影院管理项目
组建一个家庭影院:DVD 播放器、 投影仪、 自动屏幕、 环绕立体声、 爆米花机,要求完成使用家庭影院的功能, 其过程为:直接用遥控器统筹各设备开关
DVD, 选 DVD传统方式解决影院管理
每个设备都对应于一个类,导致客户端依次调用类的方法, 使用时,直接依赖于具体的类
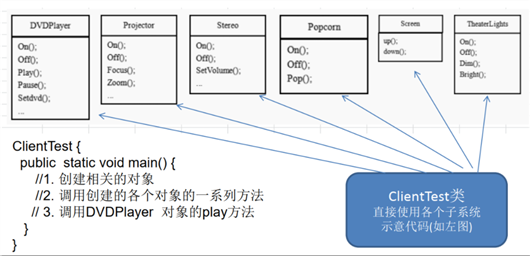
传统方式解决影院管理问题分析
ClientTest 的main方法中,创建各个子系统的对象,并直接去调用子系统(对象)相关方法,会造成调用过程混乱,没有清晰的过程ClientTest 代码中对子系统进行维护操作解决思路:
ready, play, pause, end),用来访问子系统中的一群接口基本介绍:
Facade), 也叫过程模式,外观模式为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,此模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用外观模式原理类图
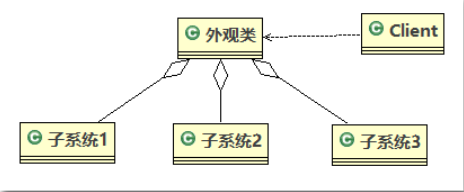
原理类图的说明(外观模式的角色)
Facade):为调用端提供统一的调用接口,外观类知道哪些子系统负责处理请求,从而将用端的请求代理给适当子系统对象Client):外观接口的调用者Facade 对象指派的任务,他是功能的实际提供者结构图:
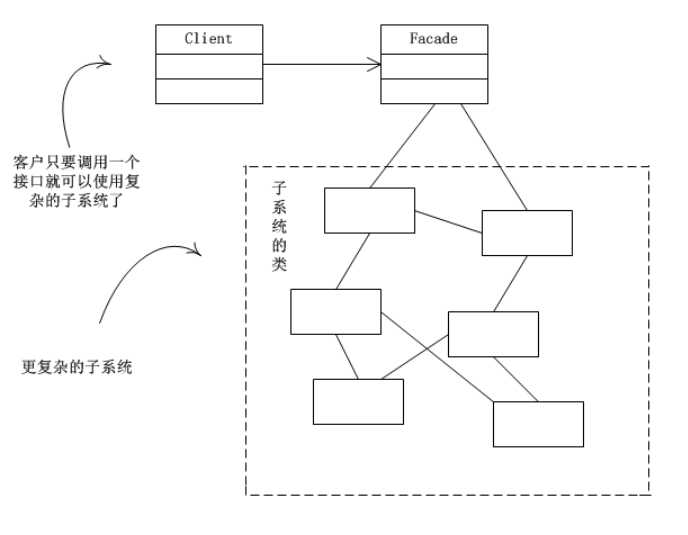
外观模式可以理解为转换一群接口,客户只要调用一个接口,而不用调用多个接口才能达到目的。 比如:在pc上安装软件的时候经常有一键安装选项(省去选择安装目录、安装的组件等等),还有就是手机的重启功能(把关机和启动合为一个操作)。
外观模式就是解决多个复杂接口带来的使用困难,起到简化用户操作的作用
所以对于一些复杂的多个系统(类)的调用, 不应该在使用方直接使用,可以将一些常用操作封装起来, 对外暴露一个"外观",内部对各个子系统进行调用
代码实现
类图:
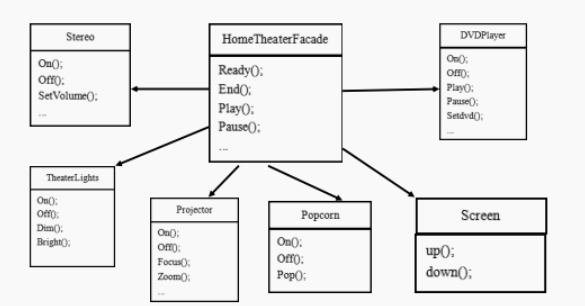
各个子系统,
public class DVDPlayer {
// 使用单例模式, 使用饿汉式
private static DVDPlayer instance = new DVDPlayer();
public static DVDPlayer getInstanc() {
return instance;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(" dvd on ");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(" dvd off ");
}
public void play() {
System.out.println(" dvd is playing ");
}
// ....
public void pause() {
System.out.println(" dvd pause ..");
}
}
public class Popcorn {
private static Popcorn instance = new Popcorn();
public static Popcorn getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(" popcorn on ");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(" popcorn ff ");
}
public void pop() {
System.out.println(" popcorn is poping ");
}
}
public class Screen {
private static Screen instance = new Screen();
public static Screen getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public void up() {
System.out.println(" Screen up ");
}
public void down() {
System.out.println(" Screen down ");
}
}
public class Stereo {
private static Stereo instance = new Stereo();
public static Stereo getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(" Stereo on ");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(" Screen off ");
}
public void up() {
System.out.println(" Screen up.. ");
}
// ...
