1.作用
ThreadLocal用于给线程提供一个独立访问的容器。
2.ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal类中的一个静态内部类,其构造方法如下:
1 /** 2 * Construct a new map initially containing (firstKey, firstValue). 3 * ThreadLocalMaps are constructed lazily, so we only create 4 * one when we have at least one entry to put in it. 5 */ 6 ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) { 7 table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY]; 8 int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1); 9 table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue); 10 size = 1; 11 setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY); 12 }
每个Thread类对象中都有一个ThreadLocalMap变量引用,
Thread.java //其他代码 /* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained * by the ThreadLocal class. */ ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null; //其他代码
当线程首次调用ThreadLocal对象的set()方法时会新建一个ThreadLocalMap对象,这个ThreadLocalMap对象就是一个有线程隔离特性的容器(废话)。这个容器可以被认为是一个存储(K,V)的map容器。
ThreadLocal.java //其他代码 /** * Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in * InheritableThreadLocal. * * @param t the current thread * @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map */ void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); } //其他代码
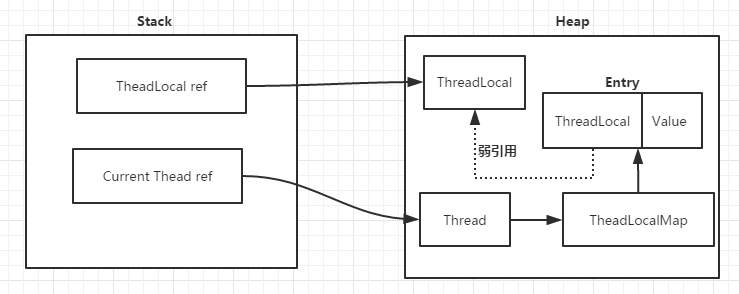
容器内部维护了一个Entry数组,每个Entry对象可以视为一个键值对(K,V),key就是ThreadLocal对象,value就是线程独享的变量,需要注意的是Entry对T和read Local对象封装了弱引用。当ThreadLocal对象的强引用指向Null
后,进行垃圾回收时,ThreadLocal对象会被回收,弱引用不能阻止垃圾回收。
1 /** 2 * The table, resized as necessary. 3 * table.length MUST always be a power of two. 4 */ 5 private Entry[] table; 6 7 8 /** 9 * The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using 10 * its main ref field as the key (which is always a 11 * ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get() 12 * == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the 13 * entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to 14 * as "stale entries" in the code that follows. 15 */ 16 static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> { 17 /** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ 18 Object value; 19 20 Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) { 21 super(k); 22 value = v; 23 } 24 }
ThreadLocal对象的set()方法:
1 /** 2 * Sets the current thread‘s copy of this thread-local variable 3 * to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to 4 * override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue} 5 * method to set the values of thread-locals. 6 * 7 * @param value the value to be stored in the current thread‘s copy of 8 * this thread-local. 9 */ 10 public void set(T value) { 11 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); 12 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); 13 if (map != null) { 14 map.set(this, value); 15 } else { 16 createMap(t, value); 17 } 18 }
ThreadLocalMap对象的set()方法:
1 /** 2 * Set the value associated with key. 3 * 4 * @param key the thread local object 5 * @param value the value to be set 6 */ 7 private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) { 8 9 // We don‘t use a fast path as with get() because it is at 10 // least as common to use set() to create new entries as 11 // it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast 12 // path would fail more often than not. 13 14 Entry[] tab = table; 15 int len = tab.length; 16 int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); 17 18 for (Entry e = tab[i]; 19 e != null; 20 e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { 21 ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); 22 23 if (k == key) { 24 e.value = value; 25 return; 26 } 27 28 if (k == null) { 29 //key == null,但是存在值(因为此处的e != null),说明之前的ThreadLocal对象已经被回收了 30 replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i); 31 return; 32 } 33 } 34 35 tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); 36 int sz = ++size; 37 //cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) 方法用于清除key为Null的entry 38 if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) 39 rehash(); 40 }
ThreadLocal防止内存泄漏的措施:
1)将Entry对ThreadLocal对象的引用定义为弱引用,一旦该对象没有强引用,垃圾回收的时候就会被回收,避免了ThreadLocal对象导致的内存泄露;
2)在get()、set()的时候,会排查key为Null的entry,并将这些entry清空;
3)另外,ThreadLocal还提供了remove(ThreadLocal key)方法,当确定当前ThreadLocal用不到了以后,可以及时的清除对key的弱引用和对value的强引用;
4)线程关闭后,容器会自动关闭。
内存泄漏的特例:
虽然有一系列措施,但是,如果:
1)容器中的value比较大;
2)当前线程一直不关闭(例如线程池),线程一直保持着对entry中value的强引用,如下图所示;
3)一直不set()或者get().
那么还是会内存泄漏。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/A-PP-Z-droplet/p/14336912.html