<dependencies>
<!--servlet依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--jsp依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.22</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--configuration核心配置文件-->
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
</configuration>
package com.lee.utils;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class mybatisUtils {
//第一步:使用mybatis获取sqlsessionfactory对象
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
static {
try {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputstream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputstream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//第二步:既然有了 SqlSessionFactory,顾名思义,我们可以从中获得 SqlSession 的实例。
// SqlSession 提供了在数据库执行 SQL 命令所需的所有方法。
public static SqlSession getSqlsession()
{
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
}
package com.lee.pojo;
public class User {
public User(int id, String name, String pwd) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
private int id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
}
Dao接口
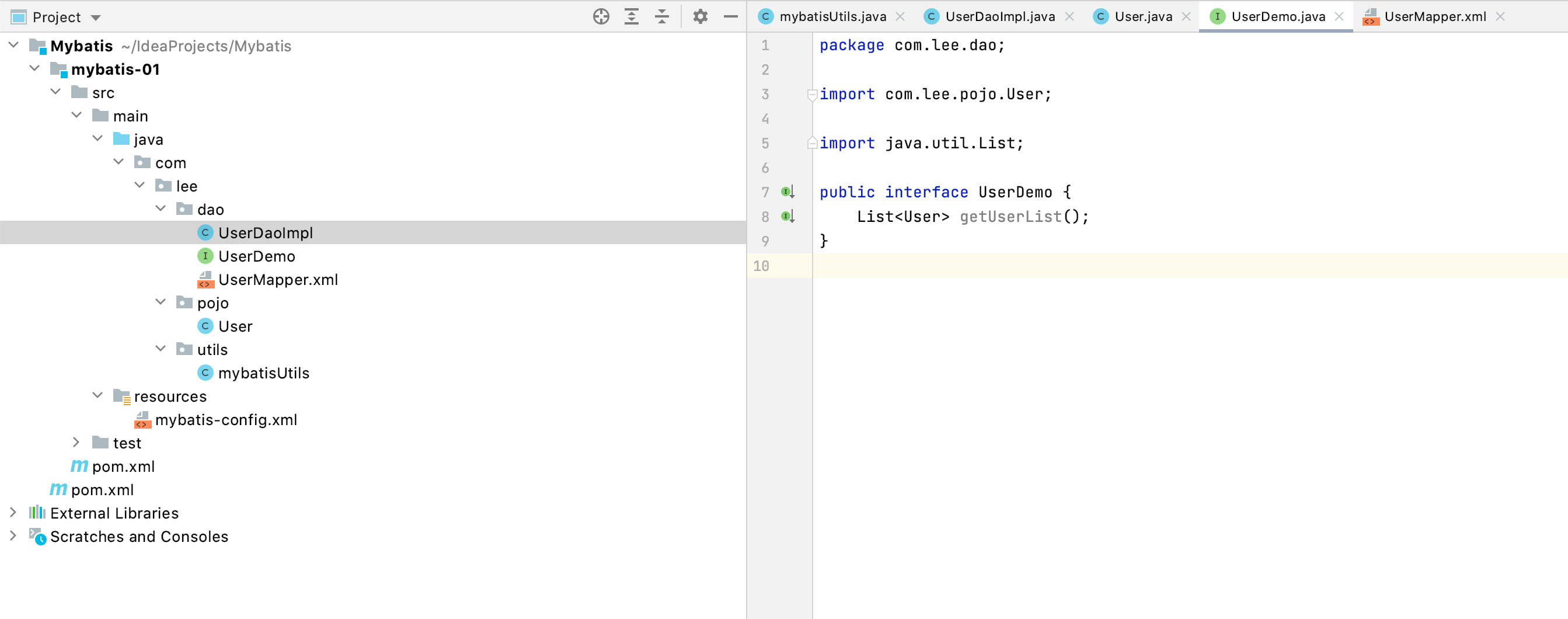
接口实现类
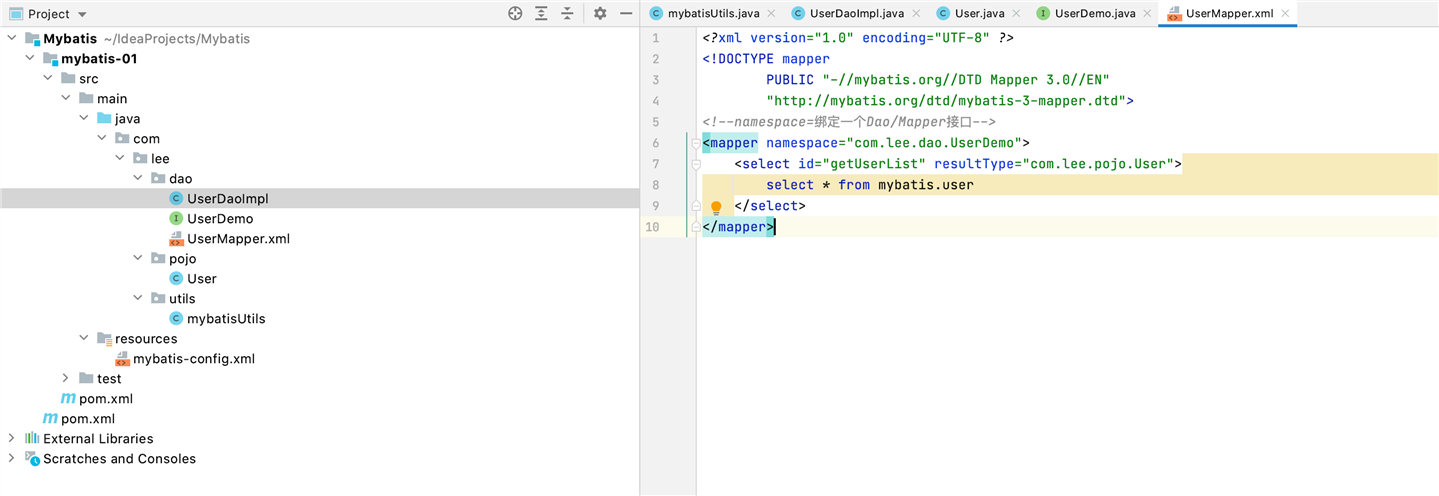
注意点:错误Type interface com.lee.dao.UserMapper is not known to the MapperRegistry.
<environments default="development"> <!--默认选择的ID-->
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"> <!--mybatis默认事务管理器-JDBC-->
<property name="..." value="..."/>
</transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED"> <!--mybatis默认数据源-POOLED-->
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="Author" type="domain.blog.Author"/>
<typeAlias alias="Blog" type="domain.blog.Blog"/>
<typeAlias alias="Comment" type="domain.blog.Comment"/>
<typeAlias alias="Post" type="domain.blog.Post"/>
<typeAlias alias="Section" type="domain.blog.Section"/>
<typeAlias alias="Tag" type="domain.blog.Tag"/>
</typeAliases>
- 也可以指定一个包名,MyBatis 会在包名下面搜索需要的 Java Bean;每一个在包中的 Java Bean,在没有注解的情况下,会使用 Bean 的首字母小写的非限定类名来作为它的别名。比如 domain.blog.Author 的别名为 author.
