这里我们需要了解两个接口 这个是开胃菜
java.lang.Comparable 重写compareTo()方法
对引用类型进行排序的时候,我们需要知道比较规则,这个时候去实现Comparab接口,重写compareTo()方法,定义比较规则
代码:
Comparable接口:
public interface Comparable<T> {
int compareTo(T t);
}
Cat实体类:
public class Cat implements Comparable<Cat> {
int W;
int H;
public Cat(int w, int h) {
W = w;
H = h;
}
@Override
//这里定义比较规则
public int compareTo(Cat cat){
if (this.W < cat.W){
return -1;
}else if (this.W > cat.W){
return 1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"W=" + W +
", H=" + H +
‘}‘;
}
}
Dog实体:
public class Dog implements Comparable<Dog>{
int food;
public Dog(int food) {
this.food = food;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Dog dog) {
if (this.food < dog.food){
return -1;
}else if (this.food < dog.food){
return 1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"food=" + food +
‘}‘;
}
}
选择排序:
import java.util.Arrays;
//选择排序
public class SelectedSort {
/**
* @param arr int[]
* 对数组进行选择排序
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
//找到数组种最小的下标,默认是0
int minPosition = i;
//找到数组种最小值的index
for (int j = i+1; j <arr.length ; j++) {
if (arr[j].compareTo(arr[minPosition]) == -1 ) {
//将小的下标赋值给minPosition
minPosition = j;
}
}
//交换
swap(arr,i,minPosition);
}
}
/**
* @param arr int[]
* @param i 需要交换的数组下标
* @param j 同上
*/
public static void swap(Comparable[] arr,int i,int j){
//交换
Comparable temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
main 测试:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int[] arr = {2,3,6,7,0,9,8,64,1};
// Cat cat1 = new Cat(4, 1);
// Cat cat2 = new Cat(2, 2);
// Cat cat3 = new Cat(3, 3);
//
// Cat[] cats = {cat1,cat2,cat3};
Dog[] dogs = {new Dog(10),new Dog(20),new Dog(5)};
SelectedSort.sort(dogs);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dogs));
}
}
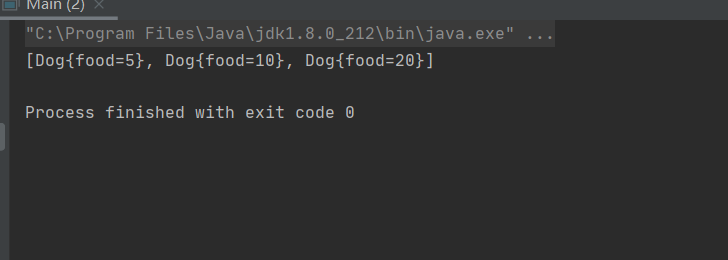
根据指定排序规则进行排序
缺点:
java.util.Comparator 比较器
可以扩展定义多个比较器,重写 int compare(T o1, T o2);方法,定义多种比较策略,在进行比较的时候将比较策略一并传过去就行了
更改后的代码:
选择排序:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
//选择排序
public class SelectedSort<T> {
/**
* @param arr int[]
* 对数组进行选择排序
*/
public void sort(T[] arr, Comparator<T> comparator){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
//找到数组种最小的下标,默认是0
int minPosition = i;
//找到数组种最小值的index
for (int j = i+1; j <arr.length ; j++) {
if (comparator.compare(arr[j],arr[minPosition]) == -1 ) {
//将小的下标赋值给minPosition
minPosition = j;
}
}
//交换
swap(arr,i,minPosition);
}
}
/**
* @param arr int[]
* @param i 需要交换的数组下标
* @param j 同上
*/
public void swap(T[] arr,int i,int j){
//交换
T temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
猫宽度比较器:
import java.util.Comparator;
//这里可以使用lanmda表达式 就不用定义类了
public class CatWComparator implements Comparator<Cat> {
@Override
public int compare(Cat o1, Cat o2) {
if (o1.W < o2.W){
return -1;
}else if (o1.W > o2.W){
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
Main 测试:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] arr = {2,3,6,7,0,9,8,64,1};
SelectedSort<Integer> selectedSort = new SelectedSort<Integer>();
selectedSort.sort(arr,(o1,o2)->{
if (o1.intValue() < o2.intValue()){
return -1;
}else if (o1.intValue() > o2.intValue()){
return 1;
}
return 0;
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
//
// Cat cat1 = new Cat(4, 1);
// Cat cat2 = new Cat(2, 2);
// Cat cat3 = new Cat(3, 3);
//
// Cat[] cats = {cat1,cat2,cat3};
//
//// Dog[] dogs = {new Dog(8),new Dog(2),new Dog(5)};
//
// SelectedSort<Cat> selectedSort = new SelectedSort<Cat>();
// //lamda 表达式
//// selectedSort.sort(dogs,(o1,o2)->{
//// if (o1.food < o2.food){
//// return -1;
//// }else if (o1.food > o2.food){
//// return 1;
//// }
//// return 0;
//// });
//
// selectedSort.sort(cats,new CatWComparator());
//
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(cats));
//
}
}
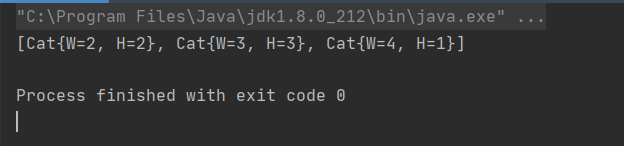
这里按照W 排序!!
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/immortal-mode/p/14375561.html