1、properties类
properties是hashtable的子类,map集合中的方法都可以用
该类没有泛型,键值都是以字符串的形式存在
可以是一个属性集,也可以存储在持久化设备上
有和流相关的技术相结合的方法
代码展示
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个propertise集合
Properties pro=new Properties();
//存值
pro.put("dirver", "com.oracle.jdbc.Dirver");
pro.put("user", "root");
//取值
System.out.println(pro.get("dirver"));
System.out.println(pro.getProperty("user"));
}
常用方法
load(InputStream) 是指定流所指定的文件数据读取出来放在properties类中
load(reader)与上述一致
store(OutputStream,commonts)把集合中的数据写入到指定流所对应的文件,以及描述,描述如果没有也得写个空字符串,必须写
stroe(Writer,comments)与上述一致
代码展示,将指定流的文件中的数据读取出来存到properties类中
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//明确数据源
FileReader fr=new FileReader("src/com/oracle/demo02/pro.properties");
//创建pro集合
Properties pro=new Properties();
//通过load将文件中的键值对读取得到集合中
pro.load(fr);
System.out.println(pro);
}
代码展示,将集合中的数据写入到流对应的文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//明确目的地
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("src/com/oracle/demo02/pro.properties",true);
//创建pro集合
Properties pro=new Properties();
pro.put("name", "admin");
pro.put("age", "123");
//写入
pro.store(fw, "");
}
举例之前封装的JDBC工具类
首先先建一个properties文件将要经常改动的那四个属性写在里边
dirver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java1127?characterEncoding=utf-8 user=root pwd=123456 这个文件名叫 db.properties
然后我们再在之前封装的JDBC工具类中创建一个properties集合 通过输入流,将db.properties文件中的数据读取并且存在properties集合中,再通过该集合的方法取到键的值
//获取链接对象
public static Connection getConn(){
Connection conn=null;
Properties pro=new Properties();
try {
//明确数据源
FileReader fr=new FileReader("src/com/oracle/tools/db.properties");
//将文件中的键值对读取到集合中
pro.load(fr);
//注册驱动
Class.forName(pro.getProperty("dirver"));
//获得链接对象
String url=pro.getProperty("url");
String user=pro.getProperty("user");
String pwd=pro.getProperty("pwd");
conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,pwd);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
//增删改释放资源
public static void close(Connection conn,PreparedStatement pst){
if(pst!=null){
try {
pst.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//查询释放资源
public static void close(Connection conn,PreparedStatement pst,ResultSet rs){
if(rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(pst!=null){
try {
pst.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=getConn();
System.out.println(conn);
}
2、序列化流,反序列化流
图解
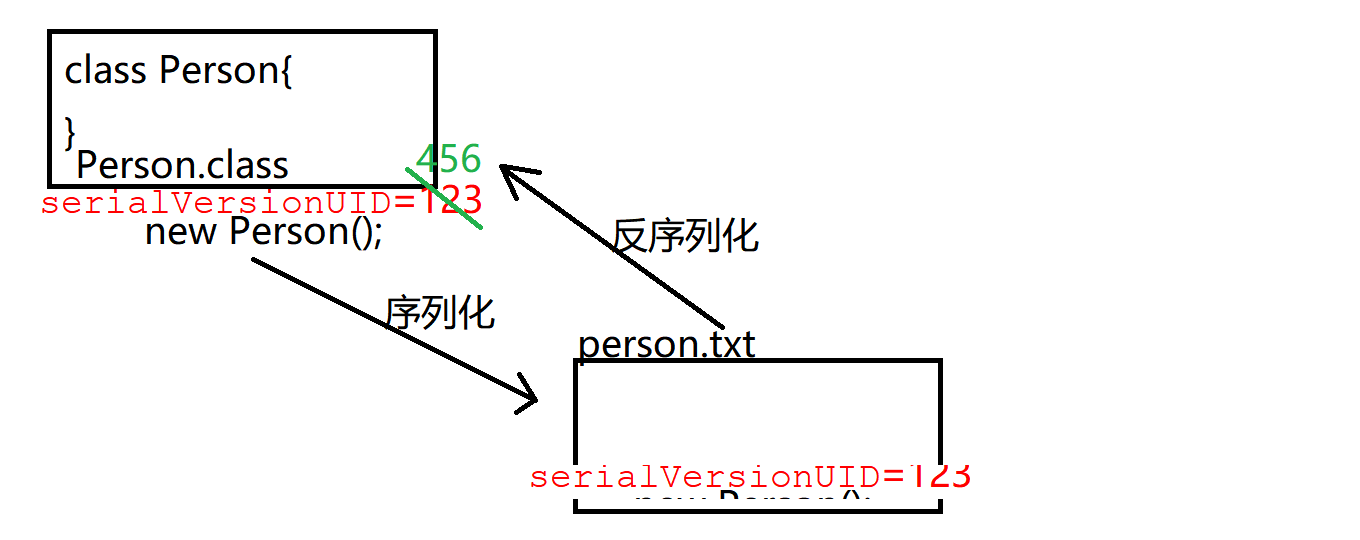
序列化流和反序列化流 是基于对象的操作,可以将对象写入文件,也可以从文件中读取对象(并不是只能new 才能创建对象,反序列化流也能得到一个类对象)
序列化流构造方法
ObjectOutPutStream(OutPutStream out)
常用方法
writeObject(Object obj)
反序列化流构造方法
ObjectInputStream(InputStream in)
常用方法
readObject()返回值是object类型
我们对对象进行操作的时候,那我们创建的这个实体类需要开启被序列化的功能 否则将不会被序列化,这时就用到了Serializable接口,必须实现这个接口才可以
代码展示
写入(序列化)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//明确目的地
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("F:\\io1127\\person.txt");
//创建序列化liuw
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
//创建对象
Person p=new Person("小红帽",18);
//写入
oos.writeObject(p);
//释放资源
oos.close();
}
读取(反序列化)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//明确数据源
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("F:\\io1127\\person.txt");
//创建反序列化
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis);
//读取
Object obj=ois.readObject();
System.out.println(obj);
ois.close();
}
类
public class Person implements Serializable{
private transient String name;
public static int age;
public static final long serialVersionUID=100L;
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {
super();
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
如果我们序列化和反序列化之后,我们对其class文件进行修改,那么我们再进行反序列化时,就会发生异常,发生原因有,版本号不匹配,该类中包含了未知的数据,访问了无参构造
那么如果版本号不匹配 我们可以定死版本号,例如上述代码中的public static final long serialVersionUID=100L;我们将版本号写死,那我们再修改然后编译的时候版本号就不会再变了
如果我们存在不想要被序列化的属性,那我们可以在其属性前加一个static关键字,因为被static关键字修饰的属性属于类,而不再属于属性,所以就不会被序列化,也可以用transient关键字修饰就不会被序列化了。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/-gongxue/p/14456881.html