本文快速回顾了Redis书籍、博客以及本人面试中遇到的基础知识点,方便大家快速回顾知识。
用作面试复习,事半功倍。
分为上下篇,上篇主要内容为:
基础
概述
数据类型
数据结构
字典
跳跃表
使用场景
会话缓存
缓存
计数器
查找表
消息队列
分布式 Session
分布式锁
其它
Redis 与 Memcached 对比
数据类型
数据持久化
单线程
分布式
内存管理机制
键的过期时间
数据淘汰策略
全复习手册文章导航:
点击公众号下方技术推文——面试冲刺
已发布知识点复习手册
Java基础知识点面试手册(上)
Java基础知识点面试手册(下)
Java容器(List、Set、Map)知识点快速复习手册(上)
Java容器(List、Set、Map)知识点快速复习手册(中)
Java容器(List、Set、Map)知识点快速复习手册(下)
Redis 是速度非常快的非关系型(NoSQL)内存键值数据库,可以存储键和五种不同类型的值之间的映射。
键的类型只能为字符串
Redis 支持很多特性,例如将内存中的数据持久化到硬盘中,使用复制来扩展读性能,使用分片来扩展写性能。
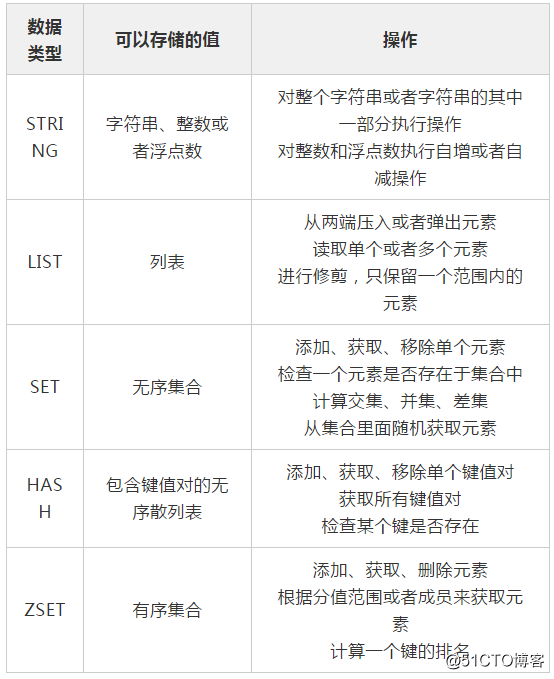
image.png
1> set hello world
2OK
3> get hello
4"world"
5> del hello
6(integer) 1
7> get hello
8(nil)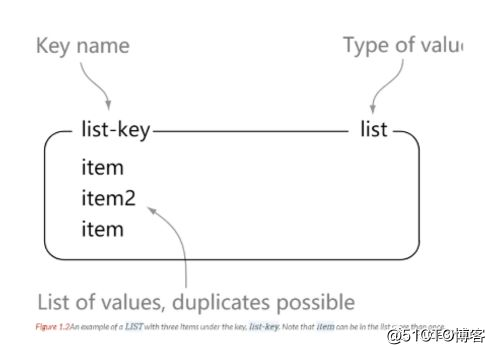
image.png
1> rpush list-key item
2(integer) 1
3> rpush list-key item2
4(integer) 2
5> rpush list-key item
6(integer) 3
7
8> lrange list-key 0 -1
91) "item"
102) "item2"
113) "item"
12
13> lindex list-key 1
14"item2"
15
16> lpop list-key
17"item"
18
19> lrange list-key 0 -1
201) "item2"
212) "item"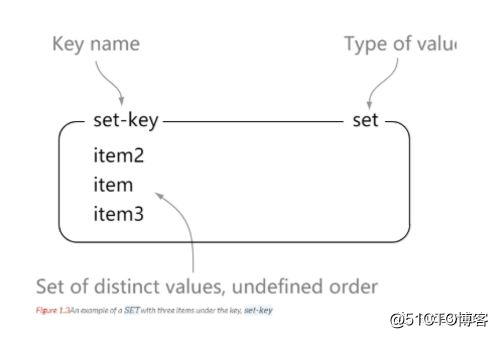
image.png
1> sadd set-key item
2(integer) 1
3> sadd set-key item2
4(integer) 1
5> sadd set-key item3
6(integer) 1
7> sadd set-key item
8(integer) 0
9
10> smembers set-key
111) "item"
122) "item2"
133) "item3"
14
15> sismember set-key item4
16(integer) 0
17> sismember set-key item
18(integer) 1
19
20> srem set-key item2
21(integer) 1
22> srem set-key item2
23(integer) 0
24
25> smembers set-key
261) "item"
272) "item3"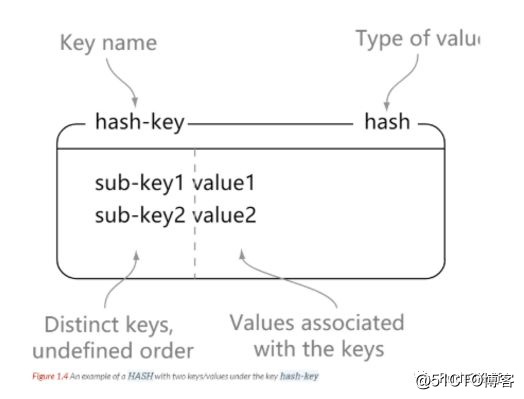
image.png
1> hset hash-key sub-key1 value1
2(integer) 1
3> hset hash-key sub-key2 value2
4(integer) 1
5> hset hash-key sub-key1 value1
6(integer) 0
7
8> hgetall hash-key
91) "sub-key1"
102) "value1"
113) "sub-key2"
124) "value2"
