Java8 lambda 的使用
1.Java8 新特性介绍
原文链接 https://my.oschina.net/chenxiaobian/blog/704421,https://www.cnblogs.com/hmdrzql/p/6354010.html
现在我们有一个需求:给一个user组成的list 按照user的年龄排序。实现不难,代码如下:

UserCompare是一个实现了Comprator的类

这种方法由于sort方法的第二个参数是Comparator 所以你要写一个实现类(我这里是UserCompare类),并且override该接口的实现方法。
java8提供了lambda来简化,有了lambda程序员从此不加班呀~

刚才那个Comparator的实现类以及内部若干代码就都省了,代之以lambda表达式。
另外,IntelliJ会提示你改成更好的写法

实现类里有多少代码,你就省了多少行代码。
高兴了半天,到底是什么原理呢?其实是java8新提供的语法糖。
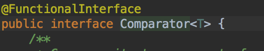
我们打开java1.8 Comparator的定义,发现了类定义上面多了一个@FunctionalInterface
对,1.8多了一个概念就是FunctionalInterface,这个Comparator就是一个FunctionalInterface
有了这个注解,原来使用实现类的地方就可以代之以lambda表达式。
写java的同学对java8肯定知道 那么java8到底有哪些特性呢,总结如下:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
最核心的当然是函数式编程了,写代码非常简单,请看下面详细例子介绍
2.Java8 lambda使用总结-结合实例介绍
很多同学一开始接触Java8可能对Java8 Lambda表达式有点陌生,下面我将结合实例介绍Java8的使用 并与Java7进行比较:
基础类
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
1.List操作
-
public class ExampleList {
-
private static List<String> items = new ArrayList<>();
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
-
-
System.out.println(item);
-
-
-
-
items.forEach(c-> System.out.println(c));
-
-
-
-
System.out.println(item);
-
-
-
-
System.out.println("--------");
-
-
-
items.stream().filter(s->s.contains("B")).forEach(c1-> System.out.println(c1));
-
-
-
2.Map操作
-
public class ExampleMap {
-
-
private static Map<String, Integer> items = new HashMap<>();
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
-
-
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry:items.entrySet()){
-
System.out.println("key:" + entry.getKey() + " value:" + entry.getValue());
-
-
-
-
items.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println("key:" + key + " value:" + value));
-
-
-
-
-
-
3.Groupingby操作
-
-
-
-
-
public class ExampleMapping {
-
-
private static List<Person> personList = Lists.newArrayList();
-
-
-
personList.add(Person.builder().id(10).address("apple").address("shanghai").build());
-
personList.add(Person.builder().id(12).address("apple").address("wuhan").build());
-
personList.add(Person.builder().id(16).address("apple").address("nanjing").build());
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
-
Map<String, List<Person>> collect = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(c -> c.getAddress()));
-
System.out.println(collect);
-
-
4.List转换为Map
-
public class ExampleListConvertMap {
-
-
private static List<Person> personList = Lists.newArrayList();
-
-
-
personList.add(Person.builder().id(20).name("zhangsan").address("shanghai").build());
-
personList.add(Person.builder().id(30).name("lisi").address("nanjing").build());
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
-
Map<Integer,Person> map_ = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((key->key.getId()),(value->value)));
-
map_.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println(key + ":" + value));
-
-
Map<Integer, Person> mappedMovies = personList.stream().collect(
-
Collectors.toMap(Person::getRank, Person::getData));
-
-
-
5.FilterMap操作
-
public class ExampleFilterMap {
-
-
private static Map<Integer,String> map_ = Maps.newHashMap();
-
-
-
map_.put(1, "linode.com");
-
map_.put(2, "heroku.com");
-
map_.put(3, "digitalocean.com");
-
map_.put(4, "aws.amazon.com");
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
-
-
for(Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry:map_.entrySet()){
-
if("heroku.com".equals(entry.getValue())){
-
result = entry.getValue();
-
-
-
-
System.out.println("Before Java 8 :" + result);
-
-
-
result = map_.entrySet().stream().
-
filter(map->"heroku.com".equals(map.getValue()))
-
.map(map->map.getValue())
-
.collect(Collectors.joining());
-
System.out.println("Java 8 :" + result);
-
-
Map<Integer,String> collect = map_.entrySet().stream()
-
.filter(c->c.getKey()==2)
-
.collect(Collectors.toMap(p->p.getKey(),p->p.getValue()));
-
System.out.println(collect);
-
-
-
6.Optional操作可以防止NullPointException
-
Optional<String> optional = Optional.of("hello");
-
System.out.println(optional.isPresent());
-
System.out.println(optional.get());
-
System.out.println(optional.orElse("false"));
-
optional.ifPresent((s)-> System.out.println(s.charAt(0)));
7.给出一个详细的例子
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public class ExampleEmployee {
-
-
private static List<Employee> employeeList = Lists.newArrayList();
-
-
-
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Matt").salary(5000).office("New York").build());
-
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Steve").salary(6000).office("London").build());
-
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Carrie").salary(20000).office("New York").build());
-
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Peter").salary(7000).office("New York").build());
-
