源码+官方文档
Runable 没有返回值、效率相比Callable相对比较低
线程、进程,如果不能用一句话说出来的技术,不扎实
进程:一个程序,qq.exe Music.exe程序的集合
一个进程往往可以包含多个线程,至少包含一个!
java默认有几个线程?2个 main、GC
线程:开了一个进程,写字,自动保存(线程负责的)
对于java而言:Thread、Runnable、Callable
java真的可以开启线程吗?开不了
public synchronized void start() {
/**
* This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added
* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.
*
* A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".
*/
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
* so that it can be added to the group‘s list of threads
* and the group‘s unstarted count can be decremented. */
group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
start0();
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
//本地方法,底层的C++,java无法直接操作硬件
private native void start0();
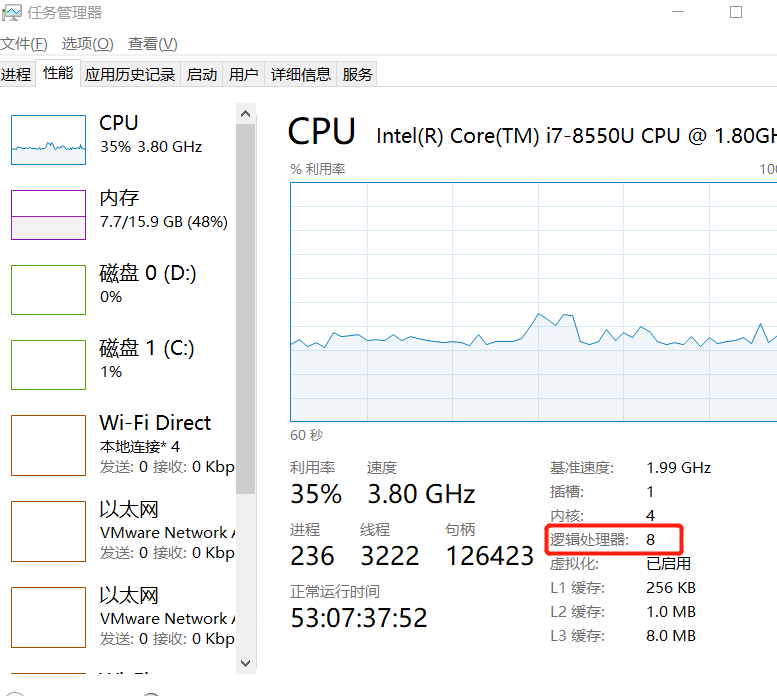
并发、并行
package com.cui;
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
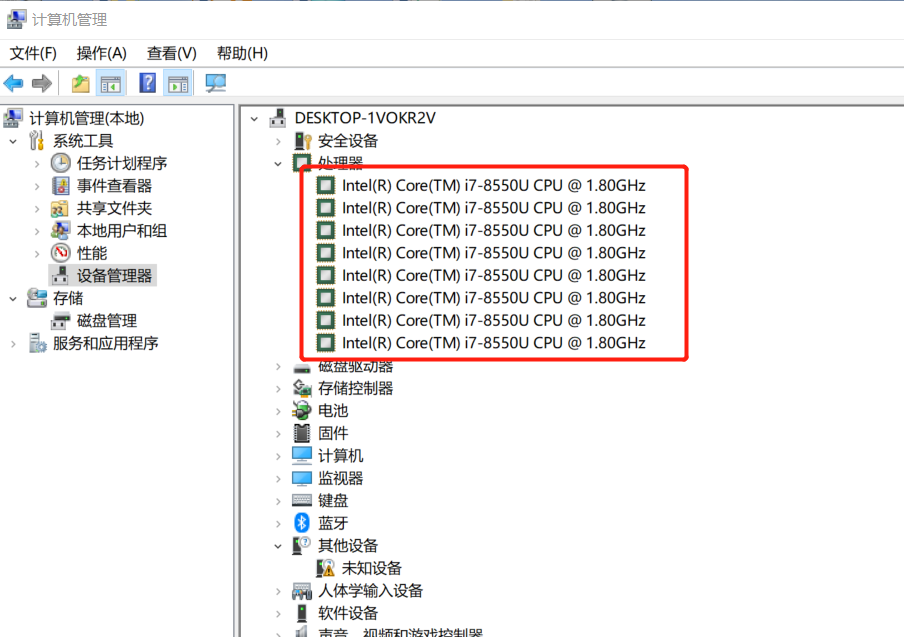
//获取cpu的核数
//CPU密集型,IO密集型
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
}
}
所有公司都很看重!