13
14> hdel hash-key sub-key2
15(integer) 1
16> hdel hash-key sub-key2
17(integer) 0
18
19> hget hash-key sub-key1
20"value1"
21
22> hgetall hash-key
231) "sub-key1"
242) "value1"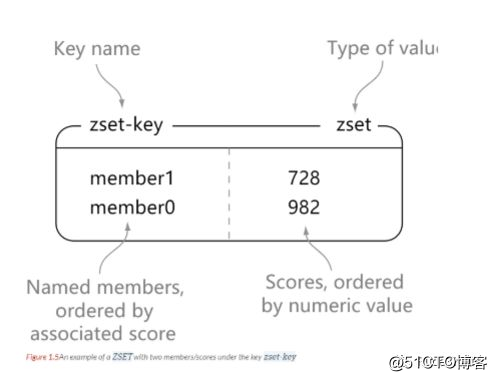
image.png
1> zadd zset-key 728 member1
2(integer) 1
3> zadd zset-key 982 member0
4(integer) 1
5> zadd zset-key 982 member0
6(integer) 0
7
8> zrange zset-key 0 -1 withscores
91) "member1"
102) "728"
113) "member0"
124) "982"
13
14> zrangebyscore zset-key 0 800 withscores
151) "member1"
162) "728"
17
18> zrem zset-key member1
19(integer) 1
20> zrem zset-key member1
21(integer) 0
22
23> zrange zset-key 0 -1 withscores
241) "member0"
252) "982"zset是set的一个升级版本,他在set的基础上增加了一个顺序属性,这一属性在添加修改元素的时候可以指定,每次指定后,zset会自动重新按新的值调整顺序。 可以对指定键的值进行排序权重的设定,它应用排名模块比较多。
跳跃表(shiplist)是实现sortset(有序集合)的底层数据结构之一
另外还可以用 Sorted Sets 来做带权重的队列,比如普通消息的 score 为1,重要消息的 score 为2,然后工作线程可以选择按 score的倒序来获取工作任务,让重要的任务优先执行。
dictht 是一个散列表结构,使用拉链法保存哈希冲突的 dictEntry。
1/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
2 * implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
3typedef struct dictht {
4 dictEntry **table;
5 unsigned long size;
6 unsigned long sizemask;
7 unsigned long used;
8} dictht;
1typedef struct dictEntry {
2 void *key;
3 union {
4 void *val;
5 uint64_t u64;
6 int64_t s64;
7 double d;
8 } v;
9 struct dictEntry *next;
10} dictEntry;Redis 的字典 dict 中包含两个哈希表 dictht,这是为了方便进行 rehash 操作。
在扩容时,将其中一个 dictht 上的键值对 rehash 到另一个 dictht 上面,完成之后释放空间并交换两个 dictht 的角色。
1typedef struct dict {
2 dictType *type;
3 void *privdata;
4 dictht ht[2];
5 long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
6 unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
7} dict;rehash 操作不是一次性完成,而是采用渐进方式,这是为了避免一次性执行过多的 rehash 操作给服务器带来过大的负担。