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Pat").salary(8000).office("London").build());
-
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Tammy").salary(29000).office("Shanghai").build());
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
-
boolean isMatch = employeeList.stream().anyMatch(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("London"));
-
System.out.println(isMatch);
-
-
-
boolean matched = employeeList.stream().allMatch(employee -> employee.getSalary()>4000);
-
System.out.println(matched);
-
-
-
Optional<Employee> hightestSalary = employeeList.stream().max((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary()));
-
System.out.println(hightestSalary);
-
-
-
List<String> names = employeeList.stream().map(employee -> employee.getName()).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(names);
-
-
-
Map<String,Employee> employeeMap = employeeList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((key->key.getName()),(value->value)));
-
employeeMap.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println(key + "=" + value));
-
-
-
long officeCount = employeeList.stream().filter(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("Shanghai")).count();
-
System.out.println(officeCount);
-
-
-
Set<String> officeSet = employeeList.stream().map(employee -> employee.getOffice()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toSet());
-
System.out.println(officeSet);
-
-
-
Optional<Employee> allMatchedEmployees = employeeList.stream().filter(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("New York")).findAny();
-
System.out.println(allMatchedEmployees);
-
-
-
List<Employee> sortEmployeeList = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e2.getSalary(),e1.getSalary())).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
-
List<Employee> sortEmployeeByName = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->e1.getName().compareTo(e2.getName())).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(sortEmployeeList);
-
System.out.println("按照名字的升序列出员工信息:" + sortEmployeeByName);
-
-
-
List<Employee> top2EmployeeList= employeeList.stream()
-
.sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e2.getSalary(),e1.getSalary()))
-
-
.collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(top2EmployeeList);
-
-
-
OptionalDouble averageSalary = employeeList.stream().mapToInt(employee->employee.getSalary()).average();
-
System.out.println("平均工资:" + averageSalary);
-
-
-
OptionalDouble averageSalaryByOffice = employeeList.stream().filter(employee -> employee.getOffice()
-
-
.mapToInt(employee->employee.getSalary())
-
-
System.out.println("New York办公室平均工资:" + averageSalaryByOffice);
-
-
-
8.Java8常见操作
-
-
public class EmployeeTest {
-
-
public static List<Employee> generateData() {
-
return Arrays.asList(new Employee("Matt", 5000, "New York"),
-
new Employee("Steve", 6000, "London"),
-
new Employee("Carrie", 10000, "New York"),
-
new Employee("Peter", 7000, "New York"),
-
new Employee("Alec", 6000, "London"),
-
new Employee("Sarah", 8000, "London"),
-
new Employee("Rebecca", 4000, "New York"),
-
new Employee("Pat", 20000, "New York"),
-
new Employee("Tammy", 9000, "New York"),
-
new Employee("Fred", 15000, "Tokyo"));
-
-
-
public static Map<String, Integer> generateMapData() {
-
Map<String, Integer> items = Maps.newHashMap();
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public void testEmployee() {
-
List<Employee> results = generateData();
-
-
-
-
if (c.getName().equals("Steve")) {
-
-
-
-
-
System.out.println("---------");
-
-
-
results.stream().filter(c -> c.getSalary() >= 60000).forEach(c -> System.out.println(c));
-
-
System.out.println("--->>>>>>----");
-
-
-
Map<String, Integer> map_ = generateMapData();
-
map_.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println("key:" + key + "," + "value:" + value));
-
-
System.out.println("---->>>>分组>>>-----");
-
-
-
Map<String, List<Employee>> groupMap = results.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(c -> c.getOffice()));
-
System.out.println(groupMap);
-
-
System.out.println("---->>>>List转化为Map>>>----");
-
-
Map<String, Object> map = results.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Employee::getName, Employee::getOffice));
-
map.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println("key:" + key + "," + "value:" + value));
-
-
System.out.println("---->>>>>>>----");
-
Map<Integer, Employee> employeeMap = results.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((key -> key.getSalary()), (value -> value)));
-
employeeMap.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + "," + value));
-
-
System.out.println("---->>遍历map>>>----");
-
-
Map<String, Integer> resultMap = map_.entrySet().stream().filter(c -> c.getValue() > 30).collect(Collectors.toMap(p -> p.getKey(), p -> p.getValue()));
-
