每个shell和系统进程都有一个当前的工作目录CWD:current work directory
显示当前shell CWD的绝对路径
pwd命令:printing working directory
eg:
[root@centos8 ~]#pwd
/root
[root@centos8 ~]#cd /home/
[root@centos8 home]#pwd
/home
**绝对路径**
以正斜杠/即根目录开始
完整的文件的位置路径
可用于任何想置定一个文件名的时候
**相对路径**
不以斜线开始
一般情况下,是指相对于当前工作目录的路径,特殊场景下,是相对于某目录的位置
可以作为一个简短的形式指定一个文件名
基名:basename,只取文件名而不要路径
目录名:dirname,只取路径,不要文件名
eg:
[root@centos8 ~]#basename /etc/sysconfig/network
network
[root@centos8 ~]#dirname /etc/sysconfig/network
/etc/sysconfig
命令cd:change directory改变目录
可以使用绝对或相对路径
*切换至父目录 cd..
*切换至当前用户主目录:cd
*切换至以前的工作目录:cd -
eg:
[root@centos8 ~]#cd /home/ason/
[root@centos8 ason]#pwd
/home/ason
[root@centos8 ason]#cd ..
[root@centos8 home]#pwd
/home
相关的环境变量:
PWD:当前目录路径
OLDPWD:上一次目录路径
eg:
[root@centos8 home]#echo $PWD
/home
[root@centos8 home]#echo $OLDPWD
/home/ason
ls命令可以列出当前目录的内容或指定目录
用法:
ls [options] [files_or_dirs]
常见选项:
-a 包含隐藏文件
-l 显示额外的信息
-R 目录递归
-ld 目录和符号链接信息
-1 文件分行显示
-S 按从大到小排序
-t 按mtime排序
-U 按目录存放顺序显示
-X 按文件后缀排序
说明:ls查看不同后缀文件时的颜色由/etc/DIR_COLORS和@LS_COLORS变量定义
eg:
[root@centos8 ~]#vim /etc/DIR_COLORS
.jpg 01;31 #修改此行
[root@centos8 ~]#exit
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $LS_COLORS
rs=0:di=01;34:ln=01;36:mh=00:pi=40;33:so=01;35:do=01;35:bd=40;33;01:cd=40;33;01:
or=40;31;01:mi=01;05;37;41:su=37;41:sg=30;43:ca=30;41:tw=30;42:ow=34;42:st=37;44
:ex=01;32:*.tar=01;31:*.tgz=01;31:*.arc=01;31:*.arj=01;31:*.taz=01;31:*.lha=01;3
1:*.lz4=01;31:*.lzh=01;31:*.lzma=01;31:*.tlz=01;31:*.txz=01;31:*.tzo=01;31:*.t7z
=01;31:*.zip=01;31:*.z=01;31:*.dz=01;31:*.gz=01;31:*.lrz=01;31:*.lz=01;31:*.lzo=
01;31:*.xz=01;31:*.zst=01;31:*.tzst=01;31:*.bz2=01;31:*.bz=01;31:*.tbz=01;31:*.t
bz2=01;31:*.tz=01;31:*.deb=01;31:*.rpm=01;31:*.jar=01;31:*.war=01;31:*.ear=01;31
:*.sar=01;31:*.rar=01;31:*.alz=01;31:*.ace=01;31:*.zoo=01;31:*.cpi o=01;31:*.7z=0
1;31:*.rz=01;31:*.cab=01;31:*.wim=01;31:*.swm=01;31:*.dwm=01;31:*.esd=01;31:*.jp
g=01;31:*.jpeg=01;35:*.mjpg=01;35:*.mjpeg=01;35:*.gif=01;35:*.bmp=01;35:*.pbm=01
;35:*.pgm=01;35:*.ppm=01;35:*.tga=01;35:*.xbm=01;35:*.xpm=01;35:*.tif=01;35:*.ti
ff=01;35:*.png=01;35:*.svg=01;35:*.svgz=01;35:*.mng=01;35:*.pcx=01;35:*.mov=01;3
5:*.mpg=01;35:*.mpeg=01;35:*.m2v=01;35:*.mkv=01;35:*.webm=01;35:*.ogm=01;35:*.mp
4=01;35:*.m4v=01;35:*.mp4v=01;35:*.vob=01;35:*.qt=01;35:*.nuv=01;35:*.wmv=01;35:
*.asf=01;35:*.rm=01;35:*.rmvb=01;35:*.flc=01;35:*.avi=01;35:*.fli=01;35:*.flv=01
;35:*.gl=01;35:*.dl=01;35:*.xcf=01;35:*.xwd=01;35:*.yuv=01;35:*.cgm=01;35:*.emf=
01;35:*.ogv=01;35:*.ogx=01;35:*.aac=01;36:*.au=01;36:*.flac=01;36:*.m4a=01;36:*.