线程有几个状态
public enum State {
//新生
NEW,
//运行
RUNNABLE,
//阻塞
BLOCKED,
//等待
WAITING,
//超时等待
TIMED_WAITING,
//终止
TERMINATED;
}
wait/sleep的区别
1.来自不同类
wait===> Object
sleep===>Thread
2.关于锁的释放
wait会释放锁,sleep睡觉了,抱着锁睡觉,不会释放
3.使用范围不同
wait必须在同步代码块中
sleep可以在任何地方睡
4.是否需要捕获异常
wait不要捕获异常
sleep必须要捕获异常
传统方法 synchronized
package com.cui;
import sun.security.krb5.internal.Ticket;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
new Thread(()-> { for (int i=1;i<60;i++){ ticket.sale(); } },"A").start();
new Thread(()-> { for (int i=1;i<60;i++){ ticket.sale(); } },"B").start();
new Thread(()-> { for (int i=1;i<60;i++){ ticket.sale(); } },"C").start();
}
static class Ticket {
private int number = 50;
public synchronized void sale(){
if(number>0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖出了:"+(number--)+"票"+"剩余:"+number+"张票");
}
}
}
}
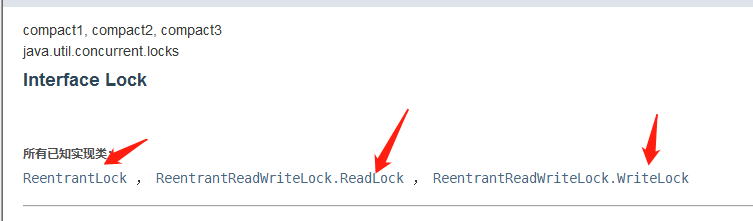
package com.cui;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
demo.Ticket ticket = new demo.Ticket();
new Thread(()-> { for (int i=1;i<60;i++){ ticket.sale(); } },"A").start();
new Thread(()-> { for (int i=1;i<60;i++){ ticket.sale(); } },"B").start();
new Thread(()-> { for (int i=1;i<60;i++){ ticket.sale(); } },"C").start();
}
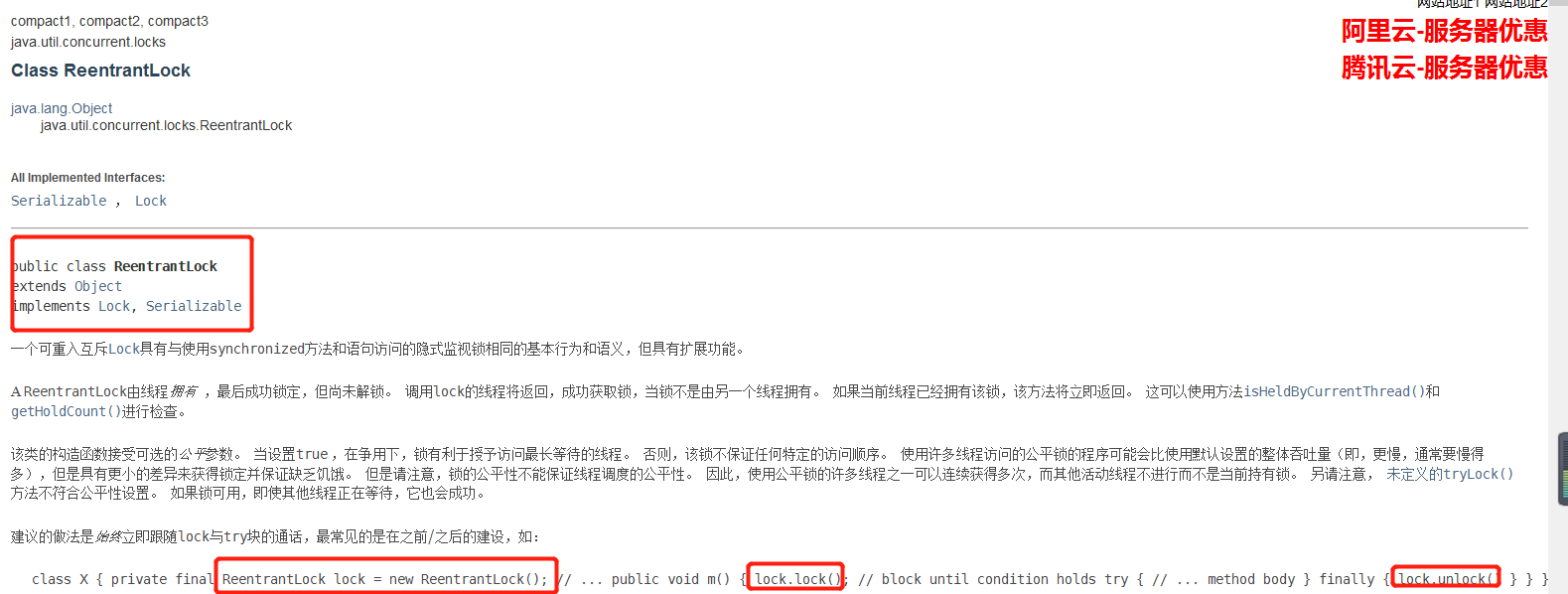
//lock三部曲
//1.new Reentrantlock();
//2.lock.lock();//加锁
//3.finally=>lock.unlock()//解锁
static class Ticket {
private int number = 50;
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void sale(){
lock.lock();
try {
if(number>0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖出了:"+(number--)+"票"+"剩余:"+number+"张票");
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
synchronized和lock区别
1.synchronized 内置的java关键字,lock是一个java类
2.synchronized 无法判断获取锁的状态,lock可以判断是否获取了锁
3.synchronized 会自动释放锁,lock必须要手动释放锁!如果不释放锁,死锁
4.synchronized 线程1(获得锁,阻塞)、线程2(等待,傻傻的等);lock锁就不一定会等待下去;
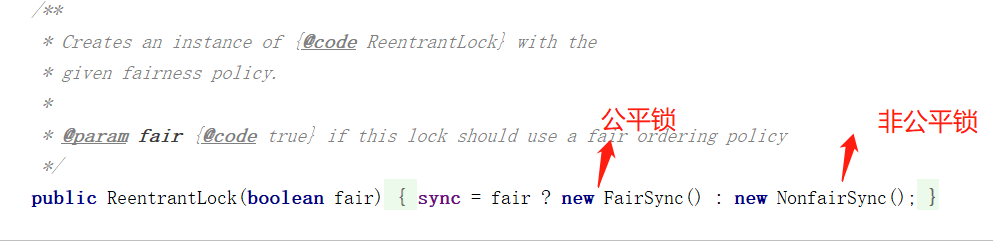
5.synchronized 可重入锁,不可中断的,非公平;lock,可重入锁,可以判断锁,非公平的(可以自己设置);
6.synchronized 适合锁少量的代码同步问题,lock适合锁大量的同步代码!
锁是什么,如何判断锁是谁!

package com.cui;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data1 data = new Data1();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
try{
data.increment();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
try{