例如:
<typeAliases>
<package name="domain.blog"/>
</typeAliases>
目前只需要挑重点记忆
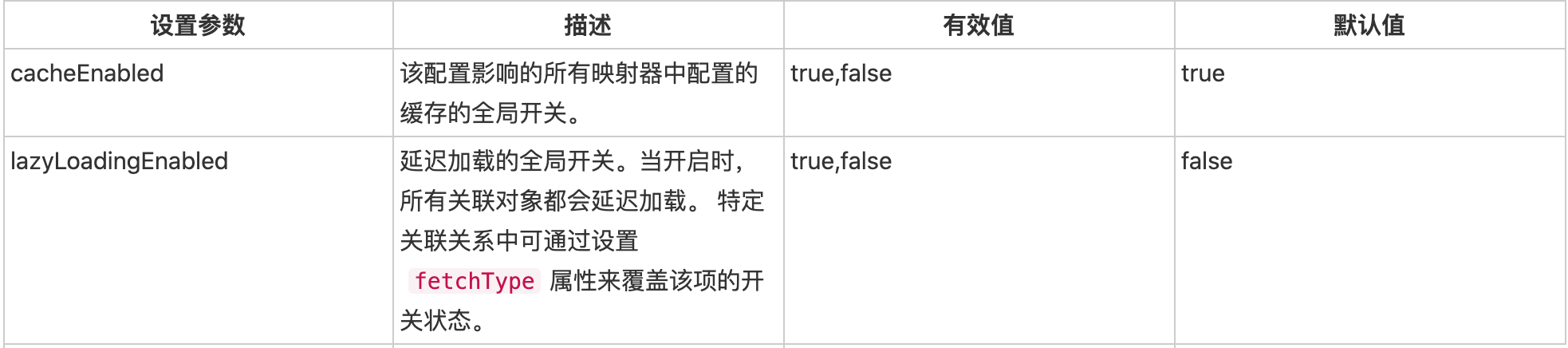

一个配置完整的 settings 元素的示例如下:
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true"/>
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="false"/>
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL"/>
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE"/>
<setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="25"/>
<setting name="safeRowBoundsEnabled" value="false"/>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="false"/>
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/>
