寡人怎么也没想到 T1写挂了,
给出一个n个未知数的方程,\(x_1,x_2,x_3......x_n\)求\(x_1+x_2+x_3....+x_n==S\)的正整数解的个数,并且要保证,对于任意\(i (1<=i< n)\) \(x_i\)与\(x_{i+1}\)相差不大于\(p\)
对于 \(30%\) 数据 \(2<=n<=10 ,p=0,S<=30;\)对于 \(100%\) 数据 \(2<=n<=10,p<=3 , S<=30;\)保证数据有梯度。
/*
by : Zmonarch
知识点 :搜索
*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <cstring>
#define int long long
using namespace std ;
inline int read()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1 ; char ch = getchar() ;
while(!isdigit(ch)) { if(ch == ‘-‘) f = - 1 ; ch = getchar() ; }
while( isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - ‘0‘ ; ch = getchar() ; }
return x * f ;
}
int n , tot , s , p ;
void search(int now , int last ,int rest)
{
//printf("sum : %d\n" ,rest) ;
if(now == n + 1 ) //现在已经加到了最后一个数
{
if (rest == 0) tot ++ ;//方案数++
return ;
}
for(int i = 1 ; i < s && abs(i - last ) <= p; i++)//前一个数和后一个数不能超过p
{
search(now + 1 , i , rest - last - i) ;
}
}
signed main()
{
// freopen("math.in" , "r" , stdin) ;
// freopen("math.out" , "w" , stdout) ;
n = read() , s = read() , p = read() ;
//for(int i = 1 ; i <= s ; i++)
if(p == 0) //因为是正整数, 所以如果相差为零, 那么也就只有一种情况, 那就是全部都是同一个数的时候,除不尽就不是正整数了
{ //这里的相差是绝对值, 特判一下 ,
if(s % n == 0) printf("1") ;
else printf("0") ;
}
else
{
search( 0 , 0 ,s) ;
printf("%lld", tot) ;
}
return 0 ;
}
/*
by : Zmonarch
知识点 :搜索
*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <cstring>
#define int long long
using namespace std ;
inline int read()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1 ; char ch = getchar() ;
while(!isdigit(ch)) { if(ch == ‘-‘) f = - 1 ; ch = getchar() ; }
while( isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - ‘0‘ ; ch = getchar() ; }
return x * f ;
}
int n , tot , s , p ;
void search(int now , int last ,int rest)
{
if(now == n) //现在已经加到了最后一个数
{
if (abs(rest - last) <= p) tot ++ ;
return ;
}
for(int i = max((long long)1 , last - p) ; i <= min(last + p , rest - n + i); i++)//前一个数和后一个数不能超过p
{
search(now + 1 , i , rest - i) ;
}
}
signed main()
{
//freopen("math.in" , "r" , stdin) ;
//freopen("math.out" , "w" , stdout) ;
n = read() , s = read() , p = read() ;
//for(int i = 1 ; i <= s ; i++)
if(p == 0) //因为是正整数, 所以如果相差为零, 那么也就只有一种情况, 那就是全部都是同一个数的时候,除不尽就不是正整数了
{ //这里的相差是绝对值, 特判一下 ,
if(s % n == 0) printf("1") ;
else printf("0") ;
}
else
{
for(int i = 1 ; i <= s-(n-1) ; i++)
search( 2 , i ,s - i) ;
printf("%lld", tot) ;
}
return 0 ;
}
给出一个\(n \times n\)的网格,有一些格子是障碍,再给出一对起点终点,求从起点到终点需要的最小步数,每次可以从一个格子走到上下左右4相邻的四个格子里.
第一行一个整数\(n\)。
以下\(n\)行\(n\)个整数,描述整个网格,其中\(0\)表示没有障碍,\(1\)表示有障碍。
最后一行四个整数,\(Sx,Sy,Tx,Ty\),描述起点和终点。
输出最少步数。
如果永远走不到输出-1。
对于30%的数据,\(n<=10\)
对于 100%的测试数据,\(n<=1000\)。
大水题 ,一眼切 , 直接过。
/*
by : Zmonarch
知识点 : 搜索
*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <cstring>
#define int long long
using namespace std ;
const int kmaxn = 1000 + 1 ;
const int inf = 2147483647 ;
inline int read()
{
int x = 0 , f = 1 ; char ch = getchar() ;
while(!isdigit(ch)) { if(ch == ‘-‘) f = - 1 ; ch = getchar() ; }
while( isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - ‘0‘ ; ch = getchar() ; }
return x * f ;
}
int n , vis[kmaxn][kmaxn] , f[kmaxn][kmaxn] , sx , sy , tx , ty , ans = inf;
int dx[4] = {0 , 0 , 1 , -1} ;
int dy[4] = {1 , -1 , 0 , 0} ;
struct node
{
int x , y , step ;
};
queue<node> q ;
bool check(int x , int y)
{
return ( x <= n && y<=n && x >= 1 && y >= 1) ;
}
void search(node now)
{
q.push(now) ;
while(!q.empty())
{
node u = q.front() ;
q.pop() ;
int x = u.x , y = u.y , step = u.step ;
if(step >= ans) continue ; //小小的优化,截去不符合条件的搜索枝
if(u.x == tx && u.y == ty)
{
ans = min(ans , step) ;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++)
{
int kx = x + dx[i] ;
int ky = y + dy[i] ;
if(!check(kx , ky)) continue ; //检查边界
if(vis[kx][ky]) continue ;
vis[kx][ky] = 1 ;
// printf("%d %d\n" , kx , ky) ;
node nxt = {kx , ky , step + 1} ;
q.push(nxt) ;
}
}
}
signed main()
{
//freopen("grid.in" , "r" , stdin) ;
//freopen("grid.out" , "w" , stdout) ;
n = read() ;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++)
{
for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j++)
{
vis[i][j] = read() ;
}
}
sx = read() , sy = read() , tx = read() , ty = read() ;
if(vis[sx][sy] || vis[tx][ty])
{
cout <<"-1" ;
return 0 ;
}
node ss = {sx , sy , 0} ;
search(ss) ;
if(ans != inf) printf("%lld" , ans) ;
else printf("-1") ;
return 0 ;
}
戈兰斜是一种在带数字的网格上玩的日本拼图游戏。目标是在网格的每个单元格中绘制对角线,连接到每个格点的对角线个数等于他对应的数字。另外,禁止对角线形成环。
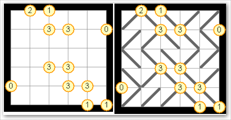
第 一个 图给 出了游戏的初始状态。 第二个图给出了对应的一个解答。数据保证问题一定存在至少一解。
输 入的 第一 行包含一个的单个整数 \(n\)表示棋盘的尺寸,棋盘是一个正方形。
然后紧接 \(n+1\)行。包含网格的初始状态。每行为一个含\(n+1\)个字符的字符串,字符要么为一个数字,要么为一个(‘.’),
其中数字都是\(0\)到\(4\)之间的任意整数,‘.’表示连接到此格点的对角线数没有限制
输出包含 \(n\)行,每行 \(n\) 个字符,每个字符为斜杠或反斜杠表示如何填充相应的棋盘。
对于 \(100%\)的数据 , \(n\leq 7\)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Zmonarch/p/14225122.html