?双向循环链表和单向循环链表一样都是线性链式存储结构,顾名思义双向循环链表就是在两个方向都可以访问任一数据。
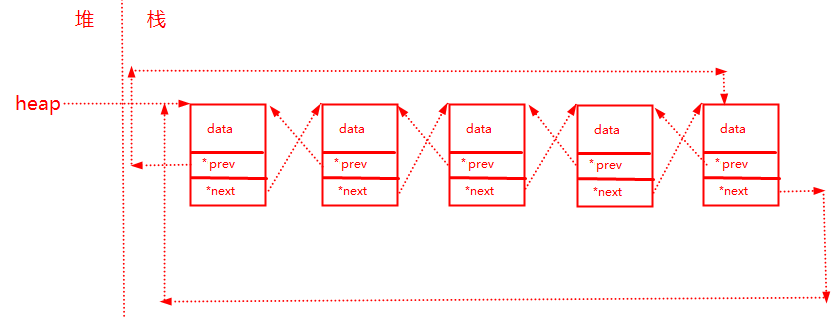
?调用下面代码创建一个结点作为头结点,让它的头指针prev和尾指针next都指向自己,最后返回这个头结点的堆地址。
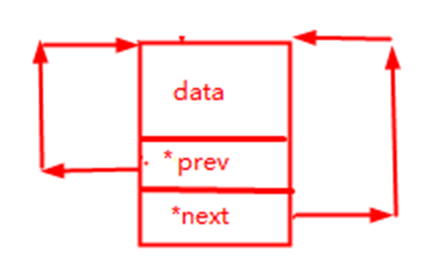
p_douoble_crclist new_node()
{
p_douoble_crclist new = calloc(1, sizeof(my_double_crclist));
if(NULL == new)
return NULL;
new->prev = new;
new->next = new;
return new;
}
?从键盘上获得数据并返回,形式参数是一个字符串,用来说明获得数据的用途。
int input_msg(char *msg)
{
int data;
printf("%s", msg);
scanf("%d", &data);
while(‘\n‘ != getchar());
return data;
}
?在任意节点后插入一个节点。
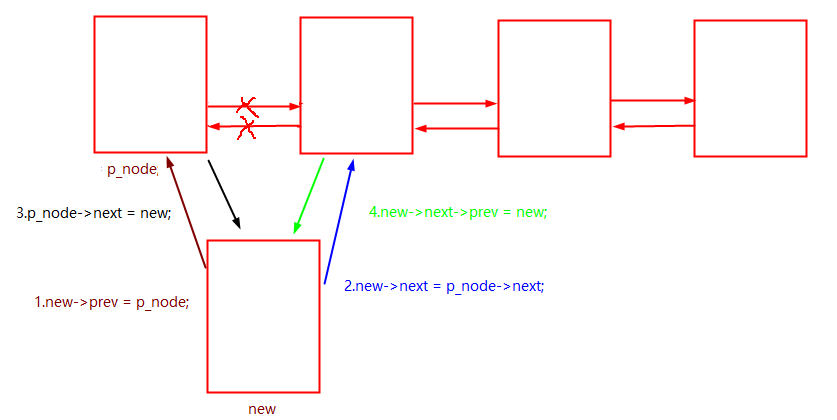
bool insert_node(p_douoble_crclist front_node, p_douoble_crclist new)
{
p_douoble_crclist p_node = front_node;//front_node为前置节点,new是需要插入的节点
if(NULL == new)//当new为空时,表示需要新创建一个节点插入链表
{
int data;
new = new_node();
if(NULL == new)
return false;
new->data = input_msg("请输入要添加的数据:");
}
new->prev = p_node;
new->next = p_node->next;
p_node->next = new;
new->next->prev = new;
return true;
}
?将链表中的所有数据打印出来。
void display_node(p_douoble_crclist head)
{
p_douoble_crclist pos = head->next;
for(int i = 0; pos != head; i++) //当将链表遍历一遍后就跳出循环
{
printf("节点%d的数据为:%d\n", i, pos->data);//每跳一个节点就将其数据打印出来
pos = pos->next;
}
}
?查找链表中是否有某个数据,有的话返回该数据所在节点的地址。
p_douoble_crclist find_data_to_list(p_douoble_crclist head, char *msg)
{
p_douoble_crclist fdpos = head->next;
int fdata;
if(msg == NULL)
{
fdata = input_msg("请输入需要查找的数据:");
}
else
{
fdata = input_msg(msg);
}
while(fdpos != head) //遍历链表
{
if(fdpos->data != fdata)//每跳一个节点就比较该节点数据是否,是需要查找的。
{
fdpos = fdpos->next;
continue;
}
else
{
return fdpos;
}
}
return NULL;
}
?删除指定节点
p_douoble_crclist del_node_to_list(p_douoble_crclist head, p_douoble_crclist del_node)
{
p_douoble_crclist dpos = head;
if(NULL == head)