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="OTHER"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="equals,clone,hashCode,toString"/>
</settings>
理解我们之前讨论过的不同作用域和生命周期类别是至关重要的,因为错误的使用会导致非常严重的并发问题。
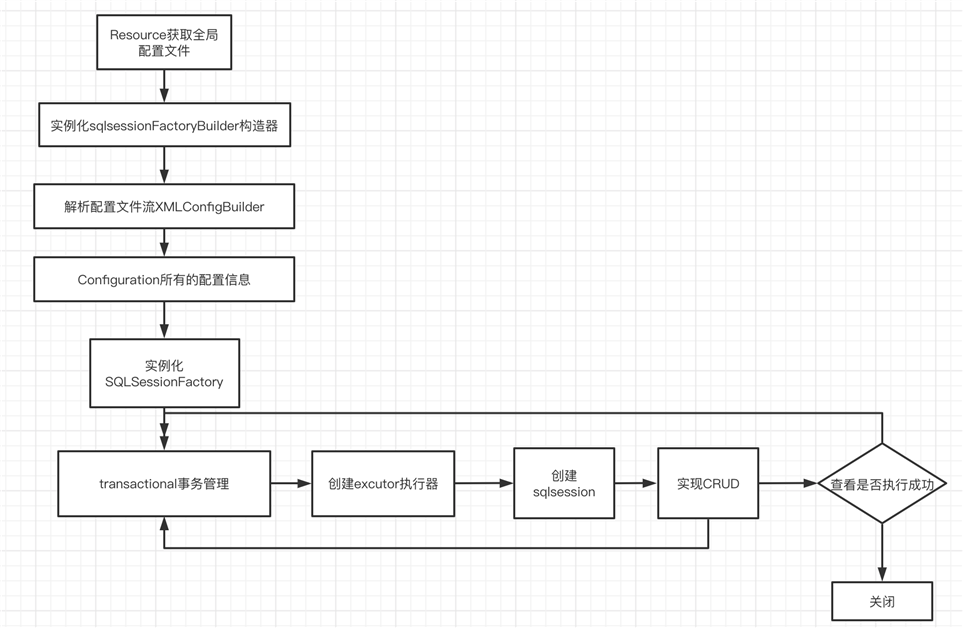
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
SqlSessionFactory
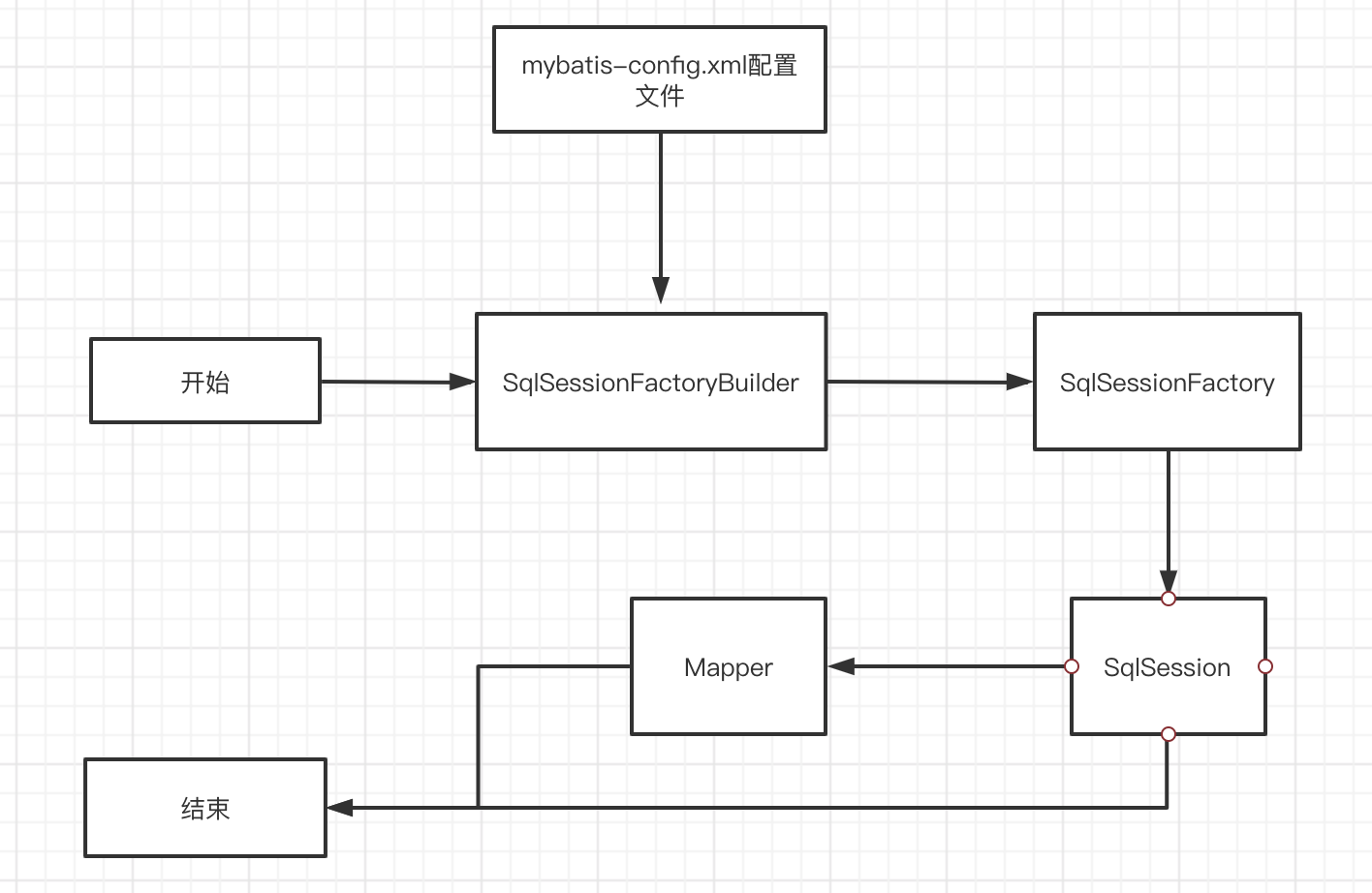

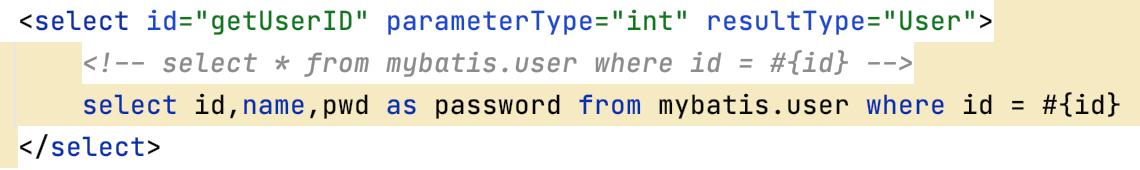
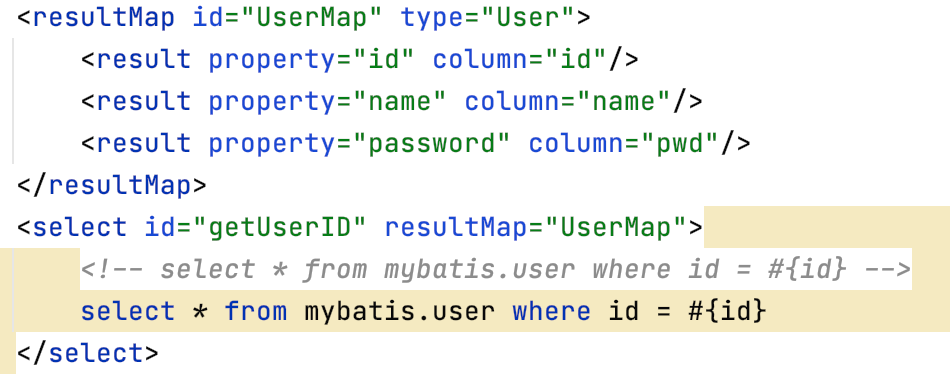
如果一个数据库操作出现了异常,我们需要拍错,日志就是最好的帮手。

<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
#将等级为DEBUG的日志信息输出到console和file这两个目的地,console和file的定义在下面的代码
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG,console,file
#控制台输出的相关设置
