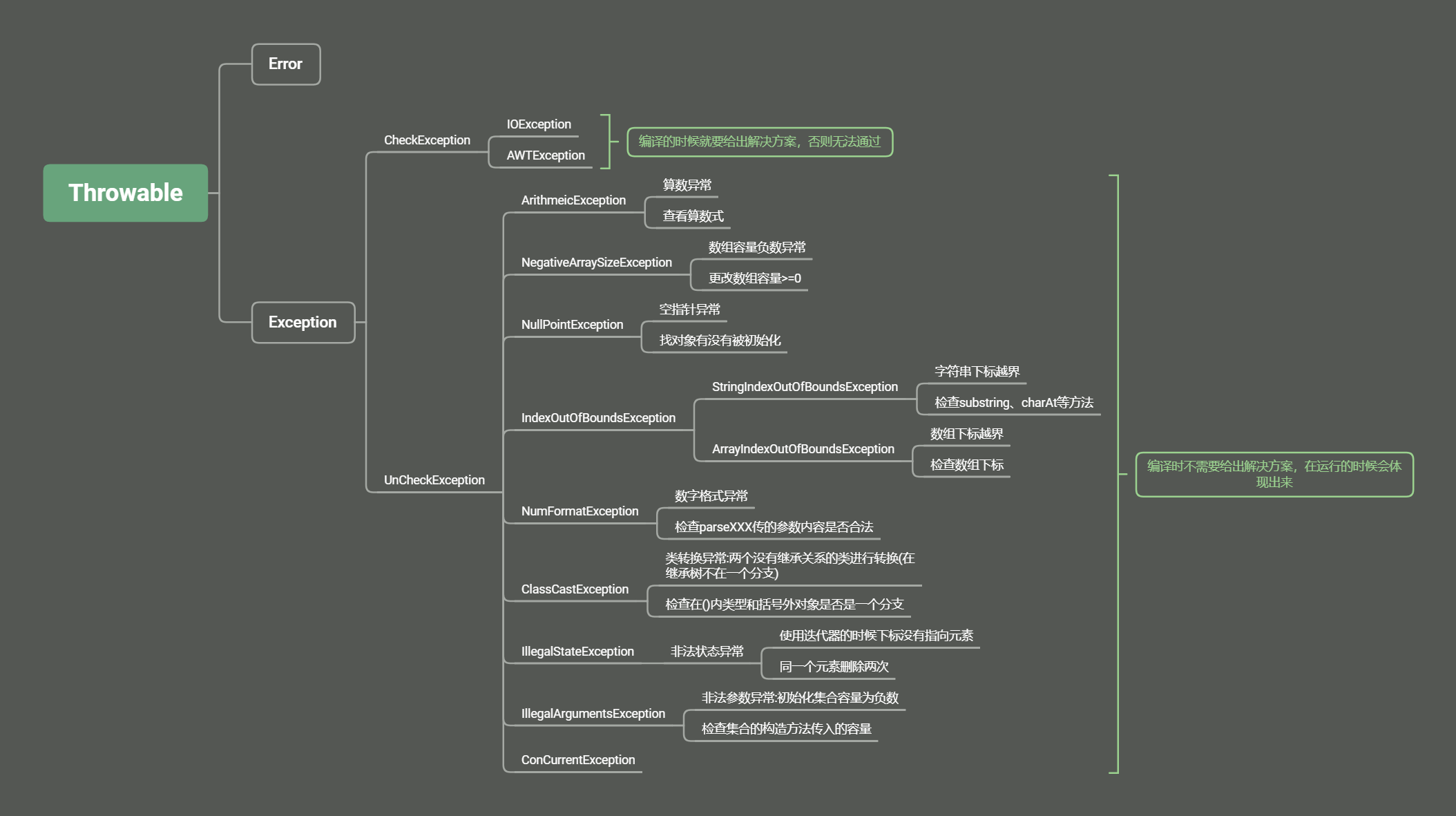
a-非运行时异常必须在运行前(编译时)给出解决方案,否则无法继续运行
b-一旦程序运行中出现异常,程序员没有处理,程序就会中断执行
throws(能解决a、不能解决b)
try{
出现异常的语句,一般只要出异常的那一句
}catch(捕获的异常){ //可以有多个catch语句,但要保证从"上往下平级或逐渐变大" ,JDK7.0开始出现多个分支时可以用 | 隔开
// 处理方式1:不处理,空
// 处理方式2:简单打印 e.getMessage()
// 处理方式3:详细处理 e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//无论有没有异常都要走这一步
//finally当中永远不应该出现return语句,否则咱们try和catch当中的return就都失去作用了
//在try(异常出现前)和catch中用System.exit(int)可跳过finally
}
throw 用在方法体当中 在本没有异常的情况下
主动制造异常出现的情况 [没事找事型]
public class Test1{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{
getInfo();
}
public static void getInfo()throws Exception{
throw new Exception("哎呀,我出现异常了");
}
}
throws 用在方法签名的最后 表达的是 本方法中出现指定种类的异常
? 方法当中不做处理 抛还给调用的上级进行处理 [有事甩锅型]
public class Test1{
public static void main(String[] args)throws MyException{
getInfo();
}
public static void getInfo()throws MyException{
throw new MyException();
}
}
class MyException extends Exception{
public MyException(){
super("哎呀我出现自定义的异常了");
}
}
class A{//扩展1:当静态变量使用可能有异常的静态方法时,可用静态代码块进行异常捕获
static int num;
static{
try{
num=getNum();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static int getNum()throws Exception{
int num=(int)(Math.random()*5);
if(num%2==0)
throw new Exception("这个数字不吉利");
return num;
}
}
public static int getLuckeyNum(){//try-catch语句中能消亡变量,应该先把变量定义在try外部,在try中只进行赋值操作
int num=0;
try{
num=(int)(Math.random()*5);
}catch(Exception e){}
return num;
}
public class Exec5{
public static void main(String[] args){
SLT s1=new SLT();
SLT s2=new SLT();
SLT s3=new SLT();
try{
s1.close();
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
//e.printStackTrace();
return;
}finally{
try{
s2.close();
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
//e.printStackTrace();
return;
}finally{
try{
s3.close();
}catch(Exception e){
//e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
return;
}
}
}
}
}
class SLT{
public void close()throws Exception{
int num=(int)(Math.random()*2);
if(num==0)
throw new Exception("水龙头拧坏了");
System.out.println("水龙头已经成功关闭了");
}
}
//try-catch代替if判断
public static boolean isNumber(String str){
try{
Integer.parseInt(str);
return true;
}catch(Exception e){
return false;
}
}
? 你要明白 其实这里的异常指的是 非运行时异常
? 所有的运行时异常 默认都被抛出
? Java当中每一个方法相当于都有一行throws RuntimeException
? 如果坏蛋问你:
? 父类的方法没有异常声明 子类在覆盖这个方法的时候 能抛异常吗?
? 能 但是只能声明抛出各种运行时异常,而这样的行为是没有意义的 ,因为每个方法默认就抛出所有运行会异常
class A{
public void get(){//每个方法后满默认是 throws RuntimeException()
System.out.println("这是父类的get方法");
}
}
class B extends A{
@Override
public void get() throws NullPointerException,IndexOutOfBoundsException{//这里可以抛运行时异常的子类
System.out.println("这是子类的get方法");
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/gxh299988/p/14471868.html