ThreadLocal类顾名思义可以理解为线程本地变量。也就是说如果定义了一个ThreadLocal,每个线程往这个ThreadLocal中读写是线程隔离,互相之间不会影响的。它提供了一种将可变数据通过每个线程有自己的独立副本从而实现线程封闭的机制。Thread类有一个类型为ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap的实例变量threadLocals,也就是说每个线程有一个自己的ThreadLocalMap。ThreadLocalMap有自己的独立实现,可以简单地将它的key视作ThreadLocal,value为代码中放入的值(实际上key并不是ThreadLocal本身,而是它的一个弱引用)。每个线程在往某个ThreadLocal里塞值的时候,都会往自己的ThreadLocalMap里存,读也是以某个ThreadLocal作为引用,在自己的map里找对应的key,从而实现了线程隔离。

public class TestThreadLocal implements Runnable { ThreadLocal studentLocal1 = new ThreadLocal(); ThreadLocal studentLocal2 = new ThreadLocal(); public static void main(String[] args) { TestThreadLocal t = new TestThreadLocal(); new Thread(t, "t1").start(); } @Override public void run() { Student s1 = new Student(); s1.setAge(10); studentLocal1.set(s1); //threadLocalHashCode = -1401181199 Student s2 = new Student(); s2.setAge(20); studentLocal2.set(s2); //threadLocalHashCode = 239350328 } } class Student { private int age; public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
1.一个ThreadLocal对象只能存储一个变量
2.Thread有一个变量 ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap,用来存储当前线程下的ThreadLocal集合
3.ThreadLocal的threadLocalHashCode是固定的,源码如下:
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode(); /** * The next hash code to be given out. Updated atomically. Starts at zero. */ private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode = new AtomicInteger(); /** * The difference between successively generated hash codes */ private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647; /** * Returns the next hash code. */ private static int nextHashCode() { return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT); }

public class TestThreadLocal implements Runnable { ThreadLocal studentLocal = new ThreadLocal(); public static void main(String[] args) { TestThreadLocal t = new TestThreadLocal(); new Thread(t, "t1").start(); new Thread(t, "t2").start(); } @Override public void run() { accessStudent(); } private void accessStudent() { Student s = this.getStudent(); Random random = new Random(); int age = random.nextInt(100); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "set age " + ":" + age); s.setAge(age); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "first get age " + ":" + s.getAge()); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "second get age " + ":" + s.getAge()); } public Student getStudent() { Student s = (Student) studentLocal.get(); if (s == null) { s = new Student(); studentLocal.set(s); } return s; } } class Student { private int age; public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
执行结果:
Thread[t2,5,main]set age :15 Thread[t1,5,main]set age :13 Thread[t1,5,main]first get age :13 Thread[t2,5,main]first get age :15 Thread[t2,5,main]second get age :15 Thread[t1,5,main]second get age :13
1.ThreadLocal的作用是提供线程内的局部变量,不同的线程之间不会相互干扰

public class ThreadLocal<T> { /** * The ThreadLocal objects act as keys,searched via threadLocalHashCode. */ private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode(); /** * The next hash code to be given out. Updated atomically. Starts at zero. */ private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode = new AtomicInteger(); /** * The difference between successively generated hash codes. */ private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647; /** * Returns the next hash code. */ private static int nextHashCode() { return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT); } /** * Returns the current thread‘s "initial value" for this thread-local variable. * @return the initial value for this thread-local */ protected T initialValue() { return null; } /** * Creates a thread local variable. The initial value of the variable is determined by invoking the {@code get} method on the {@code Supplier}. * * @param <S> the type of the thread local‘s value * @param supplier the supplier to be used