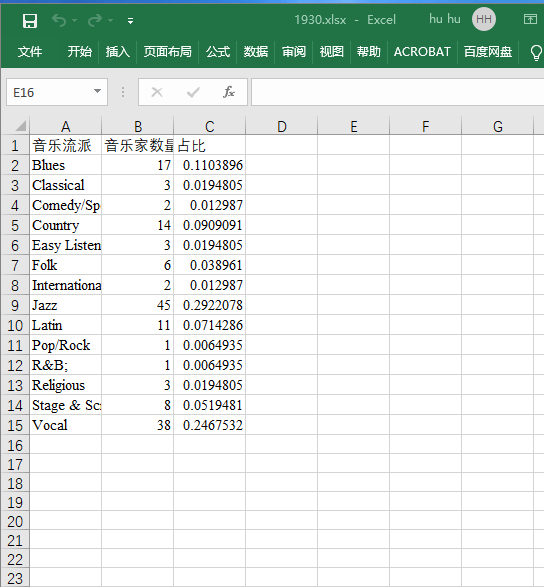
# 1930
workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(‘1930.xlsx‘)
sheet= workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
A1=[]
B1=[]
# sheet.cell_value(i,0):第i行的第0个元素
for i in range(1,sheet.nrows):
A1.append(sheet.cell_value(i,0))
B1.append(sheet.cell_value(i,1))
if len(A1)!=len(B1):
print("False")
drawBar(A1,B1,1930)
def drawBar(Music_genre,singer_num,year)参数介绍
| 参数名 | 参数含义 |
|---|---|
| Music_genre | 音乐流派名称list |
| singer_num | 音乐流派对应音乐家数量list |
| year | 读的文件的年份(因为源代码是从1840到2020的) |
def drawBar(Music_genre,singer_num,year):
arr_len=len(Music_genre)
# 由循环得到一个字典,key是音乐流派,value是这个音乐流派对应的音乐家的数量
i=0
dict_music_singer={}
while i<arr_len:
dict_music_singer[Music_genre[i]]=singer_num[i]
i=i+1
# 注释1
pyplot.bar(x=0, bottom=range(arr_len), height=0.3, width=singer_num, orientation="horizontal")
# 注释2
pyplot.yticks(range(arr_len),Music_genre)
# 加title,展示图像
pyplot.title(year)
pyplot.show()
...
...
drawBar(A1,B1,1930)
注释1:
""" 水平条形图,需要修改以下属性 orientation="horizontal" """ import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 数据 N = 5 x = [20, 10, 30, 25, 15] y = [0,1,2,3,4] # 绘图 x= 起始位置, bottom= 水平条的底部(左侧), y轴, height 水平条的宽度, width 水平条的长度 p1 = plt.bar(x=0, bottom=y, height=0.5, width=x, orientation="horizontal") pyplot.bar(range(arr_len),singer_num,align=‘center‘) pyplot.bar(x=0, bottom=range(arr_len), height=0.5, width=singer_num, orientation="horizontal") # 展示图形 plt.show()
注释2:plt.xticks的第一个参数和plt.plot的第一个参数一样,第二个参数是和第一个参数相同长度的list此例中用来代替横坐标
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = [1, 2, 3, 4] y = [1, 4, 9, 6] labels = [‘Frogs‘, ‘Hogs‘, ‘Bogs‘, ‘Slogs‘] plt.plot(x, y) # You can specify a rotation for the tick labels in degrees or with keywords. plt.xticks(x, labels, rotation=‘vertical‘) # Pad margins so that markers don‘t get clipped by the axes plt.margins(0.2) # Tweak spacing to prevent clipping of tick-labels plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.15) plt.show()

import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import xlrd
from matplotlib import pyplot
def drawBar(Music_genre,singer_num,year):
arr_len=len(Music_genre)
i=0
dict_music_singer={}
while i<arr_len:
dict_music_singer[Music_genre[i]]=singer_num[i]
i=i+1
#pyplot.bar(range(arr_len),singer_num,align=‘center‘)
pyplot.bar(x=0, bottom=range(arr_len), height=0.3, width=singer_num, orientation="horizontal")
pyplot.yticks(range(arr_len),Music_genre)
pyplot.title(year)
pyplot.show()
# 1930
workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(‘1930.xlsx‘)
sheet= workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
A1=[]
B1=[]
for i in range(1,sheet.nrows):
A1.append(sheet.cell_value(i,0))
B1.append(sheet.cell_value(i,1))
if len(A1)!=len(B1):
print("False")
drawBar(A1,B1,1930)
# 1940
workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(‘1940.xlsx‘)
sheet= workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
A2=[]
B2=[]
for i in range(1,sheet.nrows):
A2.append(sheet.cell_value(i,0))
B2.append(sheet.cell_value(i,1))
if len(A2)!=len(B2):
print("False")
drawBar(A2,B2,1940)
#
workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(‘1950.xlsx‘)
sheet= workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
A3=[]
B3=[]
for i in range(1,sheet.nrows):
A3.append(sheet.cell_value(i,0))
B3.append(sheet.cell_value(i,1))
if len(A3)!=len(B3):
print("False")
drawBar(A3,B3,1950)
# 6
workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(‘1960.xlsx‘)
sheet= workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
A4=[]
B4=[]
for i in range(1,sheet.nrows):
A4.append(sheet.cell_value(i,0))
B4.append(sheet.cell_value(i,1))
if len(A4)!=len(B4):
print("False")
drawBar(A4,B4,1960)
#
workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(‘1970.xlsx‘)
sheet= workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
A5=[]
B5=[]
for i in range(1,sheet.nrows):
A5.append(sheet.cell_value(i,0))
B5.append(sheet.cell_value(i,1))
if len(A5)!=len(B5):
print("False")
drawBar(A5,B5,1970)
#
workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(‘1980.xlsx‘)
sheet= workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
A6=[]
B6=[]
for i in range(1,sheet.nrows):
A6.append(sheet.cell_value(i,0))
B6.append(sheet.cell_value(i,1))
if len(A6)!=len(B6):
print("False")
drawBar(A6,B6,1980)
# 9
workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(‘1990.xlsx‘)
sheet= workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
A7=[]
B7=[]
for i in range(1,sheet.nrows):
A7.append(sheet.cell_value(i,0))
B7.append(sheet.cell_value(i,1))
if len(A7)!=len(B7):
print("False")
drawBar(A7,B7,1990)
# 2000
workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(‘2000.xlsx‘)
sheet= workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
A8=[]
B8=[]
for i in range(1,sheet.nrows):
A8.append(sheet.cell_value(i,0))
B8.append(sheet.cell_value(i,1))
if len(A8)!=len(B8):
print("False")
drawBar(A8,B8,2000)
#
workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(‘2010.xlsx‘)
sheet= workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
A9=[]
B9=[]
for i in range(1,sheet.nrows):
A9.append(sheet.cell_value(i,0))
B9.append(sheet.cell_value(i,1))
if len(A9)!=len(B9):
print("False")
drawBar(A9,B9,2010)
# #
# workbook=xlrd.open_workbook(‘2020.xlsx‘)
# sheet= workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
# A2=[]
# B2=[]
# for i in range(1,sheet.nrows):
# A2.append(sheet.cell_value(i,0))
# B2.append(sheet.cell_value(i,1))
# if len(A2)!=len(B2):
# print("False")
# drawBar(A2,B2,2020)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhengyuhu/p/14387544.html