象更加强调运用人类在日常的思维逻辑中采用的思想方法与原则,如抽象、分类、继承、聚合、多态等。
面向对象的三大特征:
封装(Encapsulation)
继承(lnheritance)
多态(Polymorphism)
面向对象的思想概述:
程序员从面向过程的执行者转化成了面向对象的指挥者
面向对象分析方法分析问题的思路和步骤:
1. 根据问题需要,选择问题所针对的现实世界中的实体。
2. 从实体中寻找解决问题相关的属性和功能,这些属性和功能就形成了概念世界中的类。
3. 把抽象的实体用计算机语言进行描述,形成计算机世界中类的定义。即借助某种程序语言,把类构造成计算机能够识别和处理的数据结构。
4. 将类实例化成计算机世界中的对象,对象是计算机世界中解决问题的最终工具。
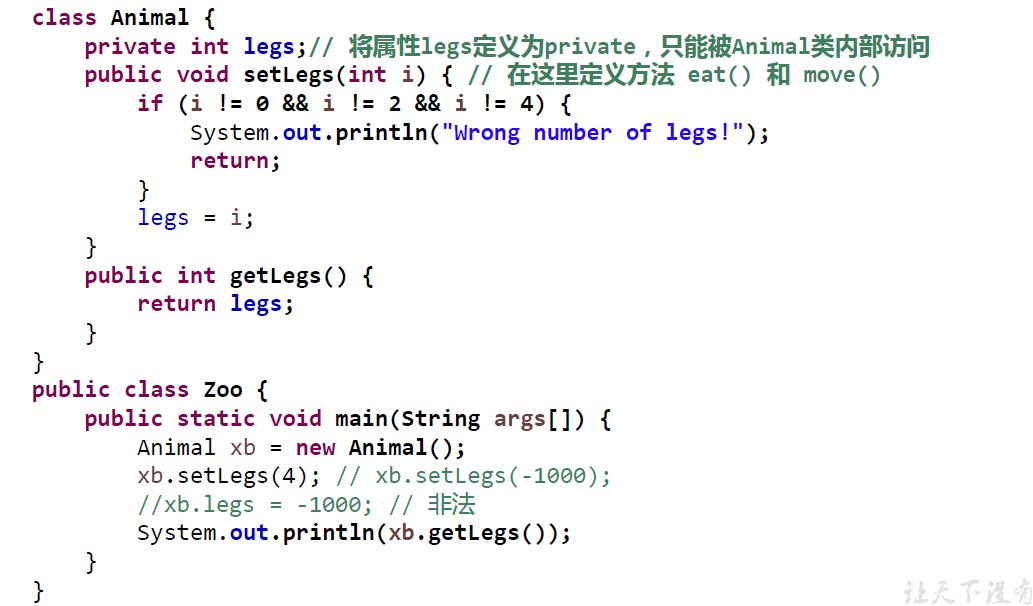
(1)类 (Class)和对象 (Object )是面向对象的核心概念。
类是对 一类事物的描述 ,是抽象的、概念上的定义 ;
对象是实际存在的该类事物的每个个体,因而也称为实例 (instance) 。
(2)“万事万物皆对象”
在Java语言范畴中,我们都将功能、结构等封装到类中,通过类的实例化,来调用具体的功能结构
? Scanner, String等
? 文件:File
? 网络资源:URL
涉及到Java语言与前端Html、后端的数据库交互时,前后端的结构在Java层面交互时,都体现为类、对象。
例子如下:
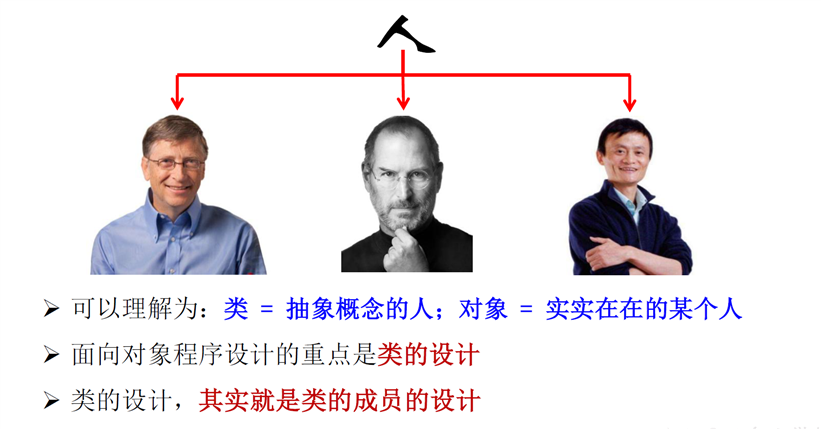
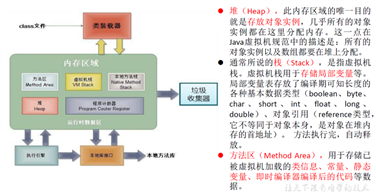
(3)java类及类的成员
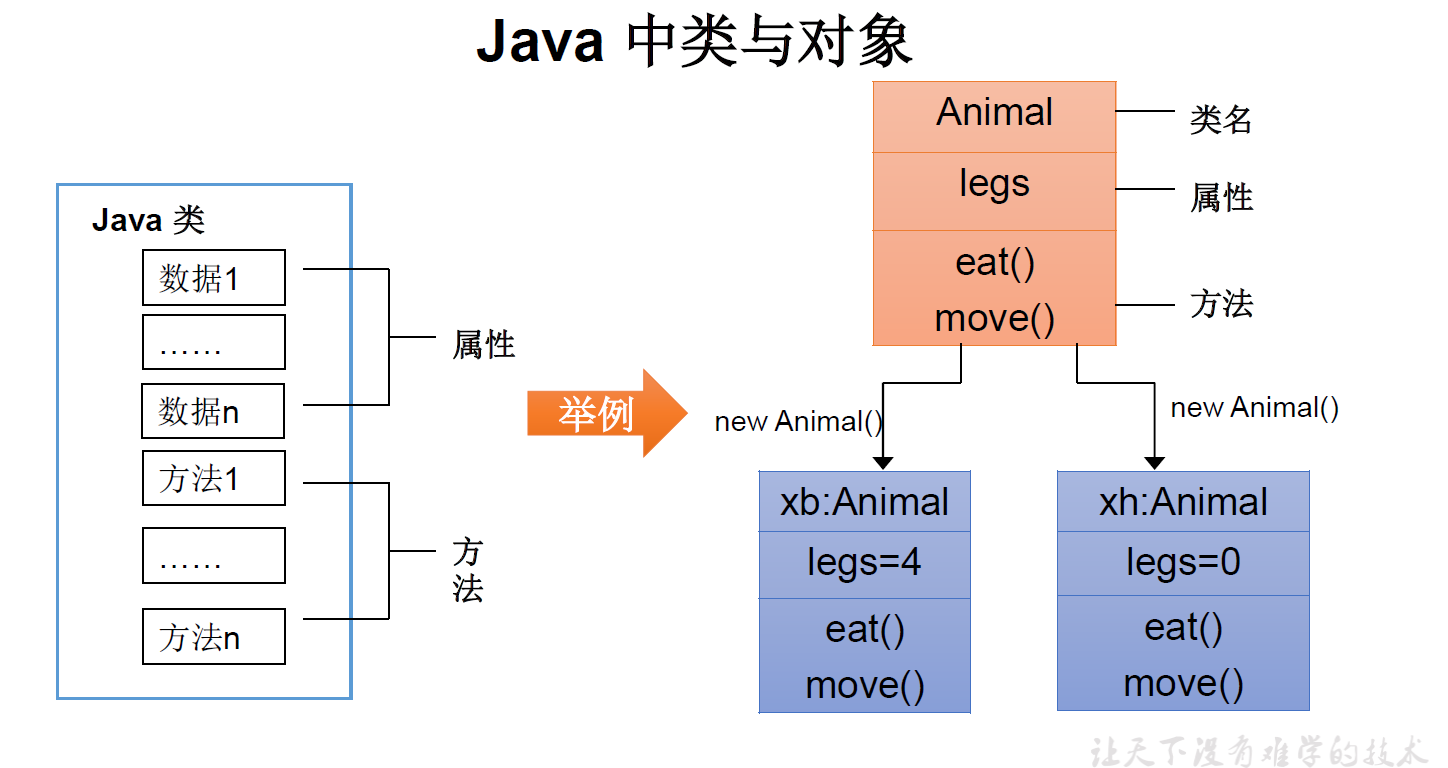
现实世界的生物体,大到鲸鱼,小到蚂蚁,都是由最基本的细胞构成的。同理,Java代码世界是由诸多个不同功能的类构成的。
现实生物世界中的细胞又是由什么构成的呢?细胞核、细胞质、....那么,Java中用类class来描述事物也是如此。常见的类的成员有:

下面为类的成员构成实际例子:

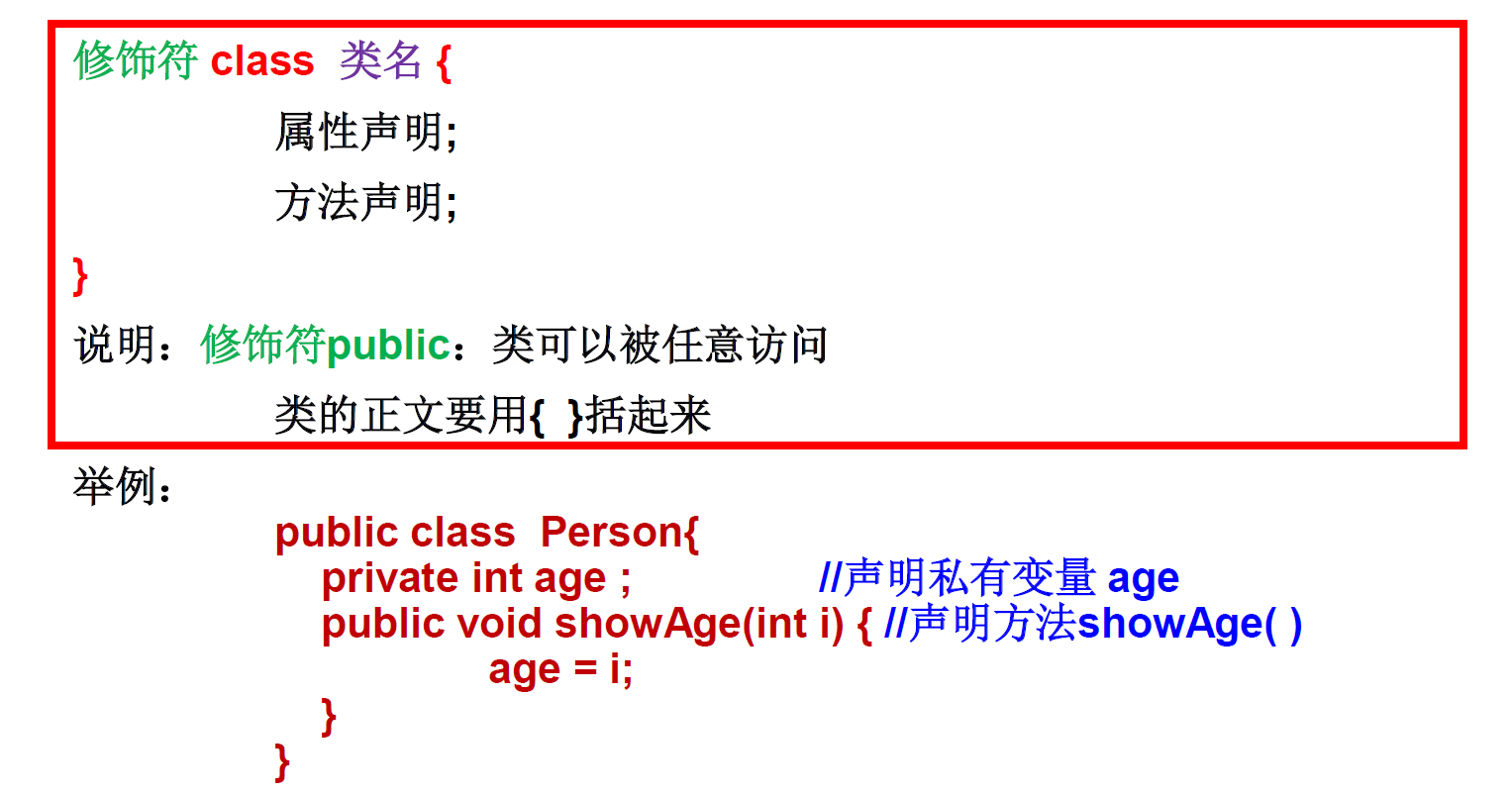
(3)类的语法格式
(1)对象的创建和使用



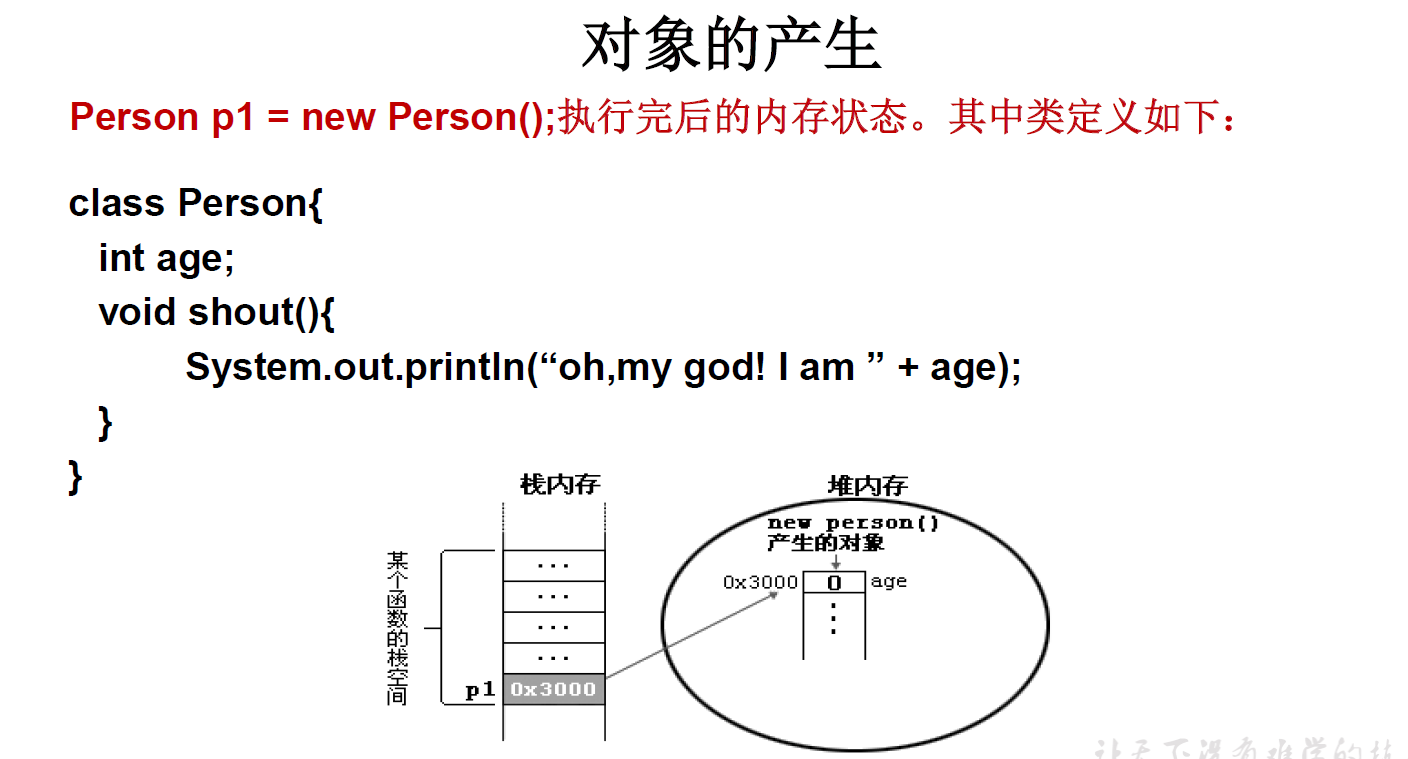
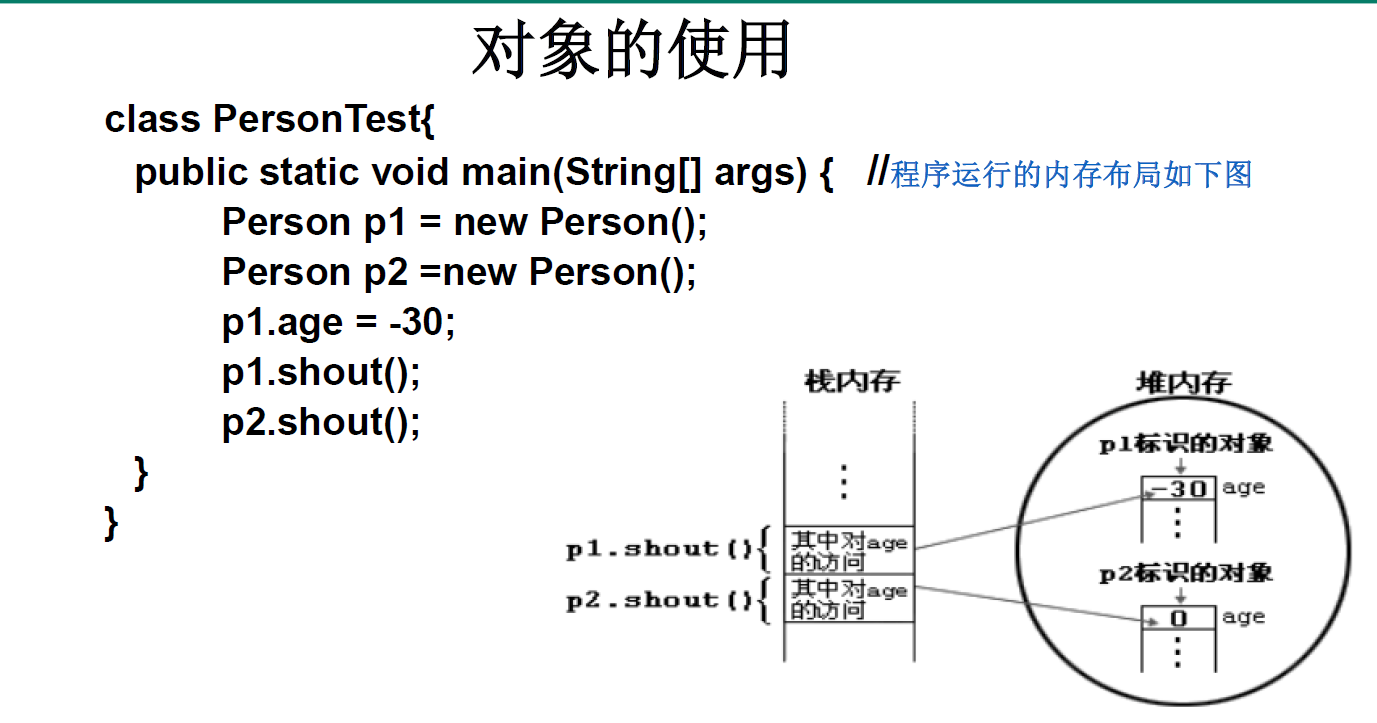