mid=01;36:*.midi=01;36:*.mka=01;36:*.mp3=01;36:*.mpc=01;36:*.ogg=01;36:*.ra=01;3
6:*.wav=01;36:*.oga=01;36:*.opus=01;36:*.spx=01;36:*.xspf=01;36:
文件相关信息:metadata,data
每个文件有三个时间戳:
access time 访问时间,atime,读取文件内容
modify time 修改时间,mtime,改变文件内容(数据)
change time 改变时间,ctime,元数据发生改变
[root@centos7 ~]# stat /etc/passwd
File: ‘/etc/passwd’
Size: 846 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file
Device: fd00h/64768d Inode: 33608491 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Context: system_u:object_r:passwd_file_t:s0
Access: 2021-01-20 09:48:39.047999902 -0500
Modify: 2021-01-18 09:00:57.125017124 -0500
Change: 2021-01-18 09:00:57.125017124 -0500
Birth: -
文件可以包含多种类型的数据,使用file命令检查文件的类型,然后确定适当的打开命令或应用程序使用
格式:
file [options] <filename>...
常用选项:
-b 列出文件辨识结果时,不显示文件名称
-f filelist列出文件filelist中文件名的文件类型
-F 使用置定分隔符号替换输出文件名后默认的“:”分隔符
-L 查看对应软连接对应文件的文件类型
--help 显示命令在线帮助
eg:
windows的文本格式和Linux的文本格式的区别
[root@centos7 ~]# cat linux.txt
a
a
b
c
[root@centos7 ~]# cat win.txt
windows
windows[root@centos7 ~]#
[root@centos7 ~]# file win.txt linux.txt
win.txt: ASCII text, with CRLF line terminators
linux.txt: ASCII text
[root@centos7 ~]# hexdump -C linux.txt
00000000 61 0a 61 0a 62 0a 63 0a |a.a.b.c.|
00000008
[root@centos7 ~]# hexdump -C win.txt
00000000 77 69 6e 64 6f 77 73 0d 0a 0d 0a 77 69 6e 64 6f |windows....windo|
00000010 77 73 |ws|
00000012
[root@centos7 ~]#
[root@centos7 ~]# yum install dos2unix
[root@centos7 ~]# dos2unix win.txt
dos2unix: converting file win.txt to Unix format ...
[root@centos7 ~]# file win.txt
win.txt: ASCII text
[root@centos7 ~]#
[root@centos7 ~]# unix2dos win.txt
unix2dos: converting file win.txt to DOS format ...
[root@centos7 ~]# file win.txt
win.txt: ASCII text, with CRLF line terminators
[root@centos7 ~]# iconv -l
[root@centos8 data]#file windows.txt
windows.txt: ISO-8859 text, with no line terminators
[root@centos8 data]#echo $LANG
en_US.UTF-8
[root@centos8 data]#cat windows.txt
??????[root@centos8 data]#
[root@centos8 data]#iconv -f gb2312 windows.txt -o windows1.txt
[root@centos8 data]#cat windows1.txt
文本内容[root@centos8 data]#ll windows1.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 12 Mar 23 10:13 windows1.txt
[root@centos8 data]#file windows1.txt
windows1.txt: UTF-8 Unicode text, with no line terminators
[root@centos8 data]#iconv -f utf8 -t gb2312 windows1.txt -o windows2.txt
[root@centos8 data]#file windows2.txt
windows2.txt: ISO-8859 text, with no line terminators
eg:
windows的文本格式转换成Linux的文本格式
[root@centos7 ~]# file linux.txt
linux.txt: ASCII text
[root@centos7 ~]# file win.txt
win.txt: ASCII text, with CRLF line terminators
[root@centos7 ~]# dos2unix win.txt
dos2unix: converting file win.txt to Unix format ...
[root@centos7 ~]# file win.txt
win.txt: ASCII text
eg:
[root@centos7 ~]# cat list.txt
/etc/
/bin
/etc/issue
[root@centos7 ~]# file -f list.txt
/etc/: directory
/bin: symbolic link to `usr/bin‘
/etc/issue: ASCII text
文件通配符可以用来匹配符合条件的多个文件,方便批量管理文件
通配符采有特定的符号,表示特定的含义,此特殊符号称为元meta字符
常见的通配符如下:
* 匹配零个或多个字符,但不匹配“.”开头的文件,即隐藏文件
? 匹配任何单个字符
~ 当前用户家目录
~$USER 用户$USER家目录
~+和. 当前工作目录
~- 前一个工作目录
[0-9] 匹配数字范围
[a-z] 字母
[A-Z] 字母
[wang] 匹配列表中的任何的一个字符
[^wang] 匹配列表中的所有字符以外的字符
另外还有在Linux系统中预定义的字符类:man 7 glob
[:digit:]:任意数字,相当于0-9
[:lower:]:任意小写字母,表示 a-z
[:upper:]:任意大写字母
[:alpha:]:任意大小写字母
[:alnum:]:任意数字或字母
[:black:]:水平空白字符
[:space:]:水平或垂直空白字符
[:punct:]:标点符号
[:print:]:可打印字符
[:cntrl:]:控制(非打印)字符
[:graph:]:图形字符
[:xdigit:]:十六进制字符
touch命令可以用来创建空文件或者刷新已有文件的时间
格式:
touch [OPTION]...FILE....