log4j.appender.console = org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.Target = System.out
log4j.appender.console.Threshold=DEBUG
log4j.appender.console.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=[%c]-%m%n
#文件输出的相关设置
log4j.appender.file = org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.file.File=./log/lee.log
log4j.appender.file.MaxFileSize=10mb
log4j.appender.file.Threshold=DEBUG
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=[%p][%d{yy-MM-dd}][%c]%m%n
#日志输出级别
log4j.logger.org.mybatis=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl"value="LOG4J"/>
</settings>

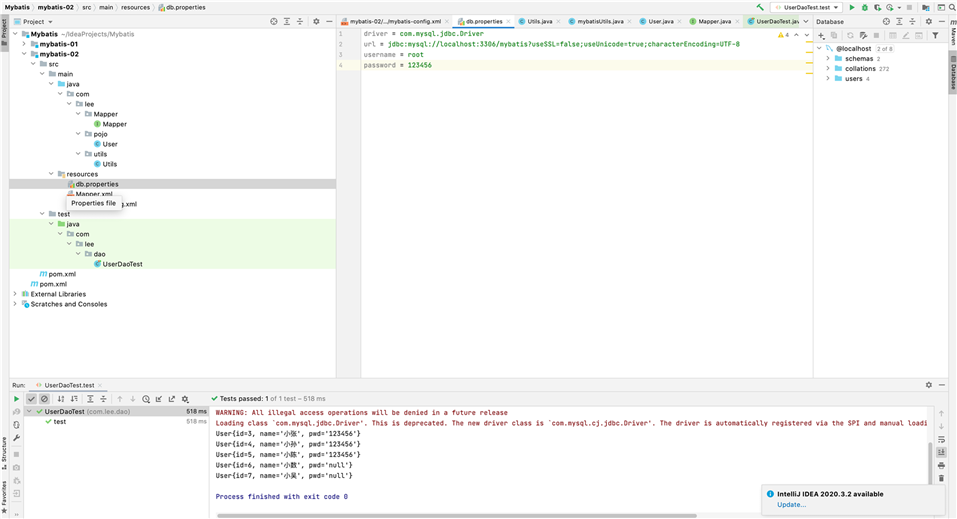
为什么要分页?