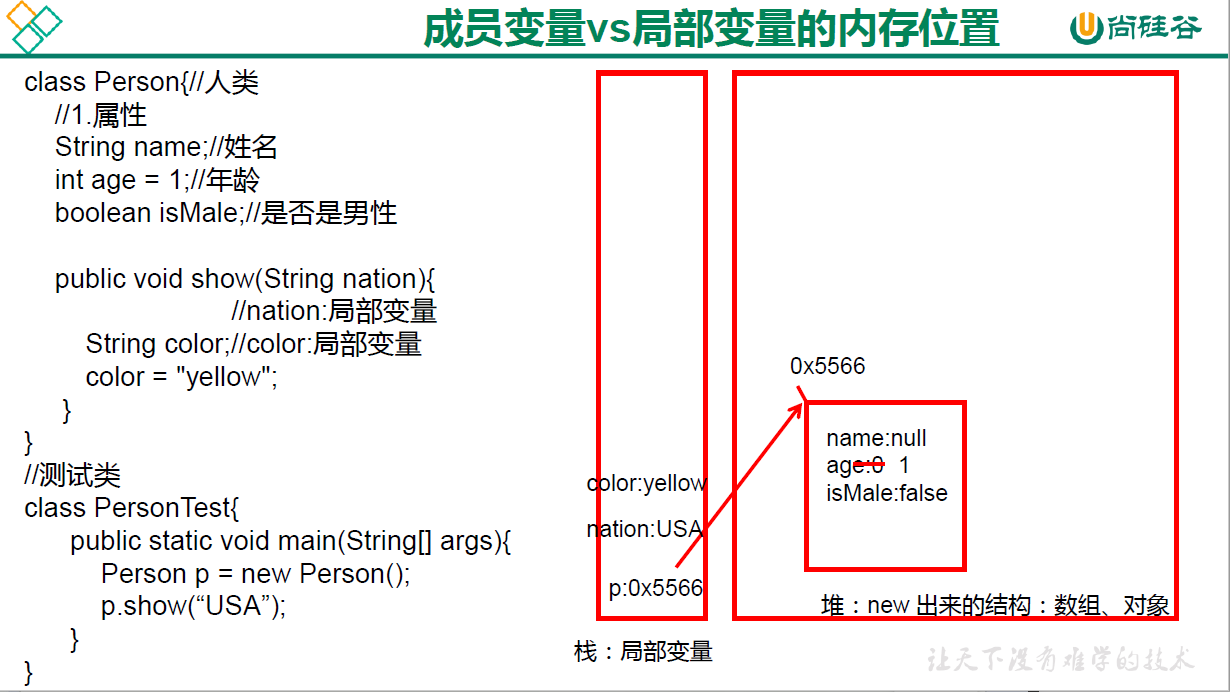
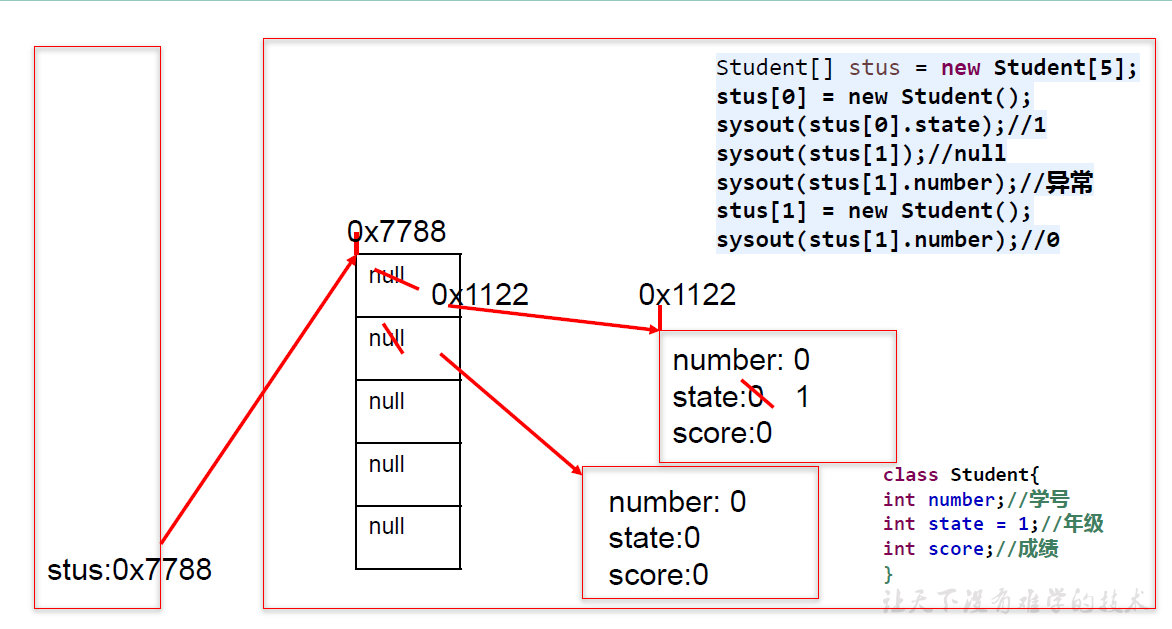
(2)内存解析
例子:
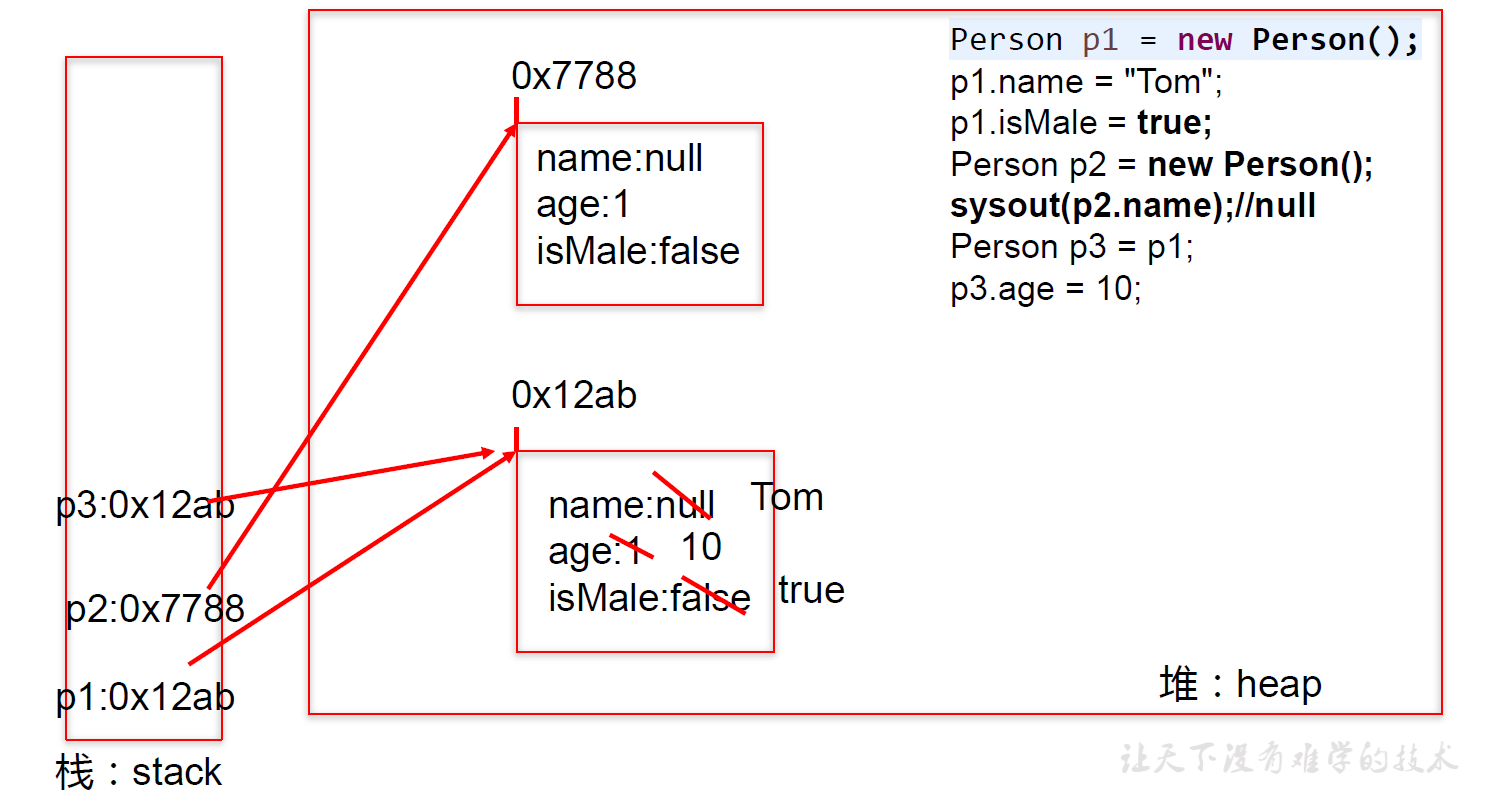
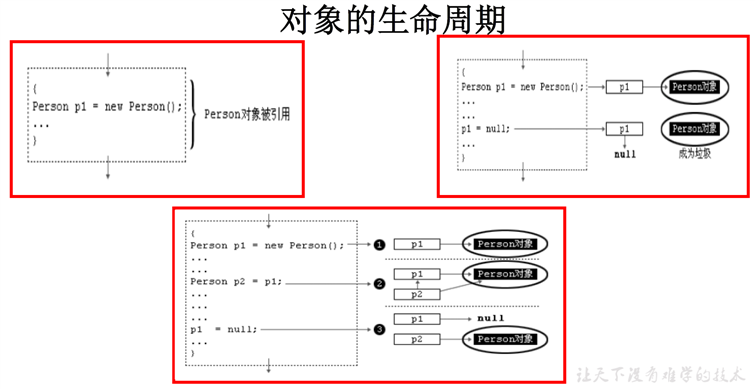
(3)内存解析小测试