渐进式 rehash 通过记录 dict 的 rehashidx 完成,它从 0 开始,然后每执行一次 rehash 都会递增。例如在一次 rehash 中,要把 dict[0] rehash 到 dict[1],这一次会把 dict[0] 上 table[rehashidx] 的键值对 rehash 到 dict[1] 上,dict[0] 的 table[rehashidx] 指向 null,并令 rehashidx++。
在 rehash 期间,每次对字典执行添加、删除、查找或者更新操作时,都会执行一次渐进式 rehash。
采用渐进式 rehash 会导致字典中的数据分散在两个 dictht 上,因此对字典的操作也需要到对应的 dictht 去执行。
1/* Performs N steps of incremental rehashing. Returns 1 if there are still
2 * keys to move from the old to the new hash table, otherwise 0 is returned.
3 *
4 * Note that a rehashing step consists in moving a bucket (that may have more
5 * than one key as we use chaining) from the old to the new hash table, however
6 * since part of the hash table may be composed of empty spaces, it is not
7 * guaranteed that this function will rehash even a single bucket, since it
8 * will visit at max N*10 empty buckets in total, otherwise the amount of
9 * work it does would be unbound and the function may block for a long time. */
10int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
11 int empty_visits = n * 10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */
12 if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
13
14 while (n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {
15 dictEntry *de, *nextde;
16
17 /* Note that rehashidx can‘t overflow as we are sure there are more
18 * elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
19 assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long) d->rehashidx);
20 while (d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
21 d->rehashidx++;
22 if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
23 }
24 de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
