实验目的
1.掌握使用TensorFlow进行逻辑回归
2.掌握逻辑回归的原理
实验原理
逻辑回归是机器学习中很简答的一个例子,这篇文章就是要介绍如何使用tensorflow实现一个简单的逻辑回归算法。
逻辑回归可以看作只有一层网络的前向神经网络,并且参数连接的权重只是一个值,而非矩阵。公式为:y_predict=logistic(X*W+b),其中X为输入,W为输入与隐含层之间的权重,b为隐含层神经元的偏置,而logistic为激活函数,一般为sigmoid或者tanh,y_predict为最终预测结果。
逻辑回归是一种分类器模型,需要函数不断的优化参数,这里目标函数为y_predict与真实标签Y之间的L2距离,使用随机梯度下降算法来更新权重和偏置。
实验步骤
1、导入实验所需要的模块
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
2、导入实验所需的数据
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("D:/jqxx/mnist/",one_hot = True)
3、设置训练参数
learning_rate=0.01 training_epochs=25 batch_size=100 display_step=1
4、构造计算图,使用占位符placeholder函数构造变量x,y,代码如下:
x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])
y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])
5、使用Variable函数,设置模型的初始权重
W=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]))
b=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
6、构造逻辑回归模型
pred=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,W)+b)
7、构造代价函数cost
cost=tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y*tf.log(pred),reduction_indices=1))
8、使用梯度下降法求最小值,即最优解
optimizer=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
9、初始化全部变量
init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
10、使用tf.Session()创建Session会话对象,会话封装了Tensorflow运行时的状态和控制。
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
11、调用会话对象sess的run方法,运行计算图,即开始训练模型。
for epoch in range(training_epochs): avg_cost = 0 total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size) for i in range(total_batch): batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) _, c = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys}) avg_cost += c / total_batch if (epoch+1) % display_step == 0: print("Epoch:", ‘%04d‘ % (epoch + 1), "Cost:","{:.09f}".format(avg_cost)) print("Optimization Finished!")
12、测试模型
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
13、评估模型的准确度。
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) print("Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({x: mnist.test.images[:3000], y: mnist.test.labels[:3000]}))
14、完整代码:

import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data #导入实验所需的数据 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("D:/jqxx/mnist/",one_hot = True) #设置训练参数 learning_rate=0.01 training_epochs=25 batch_size=100 display_step=1 #构造计算图,使用占位符placeholder函数构造变量x,y, x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784]) y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10]) # 使用Variable函数,设置模型的初始权重 W=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10])) b=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) #构造逻辑回归模型 pred=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,W)+b) #构造代价函数cost cost=tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y*tf.log(pred),reduction_indices=1)) #使用梯度下降法求最小值,即最优解 optimizer=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) #初始化全部变量 init=tf.global_variables_initializer() #.使用tf.Session()创建Session会话对象,会话封装了Tensorflow运行时的状态和控制 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) #调用会话对象sess的run方法,运行计算图,即开始训练模型 for epoch in range(training_epochs): avg_cost = 0 total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size) for i in range(total_batch): batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) _, c = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys}) avg_cost += c / total_batch if (epoch+1) % display_step == 0: print("Epoch:", ‘%04d‘ % (epoch + 1), "Cost:","{:.09f}".format(avg_cost)) print("Optimization Finished!") #测试模型 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1)) #评估模型的准确度 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) print("Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({x: mnist.test.images[:3000], y: mnist.test.labels[:3000]}))
15、运行结果为:
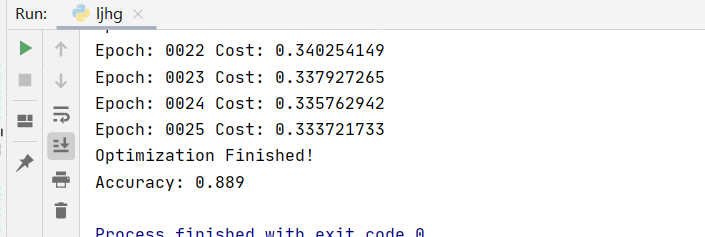
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/20183544-wangzhengshuai/p/14395254.html