select * from user startindex,pageSize
接口

Mapper.xml配置文件

测试

@Getter/@Setter: 作用类上,生成所有成员变量的getter/setter方法;作用于成员变量上,生成该成员变量的getter/setter方法。可以设定访问权限及是否懒加载等。
@Getter @Setter private boolean funny;
@ToString:作用于类,覆盖默认的toString()方法,可以通过of属性限定显示某些字段,通过exclude属性排除某些字段。
@EqualsAndHashCode:作用于类,覆盖默认的equals和hashCode
@NonNull:主要作用于成员变量和参数中,标识不能为空,否则抛出空指针异常。
@NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor, @AllArgsConstructor:作用于类上,用于生成构造函数。有staticName、access等属性。
staticName属性一旦设定,将采用静态方法的方式生成实例,access属性可以限定访问权限。
@NoArgsConstructor:生成无参构造器;
@RequiredArgsConstructor:生成包含final和@NonNull注解的成员变量的构造器;
@AllArgsConstructor:生成全参构造器
@Data:作用于类上,是以下注解的集合:@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode @Getter @Setter
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Builder:作用于类上,将类转变为建造者模式
@Log:作用于类上,生成日志变量。针对不同的日志实现产品,有不同的注解:
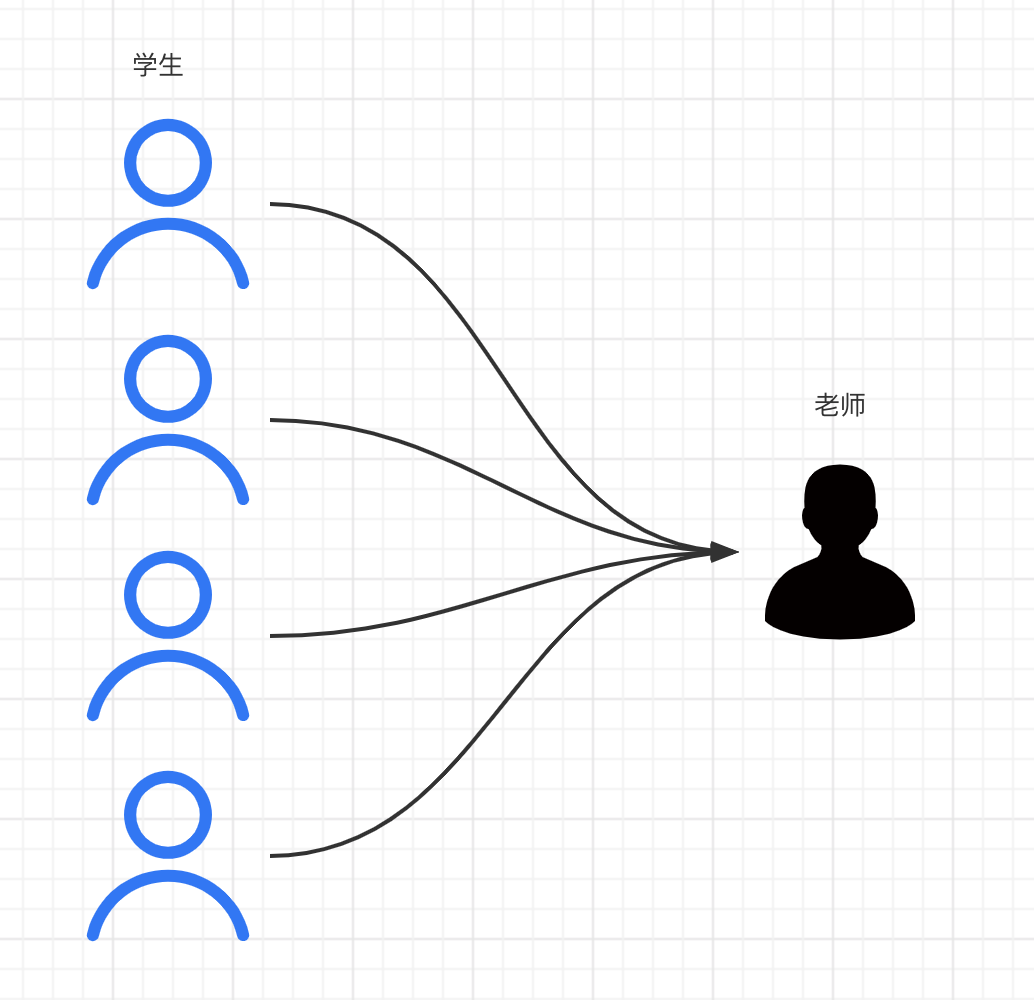
<!--
思路:按照查询嵌套处理
1.查询所以学生信息
2.根据查询出来的学生tid查询对应的老师!子查询
-->
<select id="getStudent" resultMap="Student">
select * from mybatis.student;
</select>
