条件判断
if(表达式1){
表达式2;
}
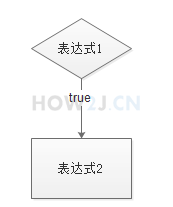
如果表达式1的值是true,
就执行表达式2
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean b = true;
//如果成立就打印yes
if(b){
System.out.println("yes");
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean b = false;
//如果有多个表达式,必须用大括弧包括起来
if(b){
System.out.println("yes1");
System.out.println("yes2");
System.out.println("yes3");
}
//否则表达式2 3 无论b是否为true都会执行
if(b)
System.out.println("yes1");
System.out.println("yes2");
System.out.println("yes3");
//如果只有一个表达式可以不用写括弧,看上去会简约一些
if(b){
System.out.println("yes1");
}
if(b)
System.out.println("yes1");
}
}
在第6行,if后面有一个分号; 而分号也是一个完整的表达式
如果b为true,会执行这个分号,然后打印yes
如果b为false,不会执行这个分号,然后打印yes
这样,看上去无论如何都会打印yes
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean b = false;
if (b);
System.out.println("yes");
}
}
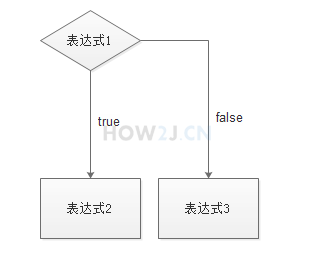
else 代表不成立的情况
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean b = false;
if (b)
System.out.println("yes");
else
System.out.println("no");
}
}
else if 是多条件判断
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//如果只使用 if,会执行4次判断
int i = 2;
if (i==1)
System.out.println(1);
if (i==2)
System.out.println(2);
if (i==3)
System.out.println(3);
if (i==4)
System.out.println(4);
//如果使用else if, 一旦在18行,判断成立, 20行和22行的判断就不会执行了,节约了运算资源
if (i==1)
System.out.println(1);
else if (i==2)
System.out.println(2);
else if (i==3)
System.out.println(3);
else if (i==4)
System.out.println(4);
}
}
switch 语句相当于 if else的另一种表达方式
switch可以使用byte,short,int,char,String,enum
注: 每个表达式结束,都应该有一个break;
注: String在Java1.7之前是不支持的, Java从1.7开始支持switch用String的,编译后是把String转化为hash值,其实还是整数
注: enum是枚举类型,在枚举章节有详细讲解
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//如果使用if else
int day = 5;
if (day==1)
System.out.println("星期一");
else if (day==2)
System.out.println("星期二");
else if (day==3)
System.out.println("星期三");
else if (day==4)
System.out.println("星期四");
else if (day==5)
System.out.println("星期五");
else if (day==6)
System.out.println("星期六");
else if (day==7)
System.out.println("星期天");
else
System.out.println("这个是什么鬼?");
//如果使用switch
switch(day){
case 1:
System.out.println("星期一");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("星期二");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("星期三");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("星期四");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("星期五");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("星期六");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("星期天");
break;
default:
System.out.println("这个是什么鬼?");
}
}
}
通过Scanner 输入月份,然后使用switch 判断季节
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入月份");
int month = s.nextInt();
String season;
switch (month) {
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
season = "春天";
break;
case 4:
case 5:
case 6:
season = "夏天";
break;
case 7:
case 8:
case 9:
season = "秋天";
break;
case 10:
case 11:
case 12:
season = "冬天";
break;
default:
season = "这是什么鬼~";
}
System.out.println(season);
}
}
while和do-while循环语句
只要while中的表达式成立,就会不断地循环执行
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印0到4
int i = 0;
while(i<5){
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
}
do{
} while 循环
与while的区别是,无论是否成立,先执行一次,再进行判断
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印0到4
//与while的区别是,无论是否成立,先执行一次,再进行判断
int i = 0;
do{
System.out.println(i);
i++;
} while(i<5);
}
}
通过Scanner 获取一个整数,然后使用while计算这个整数的阶乘
N的阶乘等于 N* (N-1) * (N-2) * ... * 1
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
int n = s.nextInt();
int fac = 1;
while(n>=1){
fac *=n;
n--;
}
System.out.println("阶乘是:" + fac);
}
}
for循环,和while一样,只是表达方式不一样
比较for和while
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用while打印0到4
int i = 0;
while(i<5){
System.out.println("while循环输出的"+i);
i++;
}
//使用for打印0到4
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
System.out.println("for 循环输出的"+j);
}
}
}
天朝有一个乞丐姓洪,去天桥要钱
第一天要了1块钱
第二天要了2块钱
第三天要了4块钱
第四天要了8块钱
以此类推
问题: 洪乞丐干10天,收入是多少?