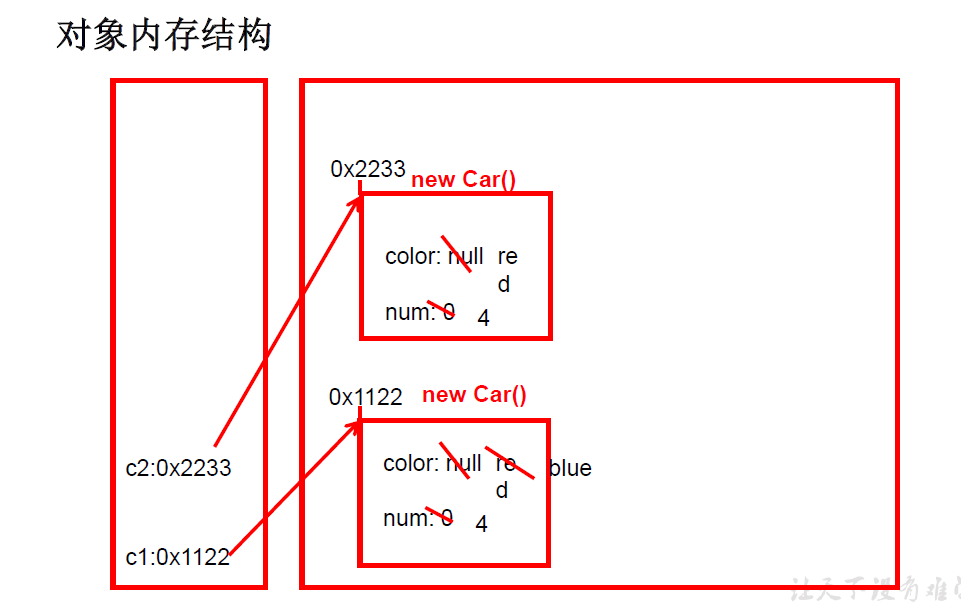
(4)匿名对象

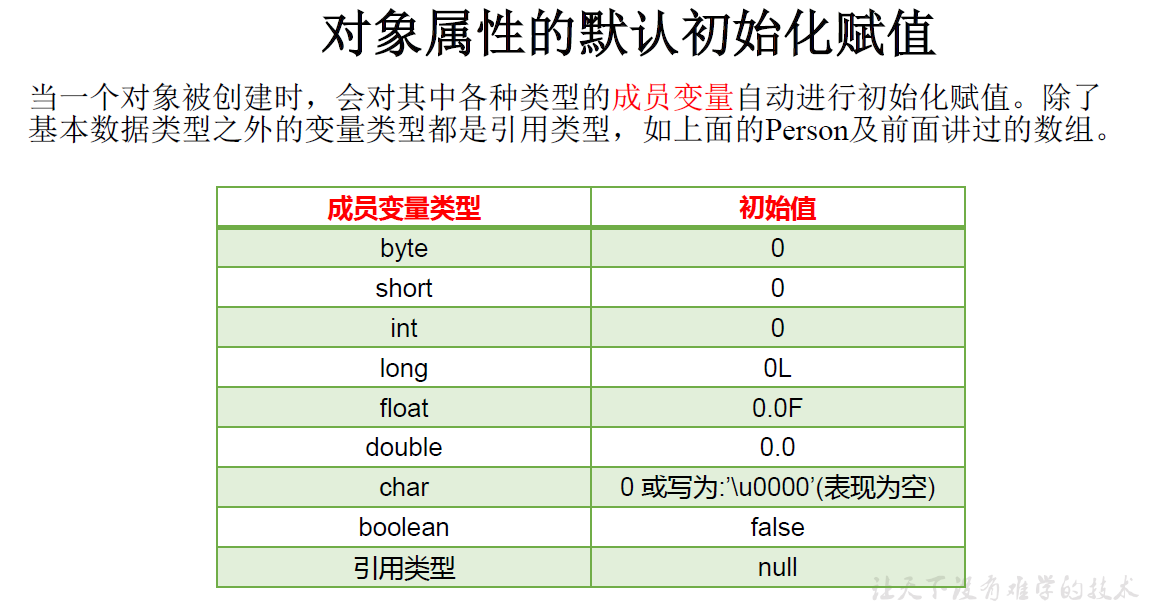
(1)属性(filed)


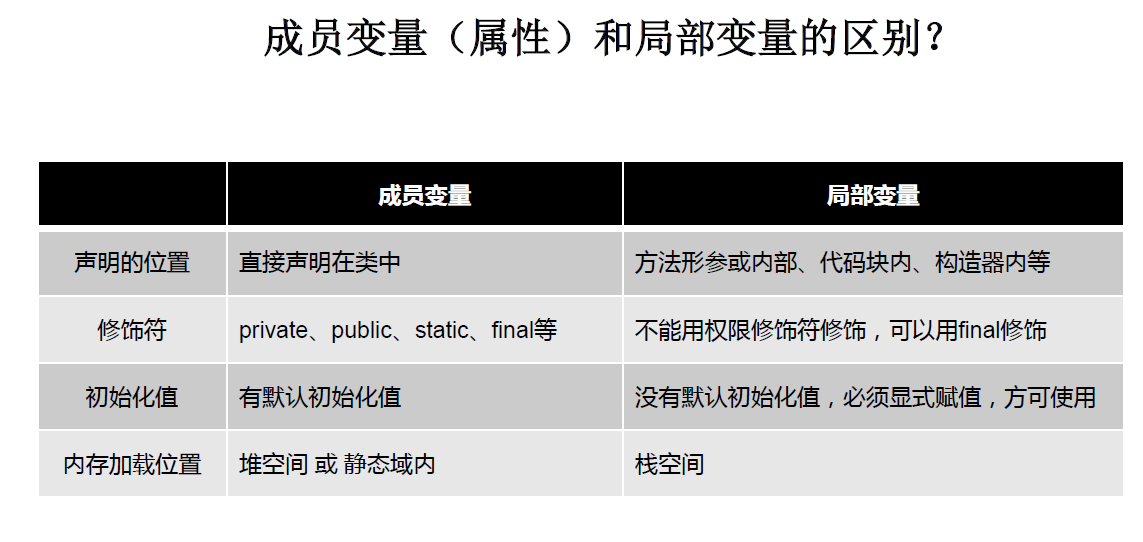
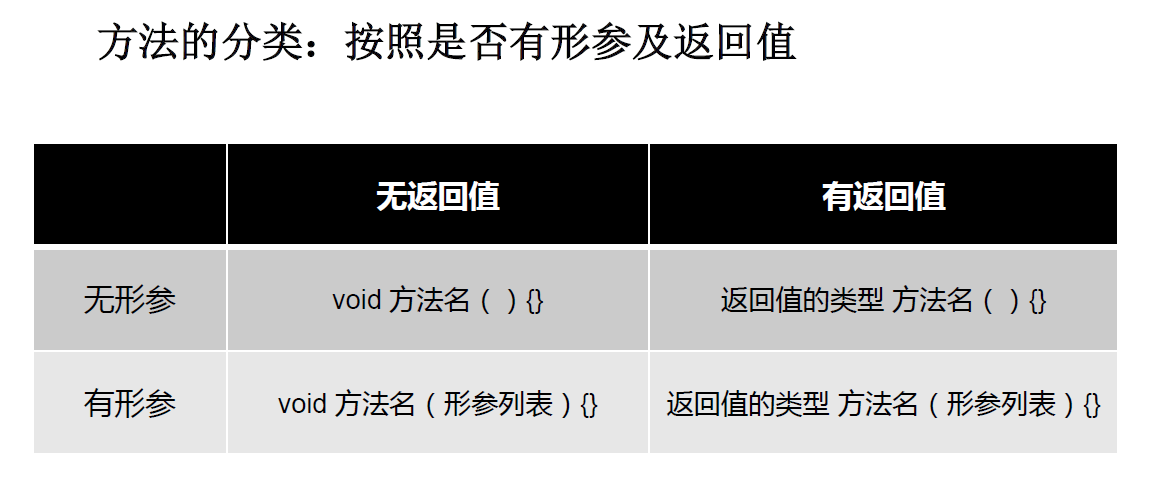
(2)方法(method)


