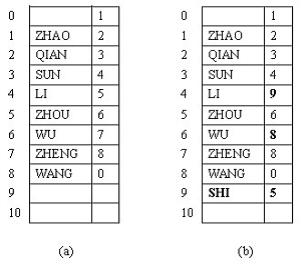

show insert 1 ZHAO show insert 2 QIAN show insert 3 SUN show insert 4 LI insert 5 ZHOU insert 6 WU insert 7 ZHENG insert 8 WANG show insert 1 ZHANG show search LI show
2
0
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
0
********************
3
2
ZHAO 0
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
0
********************
4
2
ZHAO 3
QIAN 0
5
6
7
8
9
10
0
********************
5
2
ZHAO 3
QIAN 4
SUN 0
6
7
8
9
10
0
********************
10
2
ZHAO 3
QIAN 4
SUN 5
LI 6
ZHOU 7
WU 8
ZHENG 9
WANG 0
0
********************
0
10
ZHAO 3
QIAN 4
SUN 5
LI 6
ZHOU 7
WU 8
ZHENG 9
WANG 0
ZHANG 2
********************
5
********************
0
10
ZHAO 3
QIAN 4
SUN 5
LI 6
ZHOU 7
WU 8
ZHENG 9
WANG 0
ZHANG 2
********************
提示:
1、怎样将字符串类型定义为ElemType呢?形如typedef int num一样,数组或者指针可以放在定义的类型名后面,例如将具有8个字符的姓氏定义为ElemType可以这样定义:typedef char ElemType[8]。
2、题目和书中给的算法描述还缺少静态链表的插入、删除以及显示,都需要自己写。
3、要求每个指令输出后跟一个空行,别忘了。
4、姓氏占8个字符,数字占2个字符,姓氏左对齐,可以这样输出printf("%-8s%2d");对于指令search也要输出占2个字符的数字。
5、静态链表初始化时将所有内存设为空,可以在InitSpace_SL中使用下面的方法:
memset(space, 0 ,sizeof(space));
总结:
静态链表与一般链表极为相似:使用数组来模拟内存,使用数组下表来模拟内存中的地址。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <list>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
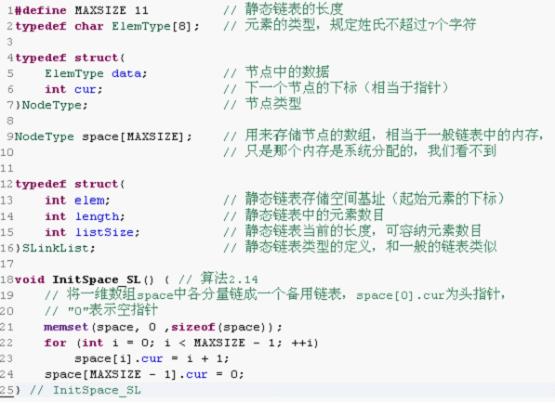
#define MAXSIZE 11//静态链表的长度
typedef char name[8];//元素的类型,规定姓氏不超过8个字符
typedef struct
{
name data;//节点中的数据
int cur;//下一个节点的下标
}NodeType;//节点类型
NodeType space[MAXSIZE];
typedef struct
{
int elem;//静态链表存储空间基址
int length;//静态链表中的元素数目
int listsize;//静态链表当前的长度
}SLinkList;//静态链表类型的定义
SLinkList s;
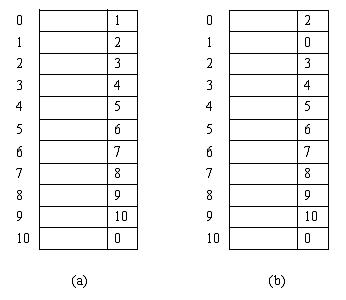
void InitSpace_SL()//初始化
{
//将一维数组space中的各分量连成一个备用链表,space【0】.cur为头指针
//‘0’表示空指针
memset(space,0,sizeof(space));
for(int i=0;i<MAXSIZE-1;++i)
{
space[i].cur=i+1;
}
space[0].cur=2;
space[1].cur=0;
space[MAXSIZE-1].cur=0;
}
int LocateElem_SL(SLinkList &s,name e)
{
//在静态链表中找到第一个值为e的元素
//若找到,返回他在链表中的位置,否则返回0
int i;
i = s.elem;//i指示表中第一个节点
while(i&&strcmp(space[i].data,e))
{
i = space[i].cur;
}
return i;
}
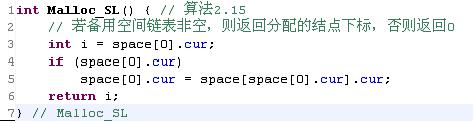
int Malloc_SL()//申请新的节点
{
//若备用空间链表非空,则返回分配的结点下标,否则返回0
int i = space[0].cur;
if(space[0].cur)
{
space[0].cur = space[space[0].cur].cur;
}
return i;
}
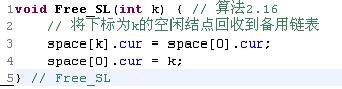
void Free_SL(int j)
{
//将下标为j的空闲节点回收到备用链表
space[j].cur = space[0].cur;
space[0].cur = j;
}
void Insert(NodeType space[], int n, char b[])//插入
{
int m = Malloc_SL();
strcpy(space[m].data, b);
int j = 1, i = 1;
while (j <n&&space[i].cur)
{
i = space[i].cur;
j++;
}
space[m].cur = space[i].cur;
space[i].cur = m;
s.length++;
}
void Delete(int n)
{
int i,j=1;
i =1;
while (j<n&&space[i].cur)
{
j++;
i= space[i].cur;
}
j = space[i].cur;
space[i].cur = space[j].cur;
space[j].cur = space[0].cur;
space[0].cur = j;
}
void Search(char b[])//搜索
{
int i = space[1].cur;
while (i&&strcmp(space[i].data, b))
{
i = space[i].cur;
}
printf("%2d\n", i);
printf("********************\n");
}
void Show()//输出
{
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++)
{
printf("%-8s%2d\n", space[i].data, space[i].cur);
}
printf("********************\n");
}
int main()
{
char a[10], b[10]; int n;
s.elem = 1, s.length = 0, s.listsize = 10;
InitSpace_SL();
while (scanf("%s", a, 10) != EOF)
{
if (!strcmp("show", a))
{
Show();
memset(a, 0, 10);
}
if (!strcmp("insert", a))
{
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%s", &b, 10);
Insert(space, n, b);
memset(a, 0, 10);
memset(b, 0, 10);
}
if (!strcmp("delete", a))
{
scanf("%d", &n);
Delete(n);
memset(a, 0, 10);
}
if (!strcmp("search", a))
{
getchar();
scanf("%s", &b, 10);
Search(b);
memset(a, 0, 10);
memset(b, 0, 10);
}
}
return 0;
}
代码来自:https://blog.csdn.net/qingchongxinshuru/article/details/51864528
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/FantasticDoubleFish/p/14401181.html