resultMap.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + "=" + value));
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
-
-
Map<String, Integer> mapResults = map_.entrySet().stream().filter(c -> c.getKey().equals("D")).collect(Collectors.toMap(p -> p.getKey(), p -> p.getValue()));
-
mapResults.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + ">>>>" + value));
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>>>Optional>>>>>>>");
-
Optional<String> optional = Optional.of("hello");
-
System.out.println(optional.isPresent());
-
-
-
-
-
public void testEmployeeExample() {
-
-
List<Employee> employeeList = generateData();
-
boolean isMatch = employeeList.stream().anyMatch(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("London"));
-
System.out.println(isMatch);
-
-
-
boolean matched = employeeList.stream().allMatch(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("London"));
-
System.out.println(matched);
-
-
-
Optional<Employee> employeeOptional = employeeList.stream().max((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary()));
-
System.out.println(employeeOptional);
-
-
-
Optional<Employee> employee = employeeList.stream().min((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary()));
-
System.out.println(employee);
-
-
-
List<String> names = employeeList.stream().map(c->c.getName()).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(names);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>");
-
-
Map<String,Employee> employeeMap = employeeList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((key->key.getName()),(value->value)));
-
employeeMap.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println(key + "=" + value));
-
-
-
long officeCount = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getOffice().equals("New York")).count();
-
System.out.println(officeCount);
-
-
long salaryCount = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getSalary()>60000).count();
-
System.out.println(salaryCount);
-
-
-
Set<String> officeSet = employeeList.stream().map(c->c.getOffice()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toSet());
-
System.out.println(officeSet);
-
-
Set<Integer> salarySet = employeeList.stream().map(c->c.getSalary()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toSet());
-
System.out.println(salarySet);
-
-
-
Optional<Employee> optionals = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getOffice().equals("New York")).findAny();
-
System.out.println(optionals);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>工资降序排序>>>>>");
-
-
List<Employee> sortSalaryEmployeeList = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e2.getSalary(),e1.getSalary())).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(sortSalaryEmployeeList);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>姓名升序排序>>>>>");
-
List<Employee> sortNameEmployeeList = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->e1.getName().compareTo(e2.getName())).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(sortNameEmployeeList);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>获取工资最高的前2条员工信息");
-
List<Employee> dispaly2EmployeeList = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e2.getSalary(),e1.getSalary())).limit(2).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(dispaly2EmployeeList);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>获取平均工资");
-
OptionalDouble averageSalary = employeeList.stream().mapToInt(c->c.getSalary()).average();
-
System.out.println(averageSalary);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>获取工作地点的平均工资");
-
OptionalDouble optionalDouble = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getOffice().equals("New York")).mapToInt(c->c.getSalary()).average();
-
System.out.println(optionalDouble);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>>Java8 Optional用法>>>>>>");
-
Optional<String> stringOptional = Optional.of("test");
-
System.out.println(stringOptional.get());
-
-
Optional<String> isOptional = Optional.ofNullable("hello");
-
System.out.println(isOptional.isPresent());
-
System.out.println(isOptional.get());
-
System.out.println(isOptional.orElse("0"));
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>");
-
-
-
Optional<String> optional = Optional.ofNullable("optional");
-
System.out.println(optional);
-
System.out.println(optional.isPresent());
-
System.out.println(optional.get());
-
System.out.println(optional.orElse("haha"));
-
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>");
-
-
Optional<Employee> employeeOptional_ = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getOffice().equals("New York")).findFirst();
-
System.out.println(employeeOptional_);
-
-
1.Java8 新特性介绍
原文链接 https://my.oschina.net/chenxiaobian/blog/704421,https://www.cnblogs.com/hmdrzql/p/6354010.html
现在我们有一个需求:给一个user组成的list 按照user的年龄排序。实现不难,代码如下:

UserCompare是一个实现了Comprator的类

这种方法由于sort方法的第二个参数是Comparator 所以你要写一个实现类(我这里是UserCompare类),并且override该接口的实现方法。
java8提供了lambda来简化,有了lambda程序员从此不加班呀~

刚才那个Comparator的实现类以及内部若干代码就都省了,代之以lambda表达式。
另外,IntelliJ会提示你改成更好的写法

实现类里有多少代码,你就省了多少行代码。
高兴了半天,到底是什么原理呢?其实是java8新提供的语法糖。

我们打开java1.8 Comparator的定义,发现了类定义上面多了一个@FunctionalInterface
对,1.8多了一个概念就是FunctionalInterface,这个Comparator就是一个FunctionalInterface
有了这个注解,原来使用实现类的地方就可以代之以lambda表达式。
写java的同学对java8肯定知道 那么java8到底有哪些特性呢,总结如下:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
最核心的当然是函数式编程了,写代码非常简单,请看下面详细例子介绍
2.Java8 lambda使用总结-结合实例介绍
很多同学一开始接触Java8可能对Java8 Lambda表达式有点陌生,下面我将结合实例介绍Java8的使用 并与Java7进行比较:
基础类
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
1.List操作
-
public class ExampleList {
-
private static List<String> items = new ArrayList<>();
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
-
-
System.out.println(item);
-
-
-
-
items.forEach(c-> System.out.println(c));
-
-
-
-
System.out.println(item);
-
-
-
-
System.out.println("--------");
-
-
-
items.stream().filter(s->s.contains("B")).forEach(c1-> System.out.println(c1));
-
-
-
2.Map操作
-
public class ExampleMap {
-
-
private static Map<String, Integer> items = new HashMap<>();
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
-
-
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry:items.entrySet()){
-
System.out.println("key:" + entry.getKey() + " value:" + entry.getValue());
-
-
-
-
items.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println("key:" + key + " value:" + value));
-
-
-
-
-
-
3.Groupingby操作
-
-
-
-
-
public class ExampleMapping {
-
-
private static List<Person> personList = Lists.newArrayList();
-
-
-
personList.add(Person.builder().id(10).address("apple").address("shanghai").build());
-
personList.add(Person.builder().id(12).address("apple").address("wuhan").build());
-
personList.add(Person.builder().id(16).address("apple").address("nanjing").build());
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
-
Map<String, List<Person>> collect = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(c -> c.getAddress()));
-
System.out.println(collect);
-
-
4.List转换为Map
-
public class ExampleListConvertMap {
-
-
private static List<Person> personList = Lists.newArrayList();
-
-
-
personList.add(Person.builder().id(20).name("zhangsan").address("shanghai").build());
-
personList.add(Person.builder().id(30).name("lisi").address("nanjing").build());
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
-
Map<Integer,Person> map_ = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((key->key.getId()),(value->value)));
-
map_.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println(key + ":" + value));
-
-
Map<Integer, Person> mappedMovies = personList.stream().collect(
-
Collectors.toMap(Person::getRank, Person::getData));
-
-
-
5.FilterMap操作
-
public class ExampleFilterMap {
-
-
private static Map<Integer,String> map_ = Maps.newHashMap();
-
-
-
map_.put(1, "linode.com");
-
map_.put(2, "heroku.com");
-
map_.put(3, "digitalocean.com");
-
map_.put(4, "aws.amazon.com");
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
-
-
for(Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry:map_.entrySet()){
-
if("heroku.com".equals(entry.getValue())){
-
result = entry.getValue();
-
-
-
-
System.out.println("Before Java 8 :" + result);
-
-
-
result = map_.entrySet().stream().
-
filter(map->"heroku.com".equals(map.getValue()))
-
.map(map->map.getValue())
-
.collect(Collectors.joining());
-
System.out.println("Java 8 :" + result);
-
-
Map<Integer,String> collect = map_.entrySet().stream()
-
.filter(c->c.getKey()==2)
-
.collect(Collectors.toMap(p->p.getKey(),p->p.getValue()));
-
System.out.println(collect);
-
-
-
6.Optional操作可以防止NullPointException
-
Optional<String> optional = Optional.of("hello");
-
System.out.println(optional.isPresent());
-
System.out.println(optional.get());
-
System.out.println(optional.orElse("false"));
-
optional.ifPresent((s)-> System.out.println(s.charAt(0)));
7.给出一个详细的例子
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public class ExampleEmployee {
-
-
private static List<Employee> employeeList = Lists.newArrayList();
-
-
-
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Matt").salary(5000).office("New York").build());
-
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Steve").salary(6000).office("London").build());
-
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Carrie").salary(20000).office("New York").build());
-
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Peter").salary(7000).office("New York").build());
-
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Pat").salary(8000).office("London").build());
-
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Tammy").salary(29000).office("Shanghai").build());