选项说明:
-a 仅改变 atime和ctime
-m 仅改变 mtime和ctime
-t [[CC]YY]MMDDhhmm[.ss] 指定atime和mtime的时间戳
-c 如果文件不存在,则不予创建
eg:
[root@centos7 open]# touch file1.txt
[root@centos7 open]# ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 21 21:14 file1.txt
[root@centos7 open]# ll /etc/issue
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 23 Nov 23 10:08 /etc/issue
[root@centos7 open]# touch /etc/issue
[root@centos7 open]# ll /etc/issue
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 23 Jan 21 21:14 /etc/issue
[root@centos7 open]# stat /etc/issue
File: ‘/etc/issue’
Size: 23 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file
Device: fd00h/64768d Inode: 67108967 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Access: 2021-01-21 21:14:42.481084716 -0500
Modify: 2021-01-21 21:14:42.481084716 -0500
Change: 2021-01-21 21:14:42.481084716 -0500
Birth: -
[root@centos7 open]# date
Thu Jan 21 21:23:32 EST 2021
[root@centos7 open]# touch `date -d "-1 day" +%F_%T`.log
[root@centos7 open]# ls
2021-01-20_21:24:01.log file1.txt
[root@centos7 open]# touch $(date -d "1 year" +%F_%T).log
[root@centos7 open]# ls
2021-01-20_21:24:01.log 2022-01-21_21:24:48.log file1.txt
[root@centos7 open]# touch `date -d "-1 day" +"%F"`.log
[root@centos7 open]# ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 21 21:24 2021-01-20_21:24:01.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 21 21:25 2021-01-20.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 21 21:24 2022-01-21_21:24:48.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 21 21:14 file1.txt
利用cp(copy)命令可以实现文件或目录的复制
格式:
cp [OPTION]....[-T] SOURCE DEST
cp [OPTION]... SOURCE... DIRECTORY
cp [OPTION]... -t DIRECTORY SOURCE...
常用选项
-i 如果目标已存在,覆盖前提示是否覆盖
-n 不覆盖,注意两者顺序
-r,R 递归复制目录及内部的所有内容
-a 归档,相当于-dR --preserv=all,常用于备份功能
-d --no-dereference --perserv=links 不复制原文件,只复制链接名
--preserv[=ATTR_LIST]
mode:权限
ownership:属主属组
timestamp:
links
xattr
context
all
-p 等同--preserv=mode,ownership,timestamp
-v --verbose
-f --force
-u --update 只复制源比目标更新文件或目录不存在的文件
-b 目标存在,覆盖前先备份,默认形式为 `filename.~#~`,可以保留多个版本
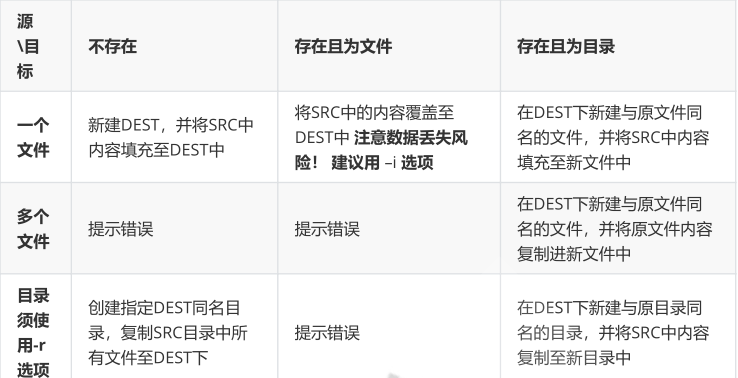
mv(move)命令可以实现文件或目录的系统和改名
同一分区移动数据,速度快,数据位置没有变化
不同分区移动数据,速度相对较慢,数据位置放生了变化
格式:
mv [OPTION]... [-T] SOURCE DEST
mv [OPTION]... SOURCE... DIRECTORY
mv [OPTION]... -t DIRECTORY SOURCE...
常用选项:
-i 交互式
-f 强制
-b 目标存在,覆盖前先备份
mv只能一次处理一个文件名,而利用rename可以批量修改文件名
格式:
rename [options] <expression> <replacement> <file>...
使用rm命令可以删除文件
注意:此命令非常危险,谨慎使用,建议使用mv代替rm
格式:
rm [OPTION].....FILE.....
常用选项:
-i 交互式
-f 强制删除
-r 递归
shred[OPTION].....FILE....
常见选项:
-z 最后一次覆盖添加0,以隐藏覆盖操作
-v 能够显示操作进度
-u 覆盖后截断并删除文件
-n # 指定覆盖文件内容的次数(默认是3次)
常见选项:
-d 只显示目录
-L level 指定显示的层级数目
-P pattern 只显示由指定wild-card parttern匹配到的路径
常见选项:
-p:存在于不报错,且可自动创建所需的各目录
-v:显示详细信息
-m MODE:创建目录时直接指定权限
常见选项:
-p:递归删除父空目录
-v:显示详细信息
注意:rmdir只能删除空目录,如果想删除非空目录,可以使用rm -r命令,递归删除目录树原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/jason-hua/p/14313090.html