Hern\(\‘{a}\)n M. and Robins J. Causal Inference: What If.
上一节介绍了modification, 这一节介绍一个类似的概念, interaction.
5.1 Interaction requires a joint intervention
之前都仅仅涉及了一个intervention (treatment) \(A\), 这里再引入另一个因素\(E \in \{0, 1\}\).
则, 此时\(Y^{a, e}\)有四种可能性:
\[Y^{0, 0},
Y^{0, 1},
Y^{1, 0},
Y^{1, 1}.
\]
则我们称intervention \(A\)与\(E\)之间存在interaction, 若
\[\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a=1,e=1}=1]
-
\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a=0,e=1}=1]
\not =
\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a=1,e=0}=1]
-
\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a=0,e=0}=1],
\]
即, \(A\)关于\(Y\)的causal effect 在set不同的\(E=e\)的时候不同.
注: 这是一个对称的概念.
5.2 Identifying interaction
当\(Y^{a, e}\)与\(E\)独立的时候, 即
\[\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a,e}]
=
\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a,e}|E=e]
=
\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a}|E=e].
\]
此时可以发现, interaction 和 上一节所介绍的modification是一致的.
5.3 Counterfactual response types and interactions
所有的人都只有如下四种情况
\[\begin{array}{ccc}
Type & Y^{a=0} & Y^{a=1} \Doomed & 1 & 1 \Helped & 1 & 0 \Hurt & 0 & 1 \Immune & 0 & 0 \\end{array}
\]
对于被诅咒的或者免疫的人来说, 是否治疗是不改变结果的, 而对于helped 或者 hurt 的实际上才是causal effect所影响的东西.
这些type称之为response type.
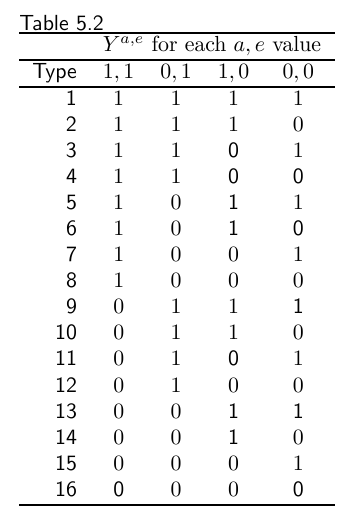
关于\(A\), \(E\)则总共有16种response types.
可以发现, interaction若想要发生, 则至少2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15中的一种发生.
5.4 Sufficient causes
此以及后面的都是讲另一套体系的, 就是研究什么因素必能推演出某个结果.
5.5 Sufficient cause interaction
5.6 Counterfactual or sufficient-component causes?
Fine Point
More on counterfactual types and interaction
From counterfactuals to sufficient-component causes, and vice versa.
Biologic interaction
More on the attribution fraction
Technical Point
Interaction on the additive and multiplicative scales
就是interaction的判定条件还可以改写为
\[\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a=1,e=1}=1]
-
\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a=0,e=0}=1]
=
\{
\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a=1,e=0}=1]
-
\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a=0,e=0}=1]
\}
+
\{
\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a=0,e=1}=1]
-
\mathrm{Pr}[Y^{a=0,e=0}=1]
\}
\]
以及相应的multiplicative的条件.
Monotonicity of causal effects
什么情况下\(Y^{a=1} \ge Y^{a=0}\)恒成立?
即不存在有人属于Helped type.
Monotonicity of causal effects and sufficient causes
Chapter 5 Interaction
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/MTandHJ/p/14458880.html