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
-
boolean isMatch = employeeList.stream().anyMatch(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("London"));
-
System.out.println(isMatch);
-
-
-
boolean matched = employeeList.stream().allMatch(employee -> employee.getSalary()>4000);
-
System.out.println(matched);
-
-
-
Optional<Employee> hightestSalary = employeeList.stream().max((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary()));
-
System.out.println(hightestSalary);
-
-
-
List<String> names = employeeList.stream().map(employee -> employee.getName()).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(names);
-
-
-
Map<String,Employee> employeeMap = employeeList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((key->key.getName()),(value->value)));
-
employeeMap.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println(key + "=" + value));
-
-
-
long officeCount = employeeList.stream().filter(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("Shanghai")).count();
-
System.out.println(officeCount);
-
-
-
Set<String> officeSet = employeeList.stream().map(employee -> employee.getOffice()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toSet());
-
System.out.println(officeSet);
-
-
-
Optional<Employee> allMatchedEmployees = employeeList.stream().filter(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("New York")).findAny();
-
System.out.println(allMatchedEmployees);
-
-
-
List<Employee> sortEmployeeList = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e2.getSalary(),e1.getSalary())).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
-
List<Employee> sortEmployeeByName = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->e1.getName().compareTo(e2.getName())).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(sortEmployeeList);
-
System.out.println("按照名字的升序列出员工信息:" + sortEmployeeByName);
-
-
-
List<Employee> top2EmployeeList= employeeList.stream()
-
.sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e2.getSalary(),e1.getSalary()))
-
-
.collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(top2EmployeeList);
-
-
-
OptionalDouble averageSalary = employeeList.stream().mapToInt(employee->employee.getSalary()).average();
-
System.out.println("平均工资:" + averageSalary);
-
-
-
OptionalDouble averageSalaryByOffice = employeeList.stream().filter(employee -> employee.getOffice()
-
-
.mapToInt(employee->employee.getSalary())
-
-
System.out.println("New York办公室平均工资:" + averageSalaryByOffice);
-
-
-
8.Java8常见操作
-
-
public class EmployeeTest {
-
-
public static List<Employee> generateData() {
-
return Arrays.asList(new Employee("Matt", 5000, "New York"),
-
new Employee("Steve", 6000, "London"),
-
new Employee("Carrie", 10000, "New York"),
-
new Employee("Peter", 7000, "New York"),
-
new Employee("Alec", 6000, "London"),
-
new Employee("Sarah", 8000, "London"),
-
new Employee("Rebecca", 4000, "New York"),
-
new Employee("Pat", 20000, "New York"),
-
new Employee("Tammy", 9000, "New York"),
-
new Employee("Fred", 15000, "Tokyo"));
-
-
-
public static Map<String, Integer> generateMapData() {
-
Map<String, Integer> items = Maps.newHashMap();
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public void testEmployee() {
-
List<Employee> results = generateData();
-
-
-
-
if (c.getName().equals("Steve")) {
-
-
-
-
-
System.out.println("---------");
-
-
-
results.stream().filter(c -> c.getSalary() >= 60000).forEach(c -> System.out.println(c));
-
-
System.out.println("--->>>>>>----");
-
-
-
Map<String, Integer> map_ = generateMapData();
-
map_.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println("key:" + key + "," + "value:" + value));
-
-
System.out.println("---->>>>分组>>>-----");
-
-
-
Map<String, List<Employee>> groupMap = results.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(c -> c.getOffice()));
-
System.out.println(groupMap);
-
-
System.out.println("---->>>>List转化为Map>>>----");
-
-
Map<String, Object> map = results.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Employee::getName, Employee::getOffice));
-
map.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println("key:" + key + "," + "value:" + value));
-
-
System.out.println("---->>>>>>>----");
-
Map<Integer, Employee> employeeMap = results.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((key -> key.getSalary()), (value -> value)));
-
employeeMap.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + "," + value));
-
-
System.out.println("---->>遍历map>>>----");
-
-
Map<String, Integer> resultMap = map_.entrySet().stream().filter(c -> c.getValue() > 30).collect(Collectors.toMap(p -> p.getKey(), p -> p.getValue()));
-
resultMap.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + "=" + value));