25 /* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
26 while (de) {
27 uint64_t h;
28
29 nextde = de->next;
30 /* Get the index in the new hash table */
31 h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
32 de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
33 d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
34 d->ht[0].used--;
35 d->ht[1].used++;
36 de = nextde;
37 }
38 d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
39 d->rehashidx++;
40 }
41
42 /* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */
43 if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
44 zfree(d->ht[0].table);
45 d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
46 _dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
47 d->rehashidx = -1;
48 return 0;
49 }
50
51 /* More to rehash... */
52 return 1;
53}什么是跳跃表?(程序员小灰)http://blog.jobbole.com/111731/
https://blog.csdn.net/qq910894904/article/details/37883953
来看看跳跃表的复杂度分析:
相关操作的时间复杂度:
它是按层建造的。底层是一个普通的有序链表。每个更高层都充当下面列表的“快速跑道”,这里在层i中的元素按概率l/p出现在层i+1中。
平均起来,每个元素都在p/(p-1)个列表中出现,而最高层的元素(通常是在跳跃列表前段的一个特殊的头元素)在O(logp n)个列表中出现。
调节p的大小可以在内存消耗和时间消耗上进行折中。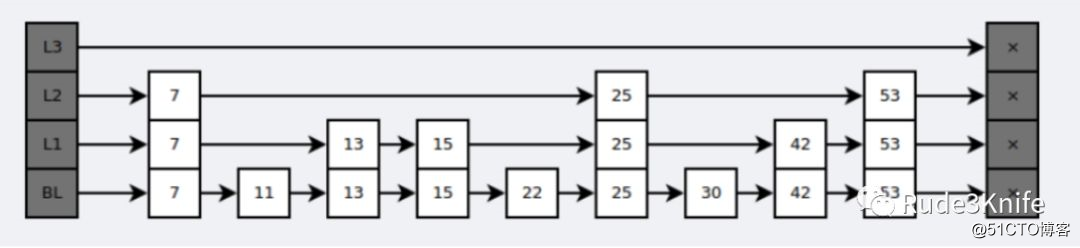
image.png
在查找时,从上层指针开始查找,找到对应的区间之后再到下一层去查找。下图演示了查找 22 的过程。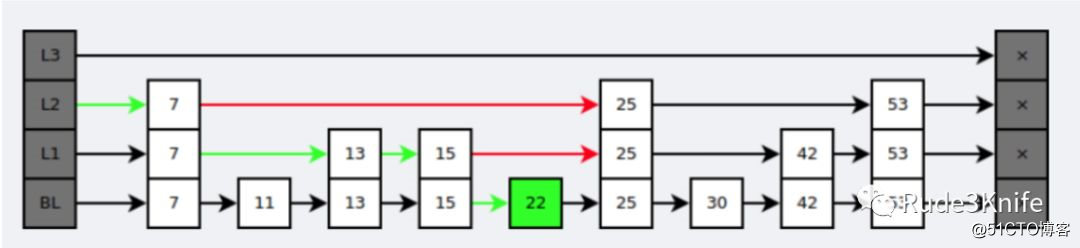
image.png
与红黑树等平衡树相比,跳跃表具有以下优点:
在分布式场景下具有多个应用服务器,可以使用 Redis 来统一存储这些应用服务器的会话信息。
当应用服务器不再存储用户的会话信息,也就不再具有状态,一个用户可以请求任意一个应用服务器。
将热点数据放到内存中,设置内存的最大使用量以及过期淘汰策略来保证缓存的命中率。
可以对 String 进行自增自减运算,从而实现计数器功能。
Redis 这种内存型数据库的读写性能非常高,很适合存储频繁读写的计数量。
例如 DNS 记录就很适合使用 Redis 进行存储。
查找表和缓存类似,也是利用了 Redis 快速的查找特性。但是查找表的内容不能失效,而缓存的内容可以失效,因为缓存不作为可靠的数据来源。
List 是一个双向链表,可以通过 lpop 和 lpush 写入和读取消息。
不过最好使用 Kafka、RabbitMQ 等消息中间件。
多个应用服务器的 Session 都存储到 Redis 中来保证 Session 的一致性。