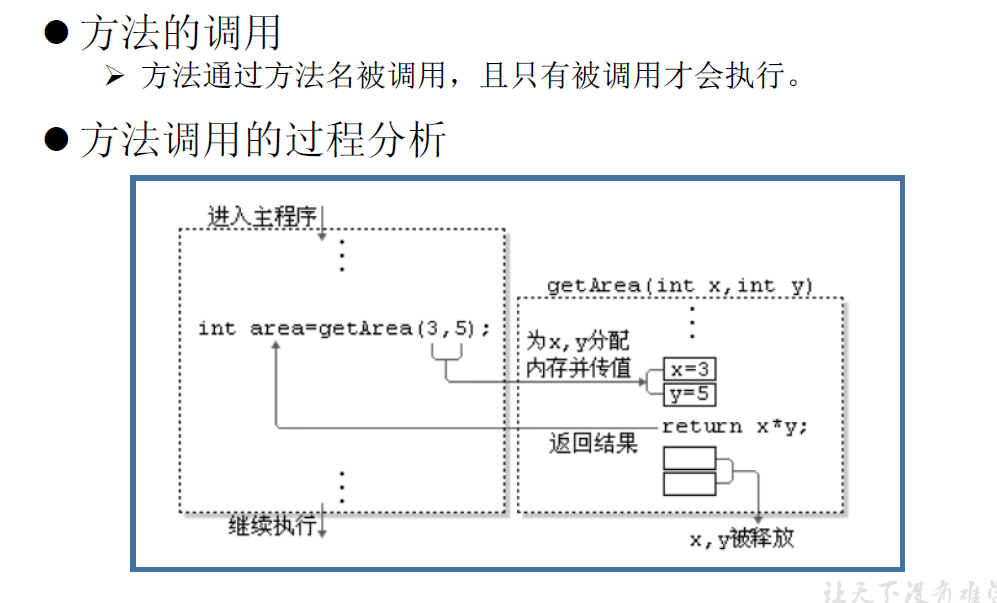


(1)方法的重载
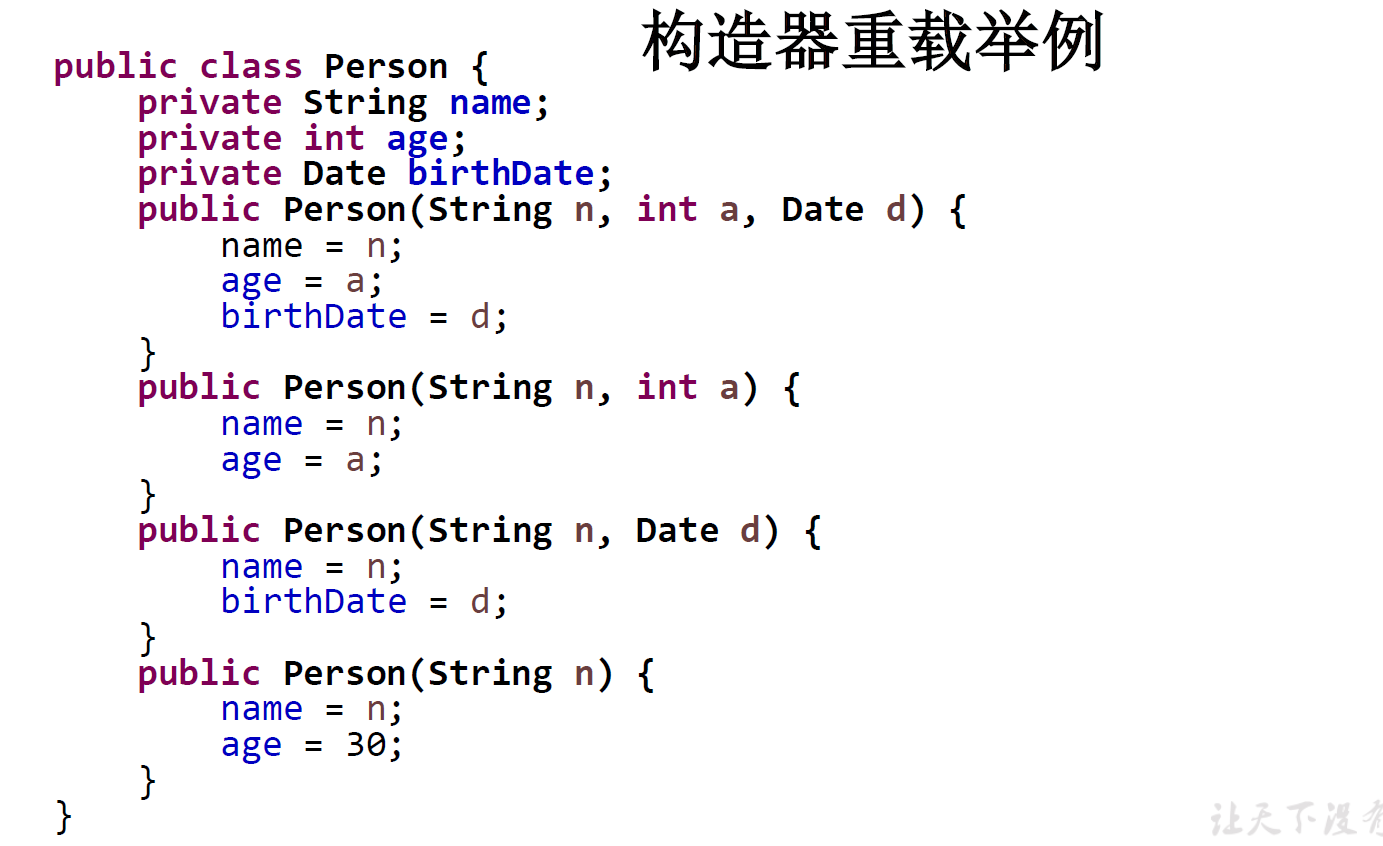
重载的概念:
在同一个类中,允许存在一个以上的同名方法,只要它们的参数个数或者参数类型不同即可。
两同一不同:同一个类、相同方法名;参数列表不同、参数个数不同、参数类型不同
重载的特点︰
与返回值类型无关,权限修饰符、形参变量名、方法体都没有关系。只看参数列表,且参数列表必须不同。调用时,根据方法参数列表的不同来区别。
重载示例︰
int add(int x,int y){return x+y;} //返回两个整数的和
int add(int x,int y,int z){return x+y+z;} //返回三个整数的和
double add(double x,double y){return x+y;} //返回两个小数的和
public class PrintStream {
public static void print(int i) {.......]
public static void print(float f) {.......]
public static void print( String s){.......]
public static void main(String[] args) {
print(3);
print(1.2f);
print ( "hello!");
}
}


(2)可变形参的方法
JavaSE 5.0中提供了Varargs(variable number of arguments)机制,允许直接定义能和多个实参相匹配的形参。从而,可以用一种更简单的方式,来传递个数可变的实参。
JDK 5.0以前:采用数组形参来定义方法,传入多个同一类型变量
public static void test(int a ,String[]books);
JDK5.0:采用可变个数形参来定义方法,传入多个同一类型变量
public static void test(int a ,String...books);
可变形参具体使用规则:
例子:


