从前一篇引导篇 here 的分析来看,如果我们想弄清楚 请求对象 HttpServletRequest 和 方法处理器 HandlerMethod 的对应关系,我们可以去 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 中去寻找“真相”。
我们看待这个类,需要从两个阶段去分析:
预处理部分:HandlerMethod 是如何 扫描注册 到 HandlerMapping 中去的?
执行部分:当一个请求 HttpServletRequest 到来,SpringMVC 又是如何 匹配获取 到合适的 HandlerMethod 的?
!提醒:考虑到篇幅安排,执行部分还需要分多篇来讲解,因此本文主要针对预处理部分进行讲解。
我还是比较喜欢写单元测试,一方面,单元测试的执行速度比启动一个完整项目要快数十倍;另一方面,单元测试的书写过程中,更容易让我们记住我们忽略了那些细节。这是我掌握源码的一个方法,如果你不喜欢,可以跳过该小节,直接进入分析部分。
有需要的可以到 Gitee here 下载源码,以 maven 打开项目,使用 handler-method-mapping 模块。
UserController.java
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/info")
public ModelAndView user(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("name=" + name);
System.out.println("age=" + age);
return null;
}
}
我们需要 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 来作为我们存储 HandlerMethod 的容器,因此我们新建这个对象。
设计测试目标:假如 getHandler 能够返回一个非空对象,那么就说明注册成功了。
Tips:getHandler 方法需要一个请求对象,来自 spring-test 的 MockHttpServletRequest 来测试最合适不过了。
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.mock.web.MockHttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExecutionChain;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;
public class UserControllerTest {
private RequestMappingHandlerMapping handlerMapping;
private MockHttpServletRequest request;
@Test
public void initTest() throws Exception {
request = new MockHttpServletRequest("GET", "/user/info");
handlerMapping = new RequestMappingHandlerMapping();
HandlerExecutionChain chain = handlerMapping.getHandler(request);
Assert.assertNotNull(chain);
}
}
测试结果:测试不通过
失败原因:一通反向追踪后发现,答案就在 initHandlerMethods() 这个方法中。节选代码片段如下:
如果不调用 afterPropertiesSet(),就不会初始化所有处理器。
在日常开发时,afterPropertiesSet() 都是 Spring Bean 的生命周期中调用的,现在我们自己来主动调用一下。
handlerMapping.afterPropertiesSet();
测试结果:测试不通过
ApplicationObjectSupport instance does not run in an ApplicationContext
失败原因:我们需要给 HandlerMethod 设置应用上下文。
ctx = new StaticWebApplicationContext();
handlerMapping.setApplicationContext(ctx);
Tips:同样使用来自 spring-test 的 StaticWebApplicationContext 会更加简单。
现在的测试代码如下
import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.mock.web.MockHttpServletRequest; import org.springframework.web.context.support.StaticWebApplicationContext; import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExecutionChain; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;public class UserControllerTest {
private RequestMappingHandlerMapping handlerMapping; private MockHttpServletRequest request; private StaticWebApplicationContext ctx; @Test public void initTest() throws Exception { request = new MockHttpServletRequest("GET", "/user/info"); handlerMapping = new RequestMappingHandlerMapping(); ctx = new StaticWebApplicationContext(); // 在 afterPropertiesSet() 调用之前设置上下文 handlerMapping.setApplicationContext(ctx); handlerMapping.afterPropertiesSet(); HandlerExecutionChain chain = handlerMapping.getHandler(request); Assert.assertNotNull(chain); }