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int moneyEachDay = 0;
int day = 10;
int sum=0;
for (int i = 1; i <= day; i++) {
if(0==moneyEachDay)
moneyEachDay = 1;
else
moneyEachDay *= 2;
sum+=moneyEachDay;
System.out.println(i + " 天之后,洪帮主手中的钱总数是: " + sum );
}
}
}
continue
继续下一次循环
如果是双数,后面的代码不执行,直接进行下一次循环
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印单数
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
if(0==j%2)
continue; //如果是双数,后面的代码不执行,直接进行下一次循环
System.out.println(j);
}
}
}
打印 1-100 之间的数,如果这个数,要么是3,要么5的倍数,就忽略掉
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <=100; i++) {
if(0==i%3 || 0 ==i%5)
continue;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
结束循环
直接结束当前for循环
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印单数
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
if(0==j%2)
break; //如果是双数,直接结束循环
System.out.println(j);
}
}
}
假设你月收入是3000,除开平时花销,每个月留下1000块钱进行投资。
然后你认真的钻研了 《股票和基金 21天从入门到精通》,达到了每年20%的投资回报率。
那么问题来了,以每个月投资1000块钱的节奏,持续投资多少年,总收入达到100万
(复利计算按照每年12000投入计算,不按照每月计息)
复利公式:
F = p* ( (1+r)^n );
F 最终收入
p 本金
r 年利率
n 存了多少年
假设情景一:
p = 10000
r = 0.05
n = 1
解读:
本金是10000
年利率是5%
存了一年 1次
复利收入 10000*( (1+0.05)^1 ) = 10500
假设情景二:
p = 10000
r = 0.05
n = 2
解读:
本金是10000
年利率是5%
存了两年
复利收入 10000*( (1+0.05)^2 ) = 11025
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int fundPerMonth = 1000;
int fundPerYear = fundPerMonth *12;
float rate = 0.20f;
//F = p* ( (1+r)^n );
int sum = 0;
int target = 1000*1000;
for (int j = 1; j < 100; j++) {
int year = j;
float compoundInterestRate = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < year; i++) {
compoundInterestRate = compoundInterestRate * (1+rate);
}
int compoundInterest = (int) (fundPerYear * compoundInterestRate);
sum +=compoundInterest;
System.out.println("经过" + year + " 年, 总收入 " + sum);
if(sum>=target){
System.out.println("一共需要" + year + "年,累计收入超过" + target );
break;
}
}
}
}
break是结束当前循环
break;只能结束当前循环
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印单数
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println(i+":"+j);
if(0==j%2)
break; //如果是双数,结束当前循环
}
}
}
}
借助boolean变量结束外部循环
需要在内部循环中修改这个变量值
每次内部循环结束后,都要在外部循环中判断,这个变量的值
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean breakout = false; //是否终止外部循环的标记
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println(i + ":" + j);
if (0 == j % 2) {
breakout = true; //终止外部循环的标记设置为true
break;
}
}
if (breakout) //判断是否终止外部循环
break;
}
}
}
在外部循环的前一行,加上标签
在break的时候使用该标签
即能达到结束外部循环的效果
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印单数
outloop: //outloop这个标示是可以自定义的比如outloop1,ol2,out5
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println(i+":"+j);
if(0==j%2)
break outloop; //如果是双数,结束外部循环
}
}
}
}
寻找某两个数相除,其结果 离黄金分割点 0.618最近
分母和分子不能同时为偶数
分母和分子 取值范围在[1-20]
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 寻找某两个数相除,其结果 离黄金分割点 0.618最近
//
// 分母和分子不能同时为偶数
// 分母和分子 取值范围在[1-20]
int range = 20; // 取值范围
float breakPoint = 0.618f; // 黄金分割点
float minDiff = 100; // 离黄金分割点的差值
int answerFenzi = 0; // 找到的分子
int answerFenmu = 0; // 找到的分母
for (int fenzi = 1; fenzi <= range; fenzi++) {
for (int fenmu = 1; fenmu <= range; fenmu++) {
// 分母和分子不能同时为偶数
if (0 == fenzi % 2 & 0 == fenmu % 2)
continue;
// 取值
float value = (float) fenzi / fenmu;
// 取离黄金分割点的差值
float diff = value - breakPoint;
// 绝对值
diff = diff < 0 ? 0 - diff : diff;
// 找出最小的差值
if (diff < minDiff) {
minDiff = diff;
answerFenzi = fenzi;
answerFenmu = fenmu;
}
}
}
System.out.println("离黄金分割点(" + breakPoint + ")最近的两个数相除是:" + answerFenzi + "/" + answerFenmu + "="
+ ((float) answerFenzi / answerFenmu));
}
}
水仙花数定义:
\1. 一定是3位数
\2. 每一位的立方,加起来恰好是这个数本身,比如153=111+555+333
寻找所有的水仙花数
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 100; i < 1000; i++) {
int baiwei = i / 100;
int shiwei = i / 10 % 10;
int gewei = i % 10;
int cube = baiwei * baiwei * baiwei + shiwei * shiwei * shiwei + gewei * gewei * gewei;
if (cube == i) {
System.out.println("找到水仙花数:" + i);
}
}
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/BenZeng/p/14416034.html