<resultMap id="Student" type="Student">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<association property="teacher" column="tid" javaType="Teacher" select="getTeacher"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getTeacher" resultType="Teacher">
select * from teacher where id=#{id};
</select>
<!--2
思路:按照结果嵌套处理
-->
<select id="getStudent" resultMap="Student">
select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname
from student s,teacher t
where s.tid=t.id;
</select>
<resultMap id="Student" type="Student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher">
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
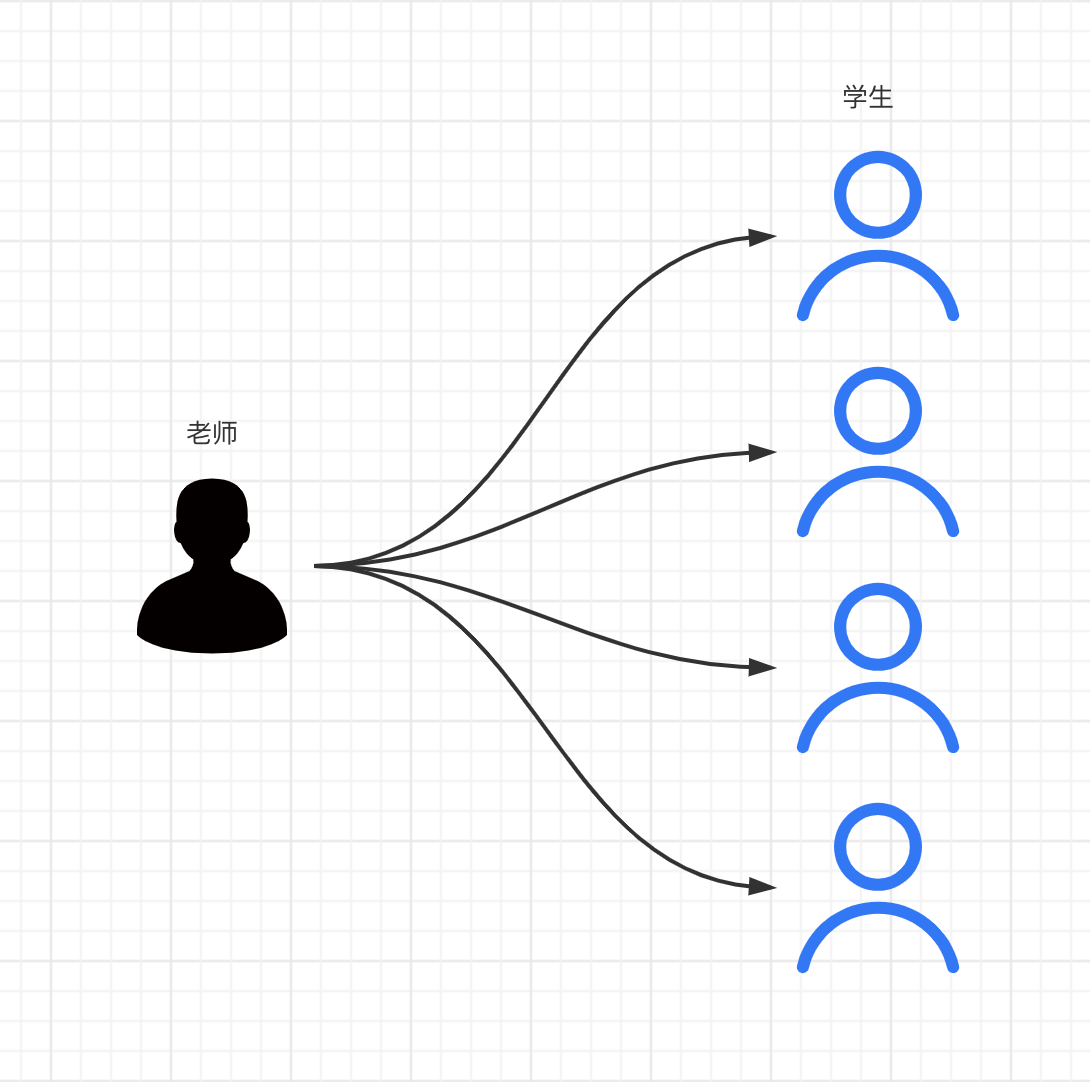
<select id="getTeacher" resultMap="Teacher">
select s.id sid,s.name sname,s.tid stid,t.id tid,t.name tname
from student s,teacher t
where s.tid=t.id and t.id=#{tid};
</select>
<resultMap id="Teacher" type="Teacher">
<result property="id" column="tid"/>
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
<collection property="students" ofType="Student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="tid" column="tid"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
小结
什么是动态SQL?