data.decrement();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"B").start();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
try{
data.increment();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"C").start();
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
try{
data.decrement();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"D").start();
}
static class Data1{
private int number = 0;
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
// condition.await(); //等待
// condition.signalAll(); //唤醒全部
//+1
public void increment() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (number!=0){
//等待
condition.await();
}
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+number);
//通知其他线程,我+1完毕
condition.signalAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void decrement(){
lock.lock();
try {
while (number==0){
//等待
condition.await();
}
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+number);
//通知其他线程,我已-1完毕
condition.signalAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
package com.cui;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class C {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data3 data = new Data3();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0;i<20;i++){
data.printA();
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0;i<20;i++){
data.printB();
}
},"B").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0;i<20;i++){
data.printC();
}
},"C").start();
}
static class Data3 {
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
private int number = 1;
public void printA() {
lock.lock();
try {
//业务,判断->执行->通知
while (number != 1) {
condition1.await();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + "AAAAAAAAAAA");
number = 2;
condition2.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void printB() {
lock.lock();
try {
//业务,判断->执行->通知
while (number != 2) {
condition1.await();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + "BBBBBBB");
number = 3;
condition3.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void printC() {
lock.lock();
try {
//业务,判断->执行->通知
while (number != 3) {
condition1.await();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + "CCCCCCCC");
number = 1;
condition1.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/lvshuizhicheng/p/14418808.html