to determine the initial value * @return a new thread local variable * @throws NullPointerException if the specified supplier is null * @since 1.8 */ public static <S> ThreadLocal<S> withInitial(Supplier<? extends S> supplier) { return new SuppliedThreadLocal<>(supplier); } /** * Creates a thread local variable. * @see #withInitial(java.util.function.Supplier) */ public ThreadLocal() { } /** * Returns the value in the current thread‘s copy of this thread-local variable. * @return the current thread‘s value of this thread-local */ public T get() { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) { ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T result = (T)e.value; return result; } } return setInitialValue(); } /** * Variant of set() to establish initialValue. Used instead of set() in case user has overridden the set() method. * @return the initial value */ private T setInitialValue() { T value = initialValue(); Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) map.set(this, value); else createMap(t, value); return value; } /** * Sets the current thread‘s copy of this thread-local variable to the specified value * @param value the value to be stored in the current thread‘s copy of this thread-local. */ public void set(T value) { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) map.set(this, value); else createMap(t, value); } /** * Removes the current thread‘s value for this thread-local variable. * @since 1.5 */ public void remove() { ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread()); if (m != null) m.remove(this); } /** * Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in InheritableThreadLocal. * @param t the current thread * @return the map */ ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.threadLocals; } /** * Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in InheritableThreadLocal. * @param t the current thread * @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map */ void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); } /** * Factory method to create map of inherited thread locals.Designed to be called only from Thread constructor. * Thread类的init(..)方法调用,将父线程的有效entry拷贝到当前线程 * @param parentMap the map associated with parent thread * @return a map containing the parent‘s inheritable bindings */ static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) { return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap); } T childValue(T parentValue) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } /** * An extension of ThreadLocal that obtains its initial value from the specified {@code Supplier}. */ static final class SuppliedThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> { private final Supplier<? extends T> supplier; SuppliedThreadLocal(Supplier<? extends T> supplier) { this.supplier = Objects.requireNonNull(supplier); } @Override protected T initialValue() { return supplier.get(); } } /** * ThreadLocalMap is a customized hash map suitable only for maintaining thread local values. */ static class ThreadLocalMap { /** * The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using its main ref field as the key (which is always a * ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get() == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced */ static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> { /** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ Object value; Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) { super(k); value = v; } } /** * The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two. */ private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; /** * The table, resized as necessary.table.length MUST always be a power of two. */ private Entry[] table; /** * The number of entries in the table. */ private int size = 0; /** * The next size value at which to resize. */ private int threshold; // Default to 