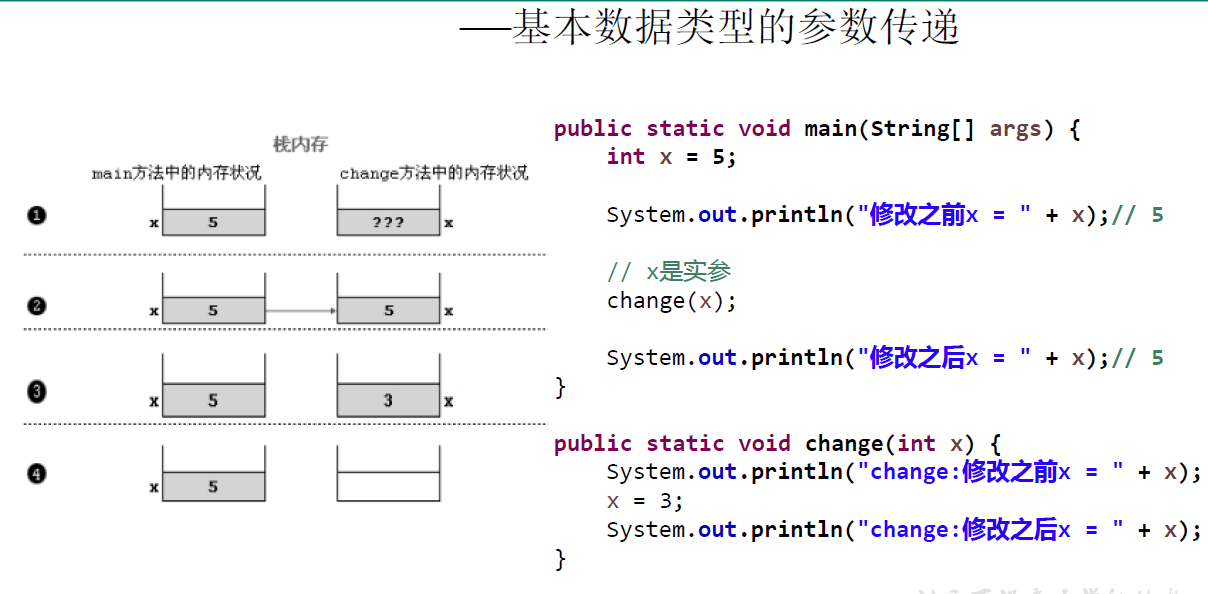


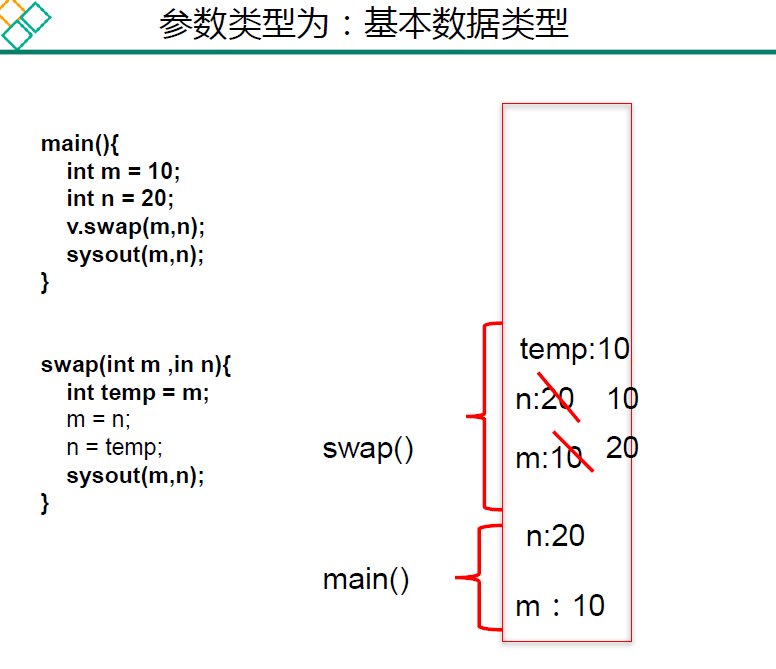
public class TransferTest1 {
public void swap(int a, int b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
System.out.println("swap方法里,a的值是" + a + ";b的值是" + b);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
TransferTest1 test = new TransferTest1();
int a = 5;
int b = 10;
test.swap(a,b);
System.out.println("交换结束后,a的值是" + a + ";b的值是" + b);
}
}
结果:
swap方法里,a的值是10;b的值是5
交换结束后,a的值是5;b的值是10
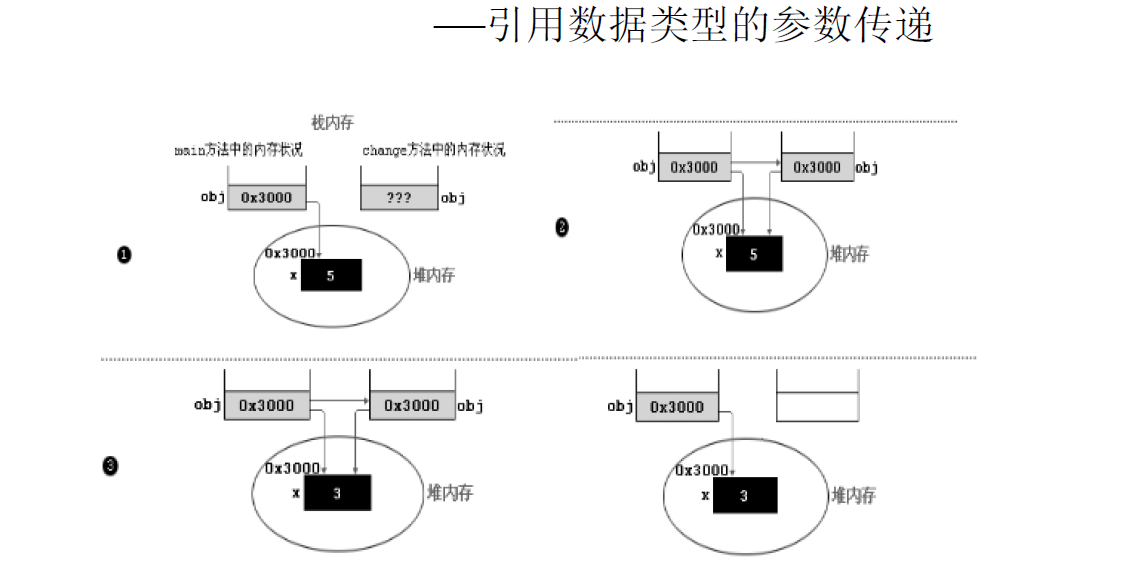
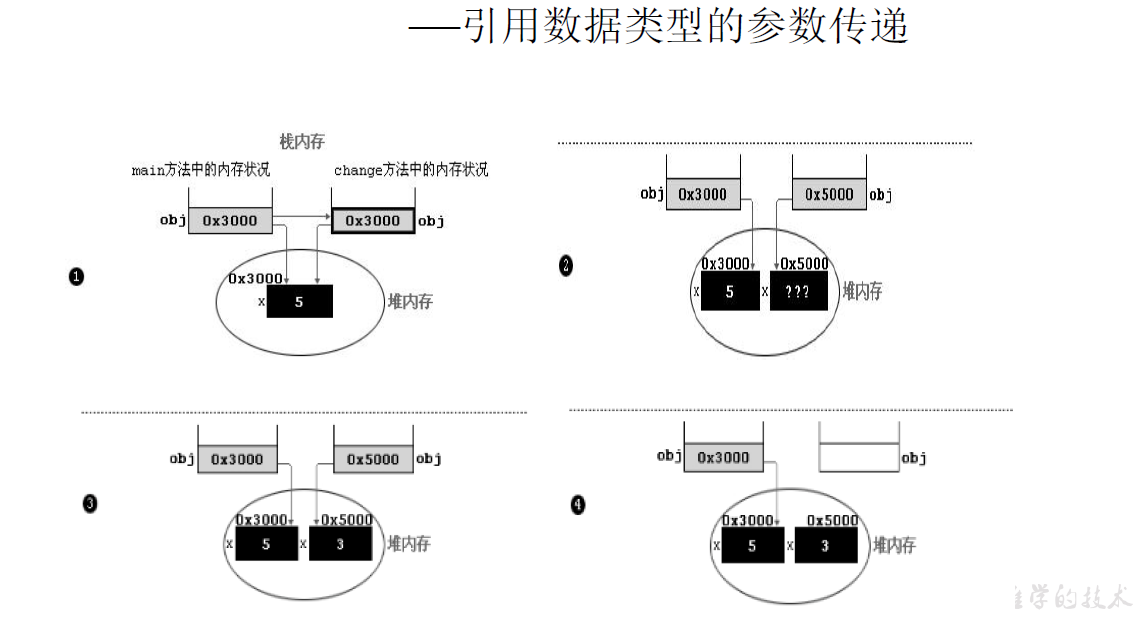
public class TransferTest2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
TransferTest2 test = new TransferTest2();
test.first();
}
public void first() {
int i = 5;
Value v = new Value();
v.i = 25;
second(v, i);
System.out.println(v.i);
}
public void second(Value v, int i) {
i = 0;
v.i = 20;
Value val = new Value();
v = val;
System.out.println(v.i + " " + i);
}
}
class Value {
int i = 15;
}
输出结果:
15,0
20
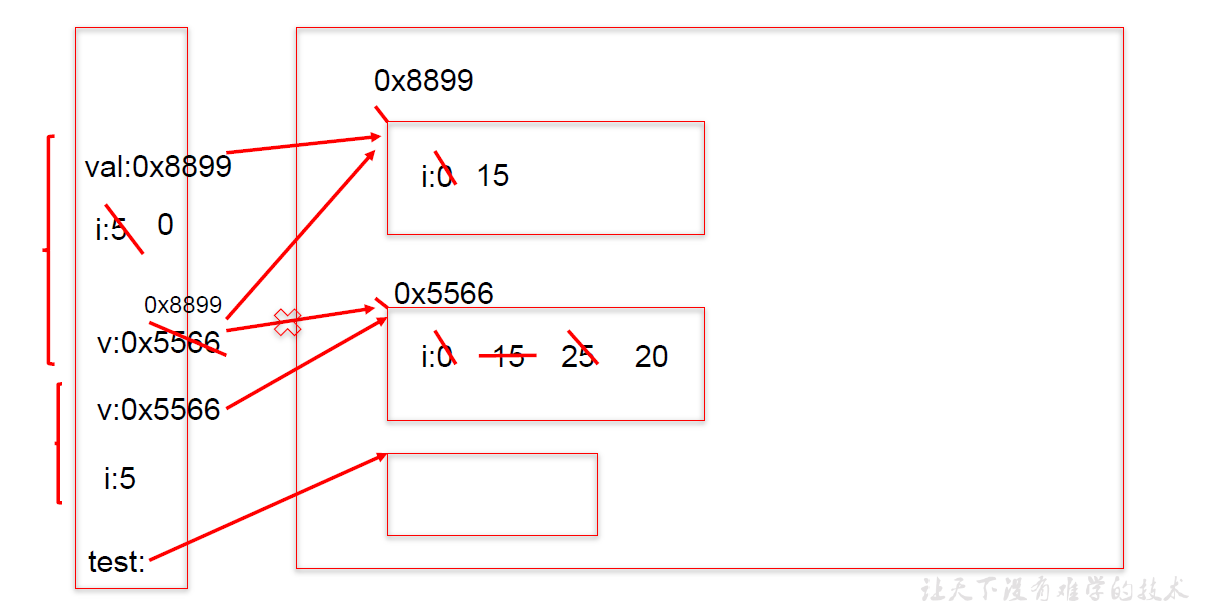
面试题:

LWI60B()VO.png)
(4)递归方法









构造器重载

总结:属性赋值过程

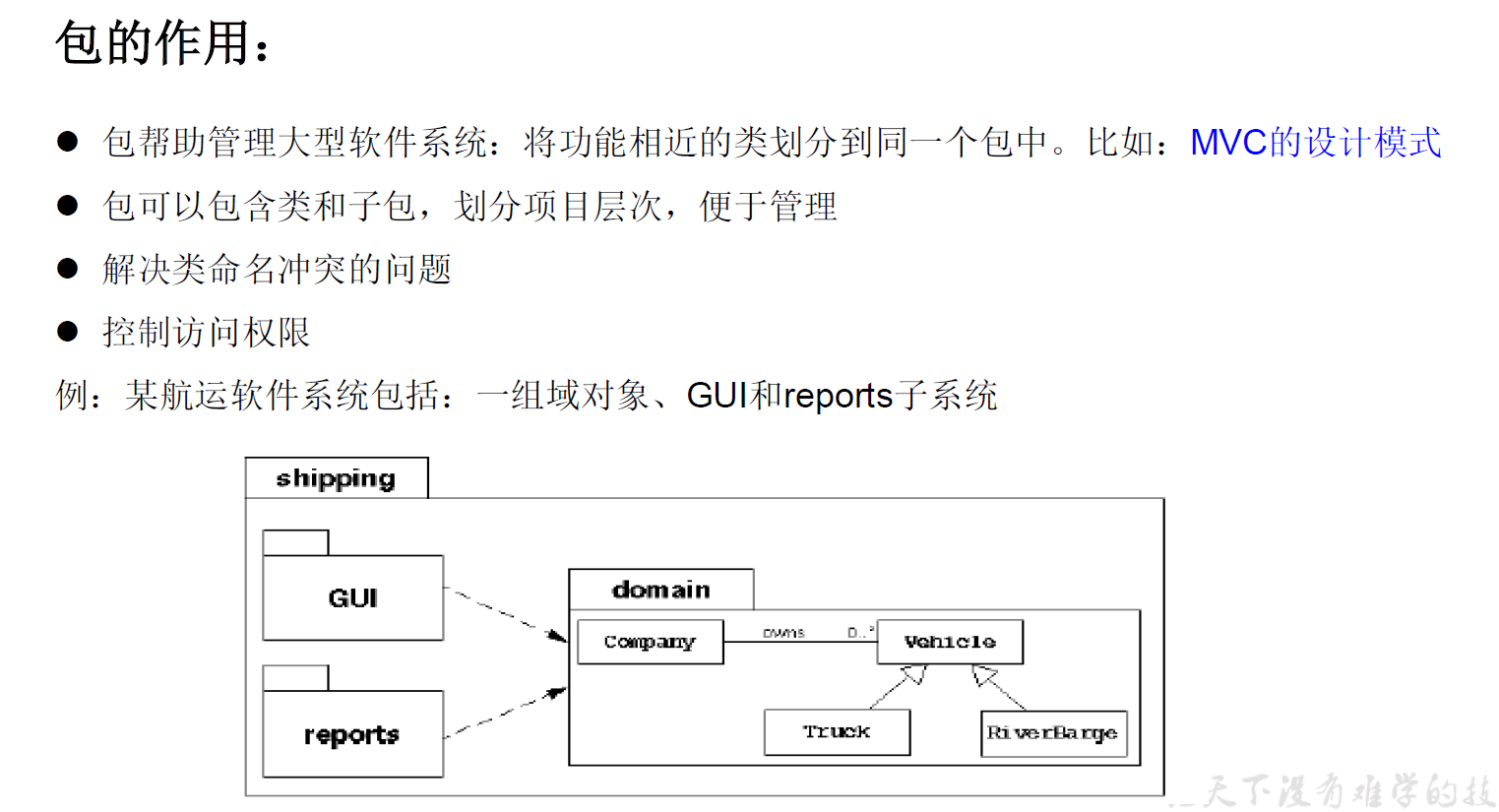
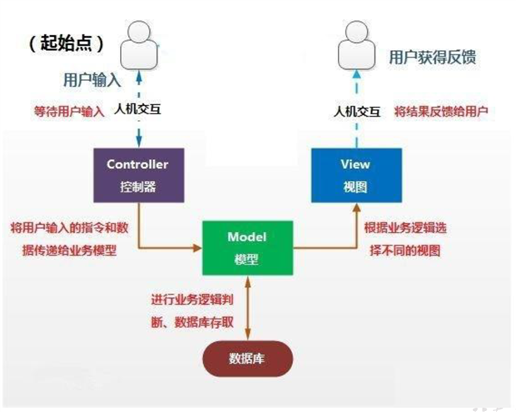
拓展知识:JavaBean


拓展知识:UML类图
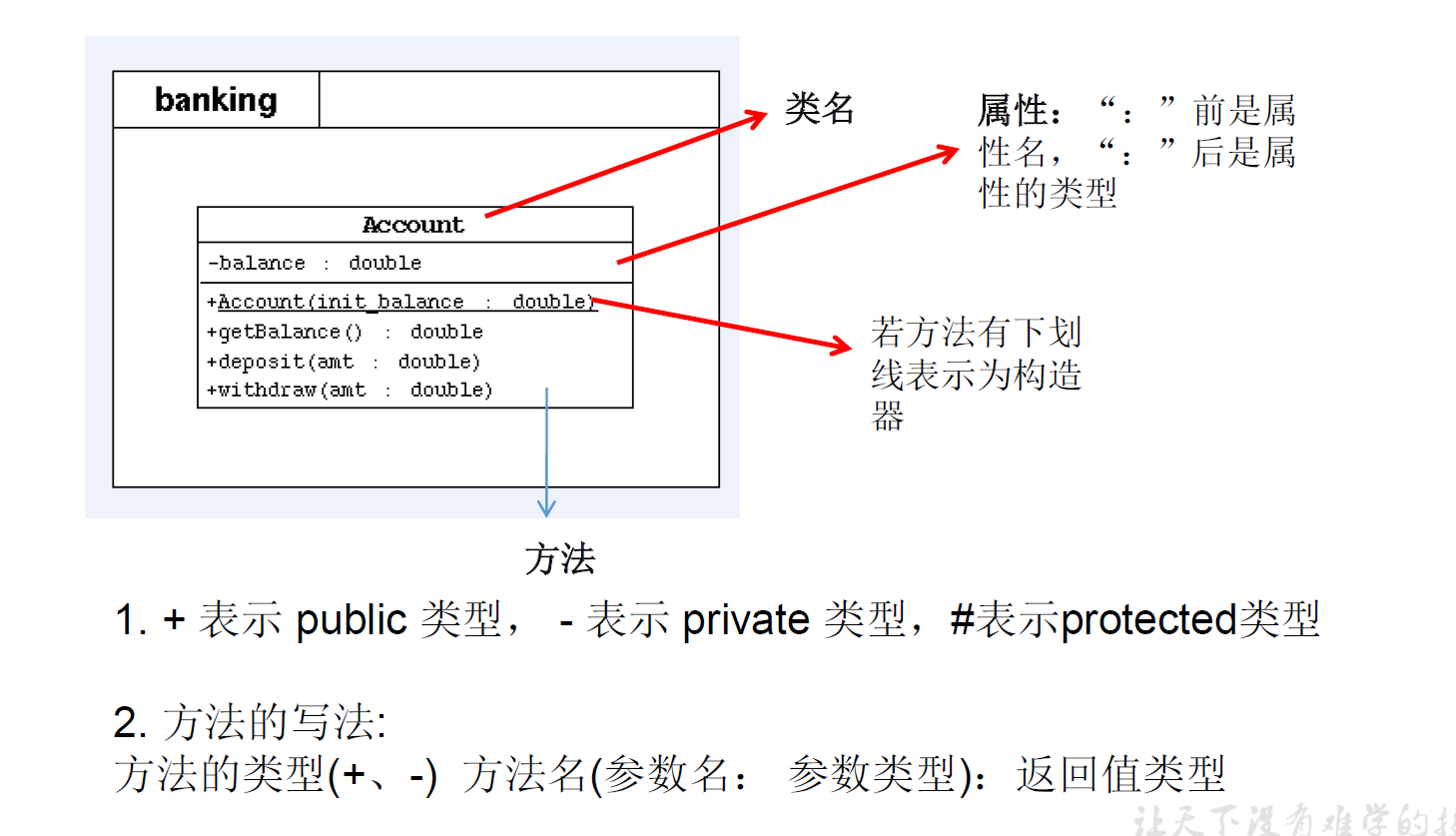



注意:






