对于 简单的 no block io ,实际还是建立的 server <-> client 的连接关系;
一般我们所了解到或听到的模型 一般都会 搭配 "多路复用"的概念;
对于多路复用实际就是 利用了 Selector(选择器)相关实现复用的目的;
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiplexer
维基百科 对 多路复用概念的解释, multi input with single output
对应在java中的相关类包含如下:
java.nio.channels.Selector
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-blocking_I/O_(Java)#Selectors
"A multiplexor of {@link SelectableChannel} objects." : java doc
支持多路复用 selectableChannel, 其管理了所有注册的channel以及每个channel的读取状态
java.nio.channels.SelectableChannel
A channel that can be multiplexed via a {@link Selector}.
java doc
作为一个抽象类定义了 关于 selectable类型的channel 需要支持的功能 例如 : register(Selector,ops) 支持将当前channel注册到指定的selector 供其管理
java.nio.channels.SelectionKey
A token representing the registration of a {@link SelectableChannel} with a {@link Selector}.
java doc
其目的是用来管理 已存在绑定关系的 selector和selectableChannel
"talk is cheap ,show me the code"
将serverSocketChannel 交由 selector 进行管理, 对于client 仍然使用 直接连接
server:
/* * Copyright (c) 2020, guoxing, Co,. Ltd. All Rights Reserved */ package com.xingguo.noblockio; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; /** * SelectorServerDemo * 对于 {@link java.nio.channels.Selector} * 由于不同的操作系统实际会存在不同的实现方式 select 和 epoll * <p> * 对于 no block io 的标准模板是 连接复用, 当只使用 {@link ServerSocketChannel#accept()}实际是每次都会建立新的连接; * 而 {@link java.nio.channels.Selector} 通过注册多个channel 与socketChannel 进行关联,通过管理channel的方式,来实现Socket的复用,从而体现了"多路复用" * * @author guoxing * @date 2020/12/11 4:49 PM * @since */ public class SelectorServerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { fixSelectorServer(); } private static void fixSelectorServer() { // 创建一个 serverSocketChannel try (ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open()) { // 绑定一个端口 8080 serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080)); // 设置为非阻塞 serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); System.out.println("当前服务器地址:" + serverSocketChannel.socket().getLocalSocketAddress()); // 创建一个 selector, 用于管理 注册的channel 和 读取状态 try (Selector selector = Selector.open()) { // 绑定 selector 和 socket 的关系 // 对于 OP_ACCEPT 实际包含了所有的类型 serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); // 对于当前返回的数据only read // selector.keys(); while (true) { System.out.println("selector is open:" + selector.isOpen()); // 获取已成功建立连接的 SelectableChannel 数量,对于当前操作,最大值为1,因为只注册了一个 channel int select = selector.select(); System.out.println("select is " + select); if (select == 0) { // 继续等待连接建立 continue; } // 返回所有成功建立连接的 selectionKey // 其表示的是 SelectableChannel 和 SelectionKey 的关系 // 对于当前返回的数据是 不可新增操作集合 Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next(); if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) { // selectionKey封装了channel 和 selector的关系 ServerSocketChannel socketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel(); // 判断当前的连接是否完成建立 SocketChannel accept = socketChannel.accept(); if (accept == null) { continue; } System.out.printf("接收到客户端请求:[%s]\n", accept.getRemoteAddress()); ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(8); // 写入当前时间 allocate.putLong(System.currentTimeMillis()); // 游标复位 allocate.flip(); while (allocate.hasRemaining()) { // 将数据数据发送给客户端 accept.write(allocate); } // 关闭当前连接 // socketChannel.close(); // this is a bug; 当关闭了socketChannel,但由于selectableChannel没有关闭,实际对于 client 而言,相当于连接一直存在 /** * selector 提供的功能实际 就是 server 复用, * 对于 原始的 serverSocket 和 socket(client) , 连接关系实际为 server <-> client * 当 使用{@link ServerSocketChannel#register(Selector, int)} 时, 连接关系就变成了 servers <-> sequence of {@link java.nio.channels.SelectableChannel} ; {@link java.nio.channels.SelectableChannel} <-> client ; 连接关系变为了 n(server) : n(selectableChannel) : n(client) */ //TODO warning 关闭正确的连接 accept.close(); System.out.println("服务端数据发送完成"); } // 移除已接收的key iterator.remove(); } } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
client: 对于client 端 其和普通的socketChannel使用没有任何区别
/* * Copyright (c) 2020, guoxing, Co,. Ltd. All Rights Reserved */ package com.xingguo.noblockio; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.SocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; /** * SocketChannelClientDemo * {@link java.nio.channels.SocketChannel} * * @author guoxing * @date 2020/12/11 8:15 PM * @since */ public class SocketChannelClientDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { /** * 对于client 端实际就不需要像{@link java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel}一样麻烦 * 对于client 而言其就是一个普通的 {@link java.nio.channels.SocketChannel} */ try (SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open()) { // 设置当前未 no block socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); /** * 由于使用的 no block 模式,因此在 {@link SocketChannel#connect(SocketAddress)}时会直接返回false,并不会真正建立连接 * 而是会等待{@link SocketChannel#finishConnect()}完成 nio 模式下的连接建立 */ // 指定要连接服务地址和端口 boolean connect = socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(8080)); // 完成 非阻塞式 连接建立 while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) { System.out.println("等待连接建立....."); } // 判断当前连接状态 while (socketChannel.isConnected()) { // 创建一个 4k 的容器 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4 * 1024); // 将接受到的数据读取出来写入到byteBuffer中 while (socketChannel.read(byteBuffer) != -1) { // 准备读取 byteBuffer中的数据 byteBuffer.flip(); while (byteBuffer.hasRemaining()) { System.out.print((char) byteBuffer.get()); } byteBuffer.clear(); } socketChannel.close(); } } } }
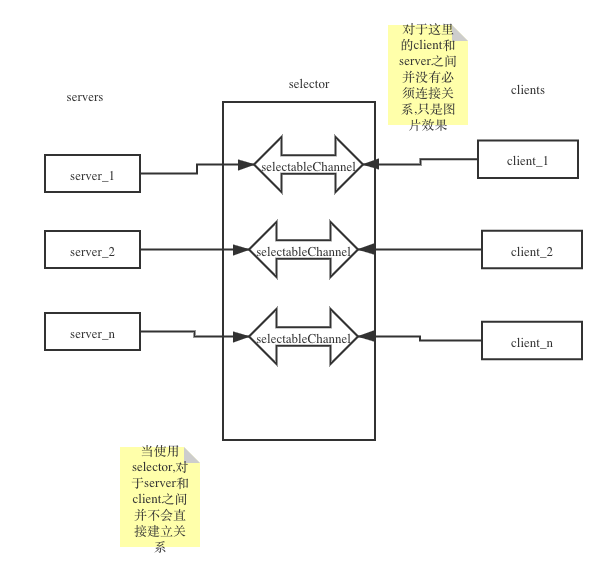
java学习-io-socketChannel-selector
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/xingguoblog/p/14124568.html