分布式锁实现
在分布式场景下,无法使用单机环境下的锁来对多个节点上的进程进行同步。
可以使用 Reids 自带的 SETNX 命令实现分布式锁,除此之外,还可以使用官方提供的 RedLock 分布式锁实现。
Set 可以实现交集、并集等操作,从而实现共同好友等功能。
ZSet 可以实现有序性操作,从而实现排行榜等功能。
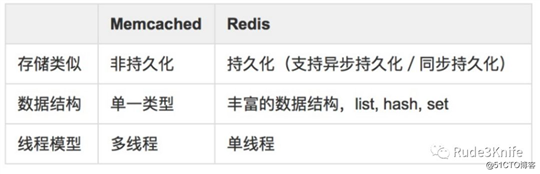
image.png
Memcached 仅支持字符串类型,而 Redis 支持五种不同种类的数据类型,使得它可以更灵活地解决问题。
Redis 支持两种持久化策略:RDB 快照和 AOF 日志,而 Memcached 不支持持久化。
https://www.cnblogs.com/syyong/p/6231326.html
Redis快的主要原因是:
完全基于内存
数据结构简单,对数据操作也简单
使用多路 I/O 复用模型
单进程单线程好处
单进程单线程弊端
其他一些优秀的开源软件采用的模型
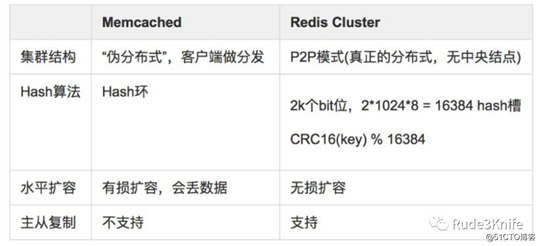
Memcached 不支持分布式,只能通过在客户端使用像一致性哈希这样的分布式算法来实现分布式存储,这种方式在存储和查询时都需要先在客户端计算一次数据所在的节点。
Redis Cluster 实现了分布式的支持。采用虚拟槽。(为何不需要计算了?不懂)
在 Redis 中,并不是所有数据都一直存储在内存中,可以将一些很久没用的 value 交换到磁盘。而Memcached 的数据则会一直在内存中。
Memcached 将内存分割成特定长度的块来存储数据,以完全解决内存碎片的问题,但是这种方式会使得内存的利用率不高,例如块的大小为 128 bytes,只存储 100 bytes 的数据,那么剩下的 28 bytes 就浪费掉了。
Redis 可以为每个键设置过期时间,当键过期时,会自动删除该键。
对于散列表这种容器,只能为整个键设置过期时间(整个散列表),而不能为键里面的单个元素设置过期时间。
可以设置内存最大使用量,当内存使用量超过时施行淘汰策略,具体有 6 种淘汰策略。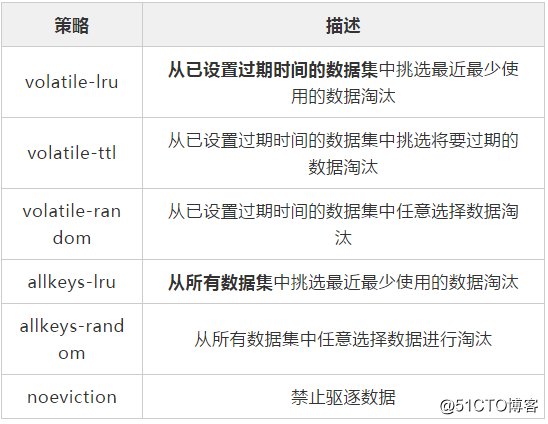
作为内存数据库,出于对性能和内存消耗的考虑,Redis 的淘汰算法实际实现上并非针对所有 key,而是抽样一小部分并且从中选出被淘汰的 key。
使用 Redis 缓存数据时,为了提高缓存命中率,需要保证缓存数据都是热点数据。可以将内存最大使用量设置为热点数据占用的内存量,然后启用 allkeys-lru 淘汰策略,将最近最少使用的数据淘汰。
Redis 4.0 引入了 volatile-lfu 和 allkeys-lfu 淘汰策略,LFU 策略通过统计访问频率,将访问频率最少的键值对淘汰。
https://github.com/CyC2018/Interview-Notebook/blob/master/notes/Redis.md
我是蛮三刀把刀,目前为后台开发工程师。主要关注后台开发,网络安全,Python爬虫等技术。
来微信和我聊聊:yangzd1102
Github:https://github.com/qqxx6661
拥有专栏:Leetcode题解(Java/Python)、Python爬虫开发
https://www.zhihu.com/people/yang-zhen-dong-1/
拥有专栏:码农面试助攻手册
https://juejin.im/user/5b48015ce51d45191462ba55
https://www.jianshu.com/u/b5f225ca2376

个人公众号:Rude3Knife
个人公众号:Rude3Knife
如果文章对你有帮助,不妨收藏起来并转发给您的朋友们~
原文:https://blog.51cto.com/15047490/2561271