0 /** * Set the resize threshold to maintain at worst a 2/3 load factor. */ private void setThreshold(int len) { threshold = len * 2 / 3; } /** * Increment i modulo len. */ private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) { return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0); } /** * Decrement i modulo len. */ private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) { return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1); } /** * Construct a new map initially containing (firstKey, firstValue). */ ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) { table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY]; int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1); table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue); size = 1; setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY); } /** * Construct a new map including all Inheritable ThreadLocals from given parent map. Called only by createInheritedMap. * @param parentMap the map associated with parent thread. */ private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) { Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table; int len = parentTable.length; setThreshold(len); table = new Entry[len]; for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) { Entry e = parentTable[j]; if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") ThreadLocal<Object> key = (ThreadLocal<Object>) e.get(); if (key != null) { Object value = key.childValue(e.value); Entry c = new Entry(key, value); int h = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1); while (table[h] != null) h = nextIndex(h, len); table[h] = c; size++; } } } } /** * Get the entry associated with key. 根据hashcode&(table.length-1)得到key在table中的下标位置,原理与hashMap一致 * @param key the thread local object * @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such */ private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) { int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1); Entry e = table[i]; if (e != null && e.get() == key) return e; else return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e); } /** * Version of getEntry method for use when key is not found in its direct hash slot. * * @param key the thread local object * @param i the table index for key‘s hash code * @param e the entry at table[i] * @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such */ private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; while (e != null) { ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); if (k == key) return e; if (k == null) //该entry对应得threadLocal已经被回收,需要清理无效得key expungeStaleEntry(i); else i = nextIndex(i, len); //环形结构,继续往后走 e = tab[i]; } return null; } /** * Set the value associated with key. * @param key the thread local object * @param value the value to be set */ private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); for (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); if (k == key) { e.value = value; return; } if (k == null) { replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i); return; } } tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); int sz = ++size; if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) rehash(); } /** * Remove the entry for key. */ private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { if (e.get() == key) { e.clear(); expungeStaleEntry(i); return; } } } /** * Replace a stale entry encountered during a set operation with an entry for the specified key. * @param key the key * @param value the value to be associated with key * @param staleSlot index of the first stale entry encountered while searching for key. */ private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value,int staleSlot) { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; Entry e; int slotToExpunge = staleSlot; for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len); (e = tab[i]) != null; i = prevIndex(i, len)) if (e.get() == null) slotToExpunge = i; // Find either the key or trailing null slot of run, whichever occurs first for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len); (e = tab[i]) != null; i = nextIndex(i, len)) { ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); if (k == key) { e.value = value; tab[i] = tab[staleSlot]; tab[staleSlot] = e; // Start expunge at preceding stale entry if it exists if (slotToExpunge == staleSlot) slotToExpunge = i; cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len); return; } if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot) slotToExpunge = i; } // If key not found, put new entry in stale slot tab[staleSlot].value = null; tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value); // If there are any other stale entries in run, expunge them if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot) cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len); } /** * 清理函数 */ private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; // expunge entry at staleSlot entry对应得ThreadLocal已经被回收,显式置为null,便于垃圾回收 tab[staleSlot].value = null; tab[staleSlot] = null; size--; // Rehash until we encounter null Entry e; int i; for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len); (e = tab[i]) != null; i = nextIndex(i, len)) { ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); if (k == null) { e.value = null; tab[i] = null; size--; } else {//对于还没有被回收的情况,需要做一次rehash.如果索引h不是当前位置,则向后线性探测到第一个空的slot。把当前entry移过去 int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1); if (h != i) { tab[i] = null; while (tab[h] != null) h = nextIndex(h, len); tab[h] = e; } } } return i; } /** * 连段清理 * @return true if any stale entries have been removed. */ private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) { boolean removed = false; Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; do { i = nextIndex(i, len); Entry e = tab[i]; if (e != null && e.get() == null) { n = len; removed = true; i = expungeStaleEntry(i); } } while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0); return removed; } /** * Re-pack and/or re-size the table. */ private void rehash() { expungeStaleEntries(); // Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4) resize(); } /** * Double the capacity of the table. */ private void resize() { Entry[] oldTab = table; int oldLen = oldTab.length; int newLen = oldLen * 2; Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen]; int count = 0; for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) { Entry e = oldTab[j]; if (e != null) { ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); if (k == null) { e.value = null; // Help the GC } else { int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1); while (newTab[h] != null) h = nextIndex(h, newLen); newTab[h] = e; count++; } } } setThreshold(newLen); size = count; table = newTab; } /** * Expunge all stale entries in the table. */ private void expungeStaleEntries() { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) { Entry e = tab[j]; if (e != null && e.get() == null) expungeStaleEntry(j); } } } }
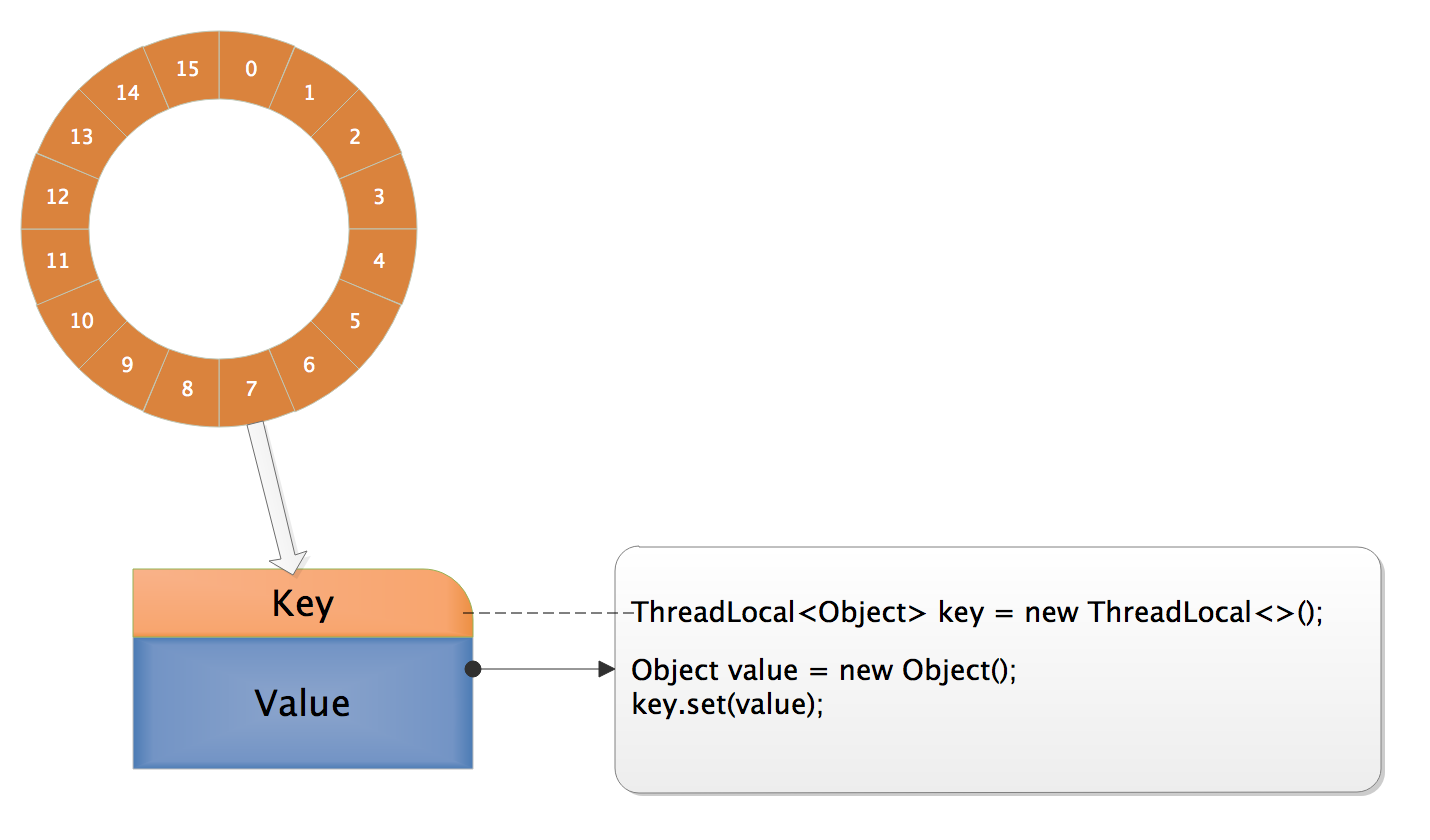
1.ThreadLocalMap中Entry[]环形数组,初始化长度16,后续每次都是2倍扩容。数组中元素Entry的逻辑上的key为某个ThreadLocal对象(实际上是指向该ThreadLocal对象的弱引用),value为代码中该线程往该ThreadLoacl变量实际塞入的值。因为如果这里使用普通的key-value形式来定义存储结构,实质上就会造成节点的生命周期与线程强绑定,只要线程没有销毁,那么节点在GC分析中一直处于可达状态,没办法被回收,而程序本身也无法判断是否可以清理节点。弱引用是Java中四档引用的第三档,比软引用更加弱一些,如果一个对象没有强引用链可达,那么一般活不过下一次GC。当某个ThreadLocal已经没有强引用可达,则随着它被垃圾回收,在ThreadLocalMap里对应的Entry的键值会失效,这为ThreadLocalMap本身的垃圾清理提供了便利。
2.InheritableThreadLocal对比ThreadLocal唯一不同是子线程会继承父线程变量,并自定义赋值函数。
3.如果使用了线程池,那么小心线程回收后ThreadLocal、InheritableThreadLocal变量要remove,否则线程池回收后,变量还在内存中(key是弱引用被回收,但是value还在,内存泄漏)。
4.ThreadLocalMap使用线性探测法来解决散列冲突,所以实际上Entry[]数组在程序逻辑上是作为一个环形存在的。虚线表示弱引用,实线表示强引用。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/ryjJava/p/14398790.html