通常搭建一个基于spring的web应用,我们需要做以下工作:
而用springboot后,一切都变得很简便快速。
@SpringBootApplication public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(App.class, args); } }
SpringBootApplication注解如下:

1 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) //注解的适用范围,其中Type用于描述类、接口或Enum声明 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //注解的生命周期,保留到Class文件中 3 @Documented //表明这个注解应该被javadoc记录 4 @Inherited //子类可以继承该注解 5 @SpringBootConfiguration //继承了Configuration,表示当前是注解类 6 @EnableAutoConfiguration //开启SpringBoot的注解功能,借助@import的支持,收集和注册依赖包中的bean定义 7 @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), 8 @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) //自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件 9 public @interface SpringBootApplication { 10 11 /** 12 * Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied. 13 * @return the classes to exclude 14 */ 15 @AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class) 16 Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; 17 18 /** 19 * Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be 20 * applied. 21 */ 22 @AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class) 23 String[] excludeName() default {}; 24 25 /** 26 * Base packages to scan for annotated components. Use {@link #scanBasePackageClasses} 27 * for a type-safe alternative to String-based package names. 28 */ 29 @AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages") 30 String[] scanBasePackages() default {}; 31 32 /** 33 * Type-safe alternative to {@link #scanBasePackages} for specifying the packages to 34 * scan for annotated components. The package of each class specified will be scanned. 35 */ 36 @AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses") 37 Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {}; 38 39 /** 40 * The {@link BeanNameGenerator} class to be used for naming detected components 41 * within the Spring container. 42 */ 43 @AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "nameGenerator") 44 Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class; 45 46 /** 47 * Specify whether {@link Bean @Bean} methods should get proxied in order to enforce 48 * bean lifecycle behavior 49 */ 50 @AliasFor(annotation = Configuration.class) 51 boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true; 52 53 }
除了普通修饰注解类的原信息,还有@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan 3个注解。
SpringBootConfiguration注解如下:

@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Configuration public @interface SpringBootConfiguration { /** * Specify whether {@link Bean @Bean} methods should get proxied in order to enforce * bean lifecycle behavior */ @AliasFor(annotation = Configuration.class) boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true; }
可以看到类上有@Configuration注解,说明它本身也是一个配置类。SpringBoot社区推荐使用基于JavaConfig的配置方式来定义Bean,所以这里的启动类标注了@Configuration之后,本身也可以认为是一个Spring Ioc容器的配置类。
<bean id="mockService" class="..MockServiceImpl"> ... </bean>
任何一个标注了@Bean的方法,其返回值将作为一个bean定义注册到Spring的IoC容器,方法名将默认成该bean定义的id。
@Configuration public class MockConfiguration{ @Bean public MockService mockService(){ return new MockServiceImpl(); } }
@ComponentScan注解如下:

1 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 2 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) 3 @Documented 4 @Repeatable(ComponentScans.class) 5 public @interface ComponentScan { 6 7 /** 8 * Alias for {@link #basePackages}. 9 */ 10 @AliasFor("basePackages") 11 String[] value() default {}; 12 13 /** 14 * Base packages to scan for annotated components. 15 */ 16 @AliasFor("value") 17 String[] basePackages() default {}; 18 19 /** 20 * Type-safe alternative to {@link #basePackages} for specifying the packages to scan for annotated components. 21 */ 22 Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {}; 23 24 /** 25 * The {@link BeanNameGenerator} class to be used for naming detected components within the Spring container. 26 */ 27 Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class; 28 29 /** 30 * The {@link ScopeMetadataResolver} to be used for resolving the scope of detected components. 31 */ 32 Class<? extends ScopeMetadataResolver> scopeResolver() default AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver.class; 33 34 /** 35 * Indicates whether proxies should be generated for detected components, which may be necessary when using scopes in a proxy-style fashion. 36 */ 37 ScopedProxyMode scopedProxy() default ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT; 38 39 /** 40 * Controls the class files eligible for component detection. 41 */ 42 String resourcePattern() default ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.DEFAULT_RESOURCE_PATTERN; 43 44 /** 45 * Indicates whether automatic detection of classes annotated with {@code @Component} 46 * {@code @Repository}, {@code @Service}, or {@code @Controller} should be enabled. 47 */ 48 boolean useDefaultFilters() default true; 49 50 /** 51 * Specifies which types are eligible for component scanning. 52 */ 53 Filter[] includeFilters() default {}; 54 55 /** 56 * Specifies which types are not eligible for component scanning. 57 * @see #resourcePattern 58 */ 59 Filter[] excludeFilters() default {}; 60 61 /** 62 * Specify whether scanned beans should be registered for lazy initialization. 63 * @since 4.1 64 */ 65 boolean lazyInit() default false; 66 67 68 /** 69 * Declares the type filter to be used as an {@linkplain ComponentScan#includeFilters 70 * include filter} or {@linkplain ComponentScan#excludeFilters exclude filter}. 71 */ 72 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 73 @Target({}) 74 @interface Filter { 75 76 /** 77 * The type of filter to use. 78 * <p>Default is {@link FilterType#ANNOTATION}. 79 * @see #classes 80 * @see #pattern 81 */ 82 FilterType type() default FilterType.ANNOTATION; 83 84 /** 85 * Alias for {@link #classes}. 86 * @see #classes 87 */ 88 @AliasFor("classes") 89 Class<?>[] value() default {}; 90 91 /** 92 * The class or classes to use as the filter. 93 */ 94 @AliasFor("value") 95 Class<?>[] classes() default {}; 96 97 /** 98 * The pattern (or patterns) to use for the filter, as an alternative 99 */ 100 String[] pattern() default {}; 101 102 }
@ComponentScan注解对应原有XML配置中的元素。@ComponentScan的功能是自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件(如@controller、@Component等),最终将这些Bean的定义加载到Ioc容器中。
我们可以通过basePackages等属性来细粒度的定制@ComponentScan自动扫描的范围,如果不指定,则默认Spring框架实现会从声明@ComponentScan所在类的package进行扫描。所以通常我们在定义SpringBoot启动类的时候,会把它放到root package下,这样就能扫描到所有需要定义的类。
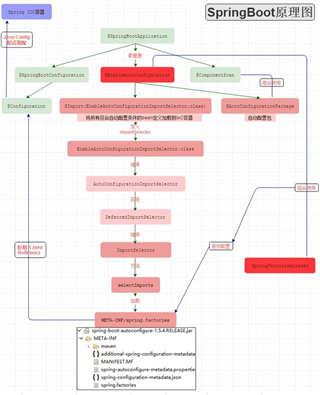
EnableAutoConfiguration的作用是从classpath中搜寻所有的META-INF/spring.factories配置文件,并将其中org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableutoConfiguration对应的配置项通过反射(Java Refletion)实例化为对应的标注了@Configuration的JavaConfig形式的IoC容器配置类,然后汇总为一个并加载到IoC容器。
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解如下:

@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @AutoConfigurationPackage @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { /** * Environment property that can be used to override when auto-configuration is * enabled. */ String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration"; /** * Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied. * @return the classes to exclude */ Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; /** * Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be * applied. * @return the class names to exclude * @since 1.3.0 */ String[] excludeName() default {}; }
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解对应原有XML配置中的元素。它之所以能自动根据条件来注册我们需要的Bean实例,主要是由其上的注解@Import导入的。
@AutoConfigurationPackage注解如下:

@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class) public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage { /** * Base packages that should be registered with {@link AutoConfigurationPackages}. */ String[] basePackages() default {}; /** * Type-safe alternative to {@link #basePackages} for specifying the packages to be * registered with {@link AutoConfigurationPackages}. */ Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {}; }
@AutoConfigurationPackage注解的作用是将 添加该注解的类所在的package 作为 自动配置package 进行管理。可以通过 AutoConfigurationPackages 工具类获取自动配置package列表。也就是说当SpringBoot应用启动时默认会将启动类所在的package作为自动配置的package。
核心方法是:
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports { @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { register(registry, new PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0])); } }
其中【new PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0])】就是启动类的包路径
在AutoConfigurationImportSelector中会调用如下方法:
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader()); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you " + "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; }
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames 方法会加载外部配置文件:
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
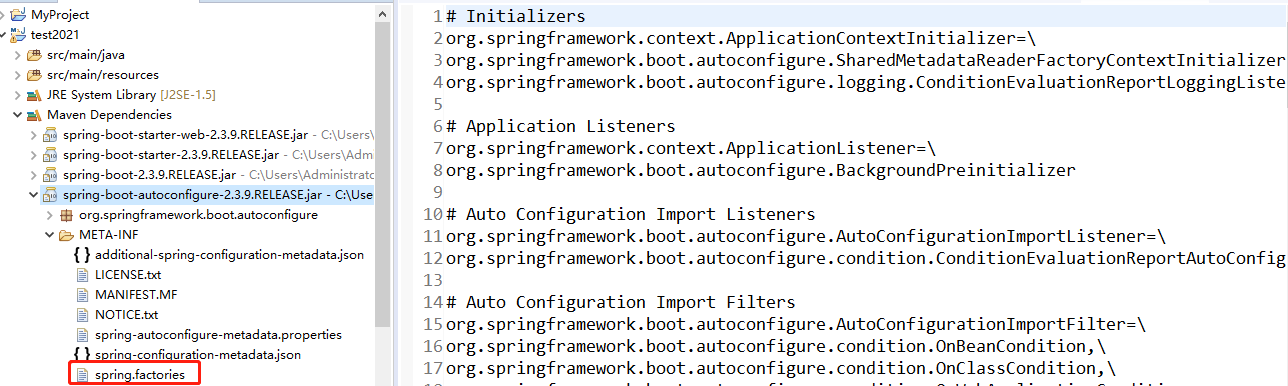
以spring-boot-autoconfigure-**.jar中spring.factories为例,如下图所示:
3.1.SpringApplication实例初始化并设置基础信息