1、写一个名为Account的类模拟账户。该类的属性和方法如下图所示。该类包括的属性:账号id,余额balance,年利率annuallnterestRate;包含的方法:访问器方法(getter和 setter方法),取款方法 withdraw(),存款方法 deposit()。
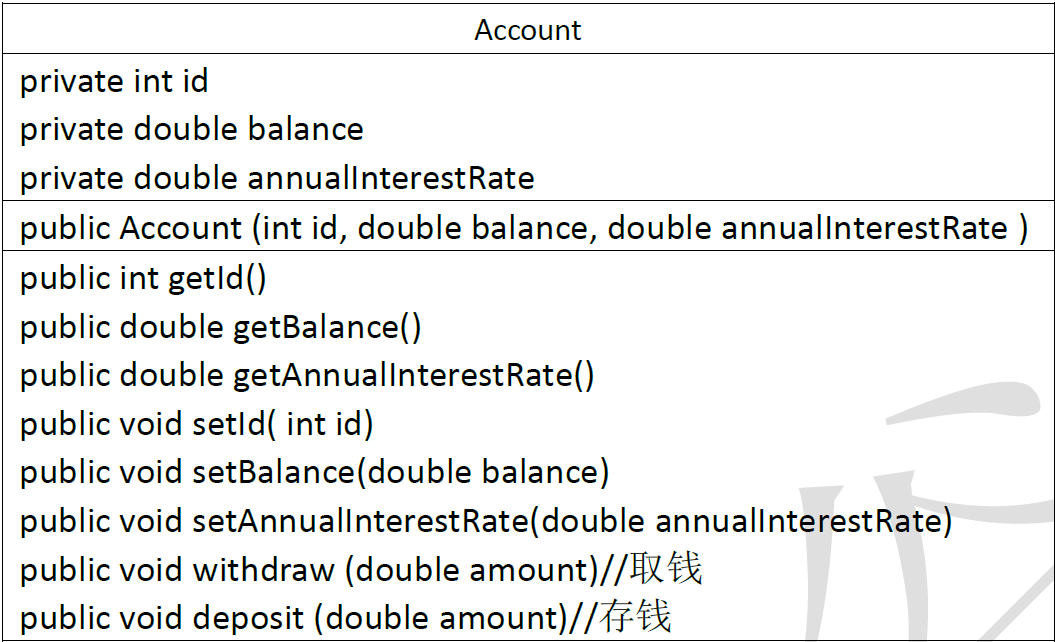
提示:在提款方法 withdraw 中,需要判断用户余额是否能够满足提款数额的要求,如果不能,应给出提示。
Account类
package oop.exercise.exer3;
public class Account {
private int id;
private double balance; //余额
private double annualInterestRate; //年利率
public Account(int id, double balance, double annualInterestRate) {
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public int getId() {
return this.id;
}
public double getBalance() {
return this.balance;
}
public double getAnnualInterestRate() {
return this.annualInterestRate;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate) {
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public void withdraw(double amount) {
if (this.balance >= amount) {
this.balance -= amount;
System.out.printf("成功取出:%.1f 元\n",amount);
}
else
System.out.println("余额不足,取款失败");
}
public void deposit(double amount) {
if (amount > 0) {
this.balance += amount;
System.out.printf("成功存入:%.1f 元\n",amount);
}
}
}
2、创建Customer‘类
a. 声明三个私有对象属性: firstName、lastName和account。
b. 声明一个公有构造器,这个构造器带有两个代表对象属性的参数(f和I)
c. 声明两个公有存取器来访问该对象属性,方法getFirstName和getLastName返回相应的属性。
d. 声明setAccount方法来对account属性赋值。
e.声明getAccount方法以获取account属性。
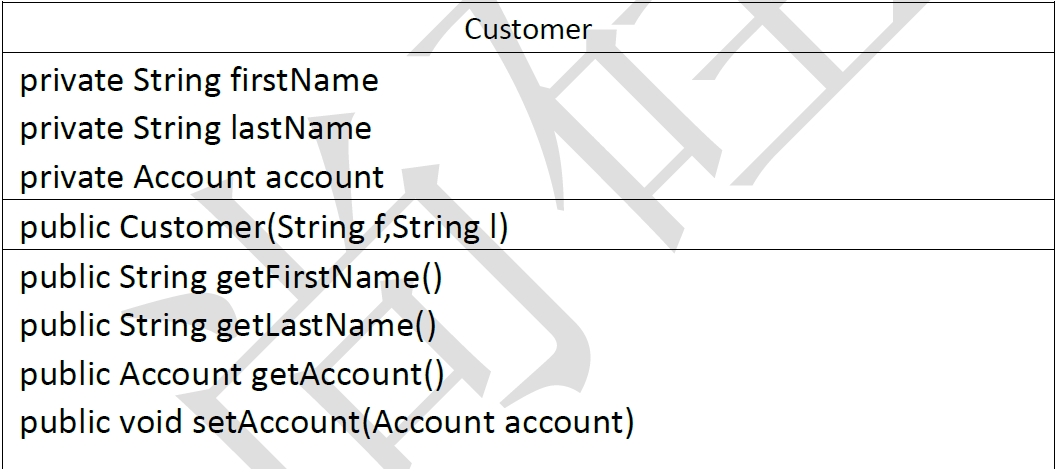
Customer类
package oop.exercise.exer3;
public class Customer {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private Account account;
public Customer(String fisrtName,String lastName) {
this.firstName = fisrtName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return this.firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return this.lastName;
}
public Account getAccount() {
return this.account;
}
public void setAccount(Account account) {
this.account = account;
}
}
3、写一个测试程序。
(1) 创建一个Customer ,名字叫Jane Smith,他有一个账号为1000,余额为2000元,年利率为1.23%的账户。
(2)对Jane Smith 操作。存入100元,再取出960元。再取出2000元。打印出Jane Smith 的基本信息。
package oop.exercise.exer3;
public class AccountCustomer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer jane = new Customer("Jane","Smith");
jane.setAccount(new Account(1000, 2000.0, 0.0123));
jane.getAccount().deposit(100.0);
jane.getAccount().withdraw(960.0);
jane.getAccount().withdraw(2000.0);
System.out.printf("Customer [%s, %s] has a account: id is %d, annualInterestRate is %.4f, balance is %.1f",jane.getFirstName(),jane.getLastName(),jane.getAccount().getId(),jane.getAccount().getAnnualInterestRate(),jane.getAccount().getBalance());
}
}
reference
1、按照如下的UML类图,创建相应的类,提供必要的结构
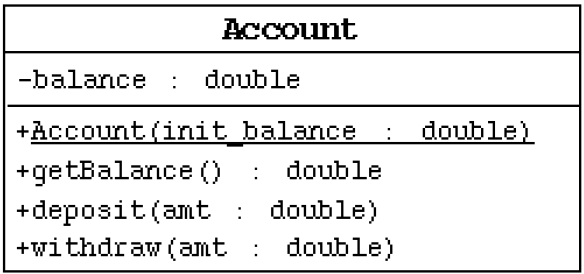
在提款方法withdraw()中,需要判断用户余额是否能够满足提款数额的要求,如果不能,应给出提示。deposit()方法表示存款。
package oop.exercise.exer4;
public class Account {
private double balance; //余额
public Account(double init_balance) {
this.balance = init_balance;
}
public double getBalance() {
return this.balance;
}
public void withdraw(double amount) {
if (this.balance >= amount) {
this.balance -= amount;
System.out.printf("成功取出:%.1f 元\n",amount);
}
else
System.out.println("余额不足,取款失败");
}
public void deposit(double amount) {
if (amount > 0) {
this.balance += amount;
System.out.printf("成功存入:%.1f 元\n",amount);
}
}
}
2、按照如下的UML类图,创建相应的类,提供必要的结构
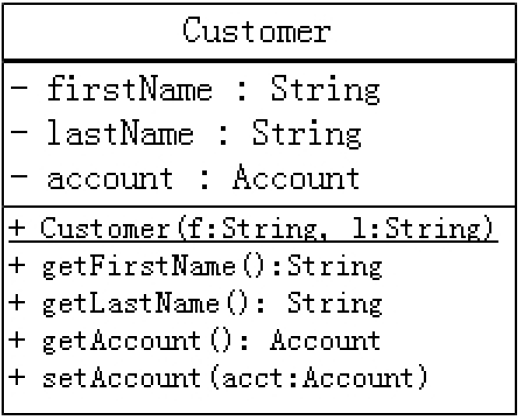
package oop.exercise.exer4;
public class Customer {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private Account account;
public Customer(String firstName,String lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return this.firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return this.lastName;
}
public Account getAccount() {
return this.account;
}
public void setAccount(Account account) {
this.account = account;
}
}
3、按照如下的UML类图,创建相应的类,提供必要的结构
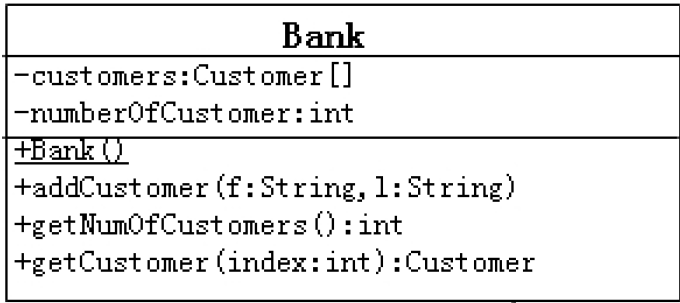
package oop.exercise.exer4;
public class Bank {
private Customer[] customers;
private int numberOfCustomer;
public Bank() {
customers = new Customer[10];
}
public void addCustomer(String firstName, String lastName) {
Customer cust = new Customer(firstName, lastName);
customers[numberOfCustomer++] = cust;
}
public int getNumberOfCustomers() {
return this.numberOfCustomer;
}
public Customer getCustomer(int index) {
if (index >=0 && index < this.numberOfCustomer)
return customers[index];
else
return null;
}
}
4、创建BankTest类,进行测试。
package oop.exercise.exer4;
public class BankTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bank b = new Bank();
b.addCustomer("Jane", "Smith");
b.getCustomer(0).setAccount(new Account(2000));
b.getCustomer(0).getAccount().withdraw(500);
double balance = b.getCustomer(0).getAccount().getBalance();
System.out.printf("客户:%s 的账户余额为%.1f 元\n",b.getCustomer(0).getFirstName(),balance);
b.addCustomer("Tom", "Green");
b.addCustomer("Joe", "Birden");
System.out.printf("银行的客户数量为:%d ",b.getNumberOfCustomers());
}
}
reference
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/victorxiao/p/14046163.html