读书的原则:不求甚解,观其大略
?《编码:隐匿在计算机软硬件背后的语言》
?《深入理解计算机系统》
?语言:C JAVA K&R《C程序设计语言》《C Primer Plus》
? 数据结构与算法: -- 毕生的学习 leetCode
–《Java数据结构与算法》《算法》
–《算法导论》《计算机程序设计艺术》//难
?操作系统:Linux内核源码解析 Linux内核设计与实现 30天自制操作系统
?网络:机工《TCP/IP详解》卷一 翻译一般
?编译原理:机工 龙书 《编译原理》 《编程语言实现模式》马语
?数据库:SQLite源码 Derby - JDK自带数据库
Intel cpu的制作过程
https://haokan.baidu.com/v?vid=11928468945249380709&pd=bjh&fr=bjhauthor&type=video
CPU是如何制作的(文字描述)
https://www.sohu.com/a/255397866_468626
计算机需要解决的最根本问题:如何代表数字
晶体管是如何工作的:
https://haokan.baidu.com/v?vid=16026741635006191272&pd=bjh&fr=bjhauthor&type=video
晶体管的工作原理:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av47388949?p=2
汇编语言的本质:机器语言的助记符 其实它就是机器语言
计算机通电 -> CPU读取内存中程序(电信号输入)
->时钟发生器不断震荡通断电 ->推动CPU内部一步一步执行
(执行多少步取决于指令需要的时钟周期)
->计算完成->写回(电信号)->写给显卡输出(sout,或者图形)
量子比特,同时表示1 0
PC -> Program Counter 程序计数器 (记录当前指令地址)
Registers -> 暂时存储CPU计算需要用到的数据
ALU -> Arithmetic & Logic Unit 运算单元
CU -> Control Unit 控制单元
MMU -> Memory Management Unit 内存管理单元
cache
一致性协议:https://www.cnblogs.com/z00377750/p/9180644.html
缓存行:
缓存行越大,局部性空间效率越高,但读取时间慢
缓存行越小,局部性空间效率越低,但读取时间快
取一个折中值,目前多用:64字节
测试:Test1 时间比Test2 时间执行大概慢1秒左右
public class Test1 { public static volatile long[] arr = new long[2]; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{ for (long i = 0; i < 10000_0000L; i++) { arr[0] = i; } }); Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{ for (long i = 0; i < 10000_0000L; i++) { arr[1] = i; } }); final long start = System.nanoTime(); t1.start(); t2.start(); t1.join(); t2.join(); System.out.println((System.nanoTime() - start)/100_0000); } }
public class Test2 { public static volatile long[] arr = new long[16]; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{ for (long i = 0; i < 10000_0000L; i++) { arr[0] = i; } }); Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{ for (long i = 0; i < 10000_0000L; i++) { arr[8] = i; } }); final long start = System.nanoTime(); t1.start(); t2.start(); t1.join(); t2.join(); System.out.println((System.nanoTime() - start)/100_0000); } }
缓存行对齐:对于有些特别敏感的数字,会存在线程高竞争的访问,为了保证不发生伪共享,可以使用缓存航对齐的编程方式
JDK7中,很多采用long padding提高效率
JDK8,加入了@Contended注解(实验)需要加上:JVM -XX:-RestrictContended
public class Test3 { @Contended volatile long x; @Contended volatile long y; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Test3 test3 = new Test3(); Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10000_0000L; i++) { test3.x = i; } }); Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10000_0000L; i++) { test3.y = i; } }); final long start = System.nanoTime(); t1.start(); t2.start(); t1.join(); t2.join(); System.out.println((System.nanoTime() - start)/100_0000); } }
参考:https://preshing.com/20120515/memory-reordering-caught-in-the-act/
指令重排序的样例:
public class 指令重排序Demo { private static int x = 0, y = 0; private static int a = 0, b =0; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { int i = 0; for(;;) { i++; x = 0; y = 0; a = 0; b = 0; Thread one = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { //由于线程one先启动,下面这句话让它等一等线程two. 读着可根据自己电脑的实际性能适当调整等待时间. //shortWait(100000); a = 1; x = b; } }); Thread other = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { b = 1; y = a; } }); one.start();other.start(); one.join();other.join(); String result = "第" + i + "次 (" + x + "," + y + ")"; if(x == 0 && y == 0) { System.err.println(result); // 肯定会有x 和 y 都为0 的时候 break; } else { System.out.println(result); } } } }
CPU层面怎么禁止指令重排序?
Intel 使用的是原语

volatile 关键字使用的是Lock锁,实现的锁屏障。
CPU层面:Intel -> 原语(mfence lfence sfence) 或者锁总线
JVM层级:8个hanppens-before原则 4个内存屏障 (LL LS SL SS)
jvm 里面对于内存屏障的实现有4 种
Load1;LoadLoad;Load2,在Load2及后续的读操作要读取的数据被访问前,保证Load1要读取的数据被读取完毕;Store1;StoreStore;Store2,在Store2及后续的写操作执行前,保证Store1的写入操作对其他处理器可见;Load1;LoadStore;Store2,在Store2及后续的写入操作被刷出前,保证Load1要读取的数据被读取完毕;Store1;StoreLoad;Load2,在Load2及后续的读操作要读取的数据被访问前,保证Store1的写入操作对其他处理器可见;StoreStoreBarrier
volatile 写操作
StoreLoadBarrier
LoadLoadBarrier
volatile 读操作
LoadStoreBarrier
??happens-before原则是Java内存模型中定义的两个操作之间的偏序关系。
比如说操作A先行发生于操作B,那么在B操作发生之前,A操作产生的“影响”都会被操作B感知到。这里的影响是指修改了内存中的共享变量、发送了消息、调用了方法等。
as-if-serial : 不管硬件什么顺序,单线程执行的结果不变,看上去像是serial
Write Combining Buffer
一般是4个字节
由于ALU速度太快,所以在写入L1的同时,写入一个WC Buffer,满了之后,再直接更新到L2
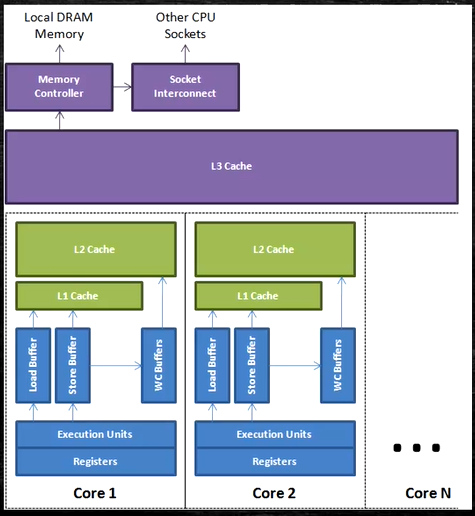
Non Uniform Memory Access
ZGC - NUMA aware 分配内存会优先分配该线程所在CPU的最近内存
先了解UMA:多个cpu访问一块内存
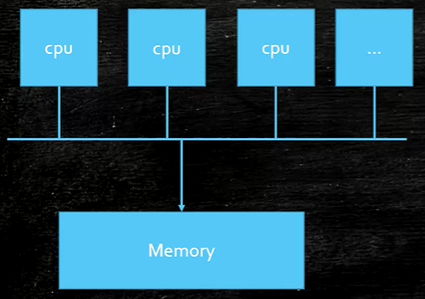
NUMA 每个cpu附近有个内存,访问就近的内存比访问别家的内存要快得多

原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/abiu/p/14376310.html