public class SpringApplication { public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) { return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args); } public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) { return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args); } public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) { this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null"); this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources)); this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath(); setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); } }
3.2.执行run方法体逻辑
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>(); configureHeadlessProperty(); SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting(); //3.2.1 try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); //3.2.2 configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); //3.2.3 context = createApplicationContext(); //3.2.4 exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context); //3.2.5 prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); //3.2.6 refreshContext(context); //3.2.7 afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } listeners.started(context); callRunners(context, applicationArguments); //3.2.8 } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } try { listeners.running(context); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } return context; }
3.2.1遍历执行所有通过SpringFactoriesLoader可以查找到并加载的SpringApplicationRunListener,调用starting()方法,通知SpringBoot开始执行;
3.2.2准备并配置当前Spring Boot应用将要使用的Environment(包括配置要使用的PropertySource以及Profile),然后通知Listeners环境准备好了;

private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) { // Create and configure the environment ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment(); configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs()); ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment); listeners.environmentPrepared(environment); bindToSpringApplication(environment); if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) { environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass()); } ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment); return environment; }
3.2.3判断bannerMode,是OFF则不打印,是LOG则输出到日志文件,否则输出到System.out;

private Banner printBanner(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { if (this.bannerMode == Banner.Mode.OFF) { return null; } ResourceLoader resourceLoader = (this.resourceLoader != null) ? this.resourceLoader : new DefaultResourceLoader(null); SpringApplicationBannerPrinter bannerPrinter = new SpringApplicationBannerPrinter(resourceLoader, this.banner); if (this.bannerMode == Mode.LOG) { return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, logger); } return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, System.out); }
3.2.4创建ApplicationContext

protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() { Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass; if (contextClass == null) { try { switch (this.webApplicationType) { case SERVLET: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); break; case REACTIVE: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); break; default: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex); } } return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); }
3.2.5从spring.factories中读取出类型为 org.springframework.boot.SpringBootExceptionReporter 对应的类。然后创建类的实例
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
3.2.6遍历调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的contextPrepared()方法,同时将之前通过@EnableAutoConfiguration获取的所有配置以及其他形式的IoC容器配置加载到已经准备完毕的ApplicationContext,然后遍历调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的contextLoaded()方法

private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) { context.setEnvironment(environment); postProcessApplicationContext(context); applyInitializers(context); listeners.contextPrepared(context); if (this.logStartupInfo) { logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null); logStartupProfileInfo(context); } // Add boot specific singleton beans ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments); if (printedBanner != null) { beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner); } if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) { ((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory) .setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding); } if (this.lazyInitialization) { context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor()); } // Load the sources Set<Object> sources = getAllSources(); Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty"); load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0])); listeners.contextLoaded(context); }
3.2.7注册ShutdownHook以便在JVM停止时优雅退出。调用ApplicationContext的refresh()方法,完成IoC容器可用的最后一道工序

private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { if (this.registerShutdownHook) { try { context.registerShutdownHook(); } catch (AccessControlException ex) { // Not allowed in some environments. } } refresh((ApplicationContext) context); }
3.2.8 查找当前ApplicationContext中是否注册有CommandLineRunner,如果有,则遍历执行它们

private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) { List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>(); runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values()); runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values()); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners); for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) { if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) { callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args); } if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) { callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args); } } }
SpringBoot(一)原理剖析:SpringApplication启动原理
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/ryjJava/p/14425462.html