{
return NULL;
}
while(dpos->next != del_node)
{
dpos = dpos->next;
}
dpos->next = del_node->next;
del_node->next->prev = dpos;
del_node->next = del_node->prev = del_node;
return del_node;
}
?修改某个节点的数据。
bool mod_node_data(p_douoble_crclist mod_node)
{
int mod_data;
if(NULL == mod_node)
{
return false;
}
printf("将数据修改为:");
scanf("%d", &mod_data);
mod_node->data = mod_data;
return true;
}
?将链表中的节点空间逐个释放。
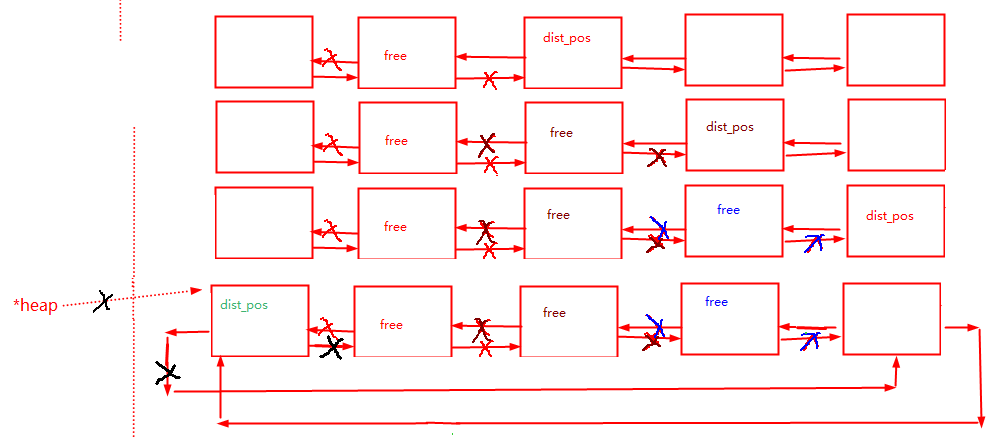
bool distory_list(p_douoble_crclist *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("该链表已近是空的!!!");
}
p_douoble_crclist dist_pos = (*head)->next;
while(dist_pos != (*head))
{
dist_pos = dist_pos->next;
dist_pos->prev->next = NULL;
dist_pos->prev->prev = NULL;
free(dist_pos->prev); //还有一个节点没有释放掉,试了很多方法就是不行
}
(*head)->next = NULL;
(*head)->prev = NULL;
free(*head);
*head = NULL;
return dist_pos;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
p_douoble_crclist head = new_node();
if(NULL == head)
return -1;
insert_node(head, NULL);
insert_node(head, NULL);
insert_node(head, NULL);
insert_node(head, NULL);
insert_node(head, NULL);
insert_node(head, NULL);
insert_node(head, NULL);
insert_node(head, NULL);
display_node(head);
p_douoble_crclist del_node;
p_douoble_crclist mv_node;
p_douoble_crclist front_node;
p_douoble_crclist mod_node;
del_node = find_data_to_list(head, "移动数据:");
mv_node = del_node_to_list(head, del_node);
display_node(head);
front_node = find_data_to_list(head, "将移出的数据插入到前置节点:");
insert_node(front_node, mv_node);
display_node(head);
mod_node = find_data_to_list(head, "修改数据:");
mod_node_data(mod_node);
display_node(head);
distory_list(&head);
return 0;
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/ding-ding-light/p/14110848.html