}
需要注意的是,setApplicationContext 的调用必须在 afterPropertiesSet 之前。
测试结果:测试不通过
失败原因:Spring 容器中没有相应的 Controller Bean,需要我们自己来注册。
// 为程序上下文注入 UserController Bean
ctx.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("userController", new UserController());
现在我们就测试通过了,现在我们再来研究一下初始化所有 HandlerMethod 的方法。
初始化所有的 HandlerMethod 的过程:
获取所有的 Bean:从 Spring 容器中获取所有的 Bean,isHandler 方法筛选出带 @RequestMapping 或者 @Controller 的 Bean。
获取所有方法:从 Bean 中取出所有的方法,筛选出带 @RequestMapping 的方法
封装 RequestMappingInfo : 根据注解封装映射条件
创建 HandlerMethod
存储映射到 MappingRegistry
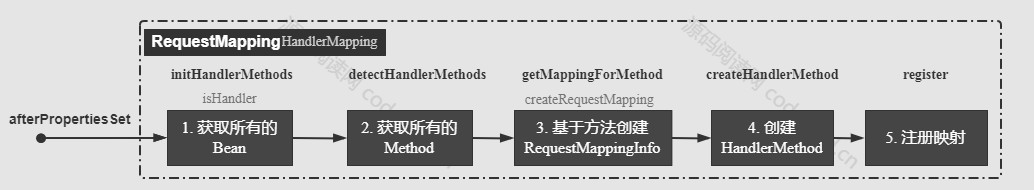
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 实现了 InitializingBean 接口。
afterPropertiesSet() 触发 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的初始化,扫描注册了所有 HandlerMethod。
因此我们的 XXXController 必须有类注解 @Controller 或者 @RequestMapping。
这个方法遍历的当前类,当前类的父类,(当前类的接口以及当前类所有父类接口)中的方法。这个功能主要依靠第一个参数 Class<?> clazz 中的成员方法。
找到了这么多 Method,但并不是所有都有用,因此需要过滤不需要的方法。此时需要借助第二个参数 MethodFilter mf,这是一个函数式接口,仅包含一个接口方法。
找到的每一个方法,都需要相同的处理策略。此时就需要借助第三个参数 MethodCallback mc,这同样是函数式接口。
总而言之,这个工具类把复杂的遍历和递归方法封装起来,调用者可以更专注于“要拿哪些 Method,做何种操作”的问题上。
对于第三个过滤参数 MethodFilter mf,源码中用到了这个:
public static final MethodFilter USER_DECLARED_METHODS =
(method -> !method.isBridge() && !method.isSynthetic() && method.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class);
这个方法过滤器对象,表示过滤桥接方法,合成方法以及Object的自带方法。换言之,筛选出应用程序员写的方法。
桥接方法,合成方法都是 JVM 编译器编译时的产物。桥接方法主要和泛型的编译有关,合成方法主要和嵌套类和私有成员的编译相关。隐秘而诡异的Java合成方法 here
这个方法,是在上面第 2 个方法的基础上,把 Java 动态代理生成的类考虑进去了。
但是这个方法的第二个参数 MetadataLookup<T> metadataLookup 也是一个函数式接口。每找到一个应用程序员写的 Controller 方法,就会回调一次,询问调用者要拿 Method 返回一个什么对象。
方法调用时机:上面第 4 个方法运行时,每找到一个“应用程序员”写的 Controller Bean 中的 Method 就会回调一次 getMappingForMethod 创建一个 RequestMappingInfo 对象。
@Override
@Nullable
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
解析:
createRequestMappingInfo 使用 @RequestMapping 注解中的属性填充 RequestMappingInfo 的成员变量。属性一一对应成员变量。
Controller 类上的注解创建的 RequestMappingInfo 需要与方法上的注解创建的 RequestMappingInfo 合并(combine)后作为日后请求的匹配条件。
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
该方法向 MappingRegistry 注册映射。
在注册时会调用
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
createHandlerMethod 将 Controller Bean(即 handler)和 Bean 的每一个 Method 组合生成一个 HandlerMethod。
在 Spring 容器创建 RequestMappingHandlerMapping Bean 的过程中,会执行初始化 afterPropertiesSet(),触发初始化所有 HandlerMethod。
初始化 HandlerMethod 的过程:
SpringMVC之RequestMapping执行过程(HandlerMapping篇)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/kendoziyu/p/springMvc-RequestMapping-HandlerMapping.html