}
public class TheaterLight {
private static TheaterLight instance = new TheaterLight();
public static TheaterLight getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(" TheaterLight on ");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(" TheaterLight off ");
}
public void dim() {
System.out.println(" TheaterLight dim.. ");
}
public void bright() {
System.out.println(" TheaterLight bright.. ");
}
}
外观类,对各个系统的调用封装
public class HomeTheaterFacade {
// 定义各个子系统对象
private TheaterLight theaterLight;
private Popcorn popcorn;
private Stereo stereo;
private Projector projector;
private Screen screen;
private DVDPlayer dVDPlayer;
// 构造器
public HomeTheaterFacade() {
super();
this.theaterLight = TheaterLight.getInstance();
this.popcorn = Popcorn.getInstance();
this.stereo = Stereo.getInstance();
this.projector = Projector.getInstance();
this.screen = Screen.getInstance();
this.dVDPlayer = DVDPlayer.getInstanc();
}
// 操作分成 4 步
public void ready() {
popcorn.on();
popcorn.pop();
screen.down();
projector.on();
stereo.on();
dVDPlayer.on();
theaterLight.dim();
}
public void play() {
dVDPlayer.play();
}
public void pause() {
dVDPlayer.pause();
}
public void end() {
popcorn.off();
theaterLight.bright();
screen.up();
projector.off();
stereo.off();
dVDPlayer.off();
}
}
client, 测试
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 这里直接调用。。。很麻烦,也不利于扩展
// 使用外观模式
HomeTheaterFacade homeTheaterFacade = new HomeTheaterFacade();
homeTheaterFacade.ready();
homeTheaterFacade.play();
homeTheaterFacade.end();
}
}
使用tomcat作为web容器时,接收浏览器发送过来的请求,tomcat会将请求信息封装成ServletRequest对象,如下图①处对象。但是大家想想ServletRequest是一个接口,它还有一个子接口HttpServletRequest,而我们知道该request对象肯定是一个HttpServletRequest对象的子实现类对象,到底是哪个类的对象呢?可以通过输出request对象,我们就会发现是一个名为RequestFacade的类的对象。
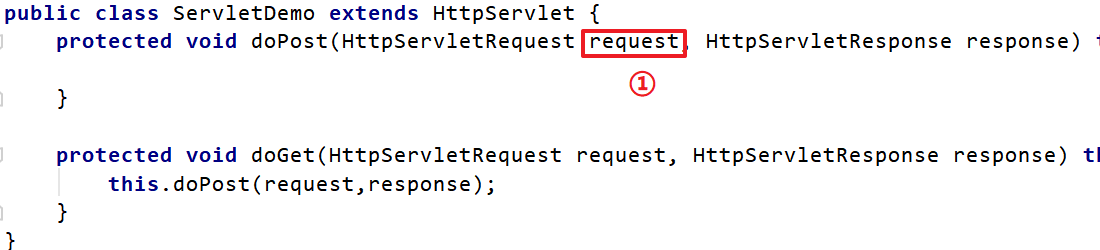
RequestFacade类就使用了外观模式。先看结构图:
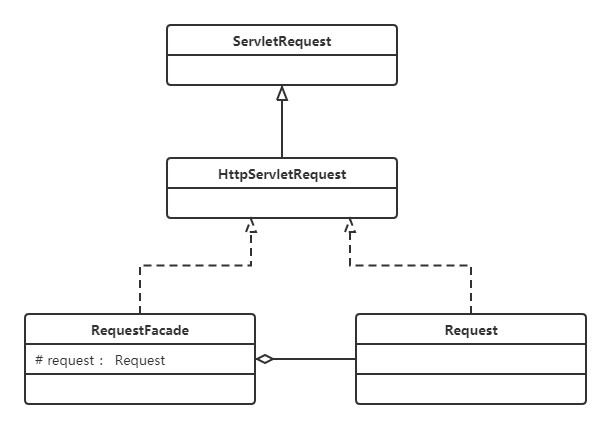
为什么在此处使用外观模式呢?
? 定义 RequestFacade 类,分别实现 ServletRequest ,同时定义私有成员变量 Request ,并且方法的实现调用 Request 的实现。然后,将 RequestFacade上转为 ServletRequest 传给 servlet 的 service 方法,这样即使在 servlet 中被下转为 RequestFacade ,也不能访问私有成员变量对象中的方法。既用了 Request ,又能防止其中方法被不合理的访问。即RequestFacade 就为 Request 的外观类, 内存对Request 进行各种复杂的操作,但是只暴露仅有的几个方法,供上层使用
Facade模式Facade类,来提供遗留系统的比较清晰简单的接口,让新系统与Facade类交互, 提高复用性原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/xjwhaha/p/14250534.html