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
-
-
Map<String, Integer> mapResults = map_.entrySet().stream().filter(c -> c.getKey().equals("D")).collect(Collectors.toMap(p -> p.getKey(), p -> p.getValue()));
-
mapResults.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + ">>>>" + value));
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>>>Optional>>>>>>>");
-
Optional<String> optional = Optional.of("hello");
-
System.out.println(optional.isPresent());
-
-
-
-
-
public void testEmployeeExample() {
-
-
List<Employee> employeeList = generateData();
-
boolean isMatch = employeeList.stream().anyMatch(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("London"));
-
System.out.println(isMatch);
-
-
-
boolean matched = employeeList.stream().allMatch(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("London"));
-
System.out.println(matched);
-
-
-
Optional<Employee> employeeOptional = employeeList.stream().max((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary()));
-
System.out.println(employeeOptional);
-
-
-
Optional<Employee> employee = employeeList.stream().min((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary()));
-
System.out.println(employee);
-
-
-
List<String> names = employeeList.stream().map(c->c.getName()).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(names);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>");
-
-
Map<String,Employee> employeeMap = employeeList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((key->key.getName()),(value->value)));
-
employeeMap.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println(key + "=" + value));
-
-
-
long officeCount = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getOffice().equals("New York")).count();
-
System.out.println(officeCount);
-
-
long salaryCount = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getSalary()>60000).count();
-
System.out.println(salaryCount);
-
-
-
Set<String> officeSet = employeeList.stream().map(c->c.getOffice()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toSet());
-
System.out.println(officeSet);
-
-
Set<Integer> salarySet = employeeList.stream().map(c->c.getSalary()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toSet());
-
System.out.println(salarySet);
-
-
-
Optional<Employee> optionals = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getOffice().equals("New York")).findAny();
-
System.out.println(optionals);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>工资降序排序>>>>>");
-
-
List<Employee> sortSalaryEmployeeList = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e2.getSalary(),e1.getSalary())).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(sortSalaryEmployeeList);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>姓名升序排序>>>>>");
-
List<Employee> sortNameEmployeeList = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->e1.getName().compareTo(e2.getName())).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(sortNameEmployeeList);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>获取工资最高的前2条员工信息");
-
List<Employee> dispaly2EmployeeList = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e2.getSalary(),e1.getSalary())).limit(2).collect(Collectors.toList());
-
System.out.println(dispaly2EmployeeList);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>获取平均工资");
-
OptionalDouble averageSalary = employeeList.stream().mapToInt(c->c.getSalary()).average();
-
System.out.println(averageSalary);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>获取工作地点的平均工资");
-
OptionalDouble optionalDouble = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getOffice().equals("New York")).mapToInt(c->c.getSalary()).average();
-
System.out.println(optionalDouble);
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>>Java8 Optional用法>>>>>>");
-
Optional<String> stringOptional = Optional.of("test");
-
System.out.println(stringOptional.get());
-
-
Optional<String> isOptional = Optional.ofNullable("hello");
-
System.out.println(isOptional.isPresent());
-
System.out.println(isOptional.get());
-
System.out.println(isOptional.orElse("0"));
-
-
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>");
-
-
-
Optional<String> optional = Optional.ofNullable("optional");
-
System.out.println(optional);
-
System.out.println(optional.isPresent());
-
System.out.println(optional.get());
-
System.out.println(optional.orElse("haha"));
-
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>");
-
-
Optional<Employee> employeeOptional_ = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getOffice().equals("New York")).findFirst();
-
System.out.println(employeeOptional_);
-
-
Java8 lambda 的使用
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/coder-wzr/p/14410981.html


![]()
![]()



![]()
![]()