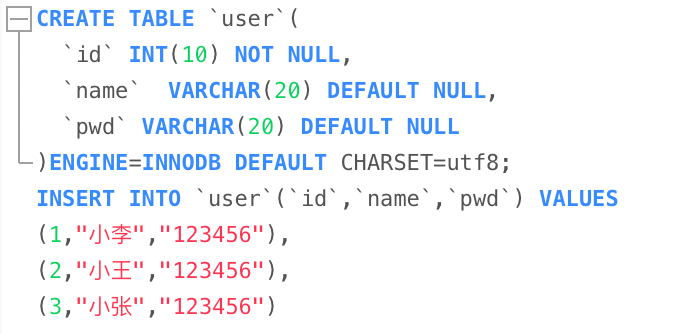
CREATE TABLE `blog`(
`id` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT ‘博客id‘,
`title` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL COMMENT ‘博客标题‘,
`author` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT ‘博客作者‘,
`create_time` DATETIME NOT NULL COMMENT ‘创建时间‘,
`views` INT(30) NOT NULL COMMENT ‘浏览量‘
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--configuration核心配置文件-->
<configuration>
<!--引入外部配置文件-->
<properties resource="db.properties"/>
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.lee.pojo.Teacher" alias="Teacher"/>
<typeAlias type="com.lee.pojo.Student" alias="Student"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="StudentMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="TeacherMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
package com.lee.Utils;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class Utils {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
static{
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
try {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
}
package com.lee.pojo;
import java.util.Date;
public class Blog {
private String id;
private String title;
private String author;
private Date createTime;
private int views;
}
动态 SQL 通常要做的事情是有条件地包含 where 子句的一部分。比如:
<select id="getBlogIF" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from mybatis.blog
where 1=1
<if test="title != null">
and title=#{title}
</if>
</select> <!--if语句-->
这条语句提供了一个可选的文本查找类型的功能。如果没有传入"title",那么所有处于"ACTIVE"状态的BLOG都会返回;反之若传入了"title",那么就会把模糊查找"title"内容的BLOG结果返回(就这个例子而言,细心的读者会发现其中的参数值是可以包含一些掩码或通配符的)。
where 元素知道只有在一个以上的if条件有值的情况下才去插入"WHERE"子句。而且,若最后的内容是"AND"或"OR"开头的,where 元素也知道如何将他们去除。
也就是说如果有如果一个以上的if条件有值的情况下,它不会去除"AND"或"OR",如果如果有多个if语句,但只有第一个语句有值的情况下,它将会省略后面的"AND"或"OR",这样则避免了后面if语句因为没有值而出错的可能。
<where>
<if test="title != null">
title=#{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</if>
</where>
有些时候,我们不想用到所有的条件语句,而只想从中择其一二。针对这种情况,MyBatis 提供了 choose 元素,它有点像 Java 中的 switch 语句。
还是上面的例子,但是这次变为提供了"title"就按"title"查找,提供了"author"就按"author"查找,若两者都没有提供,就返回所有符合条件的BLOG(实际情况可能是由管理员按一定策略选出BLOG列表,而不是返回大量无意义的随机结果)。
<select id="getBlogIF" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<choose>
<when test="title!=null">
title=#{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null">
author = #{author}
</when>
<when test="views !=null">
views = #{views}
</when>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
有时候我们可能需要将一些公共的部分抽取出来,方便复用
<sql id="sql_when">
<choose>
<when test="title!=null">
title=#{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null">
author = #{author}
</when>
<when test="views !=null">
views = #{views}
</when>
</choose>
</sql>
2 在需要的地方使用include标签进行插入
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<include refid="sql_when"/>
</where>
</select>
注意:最好基于单表定义SQL片段
foreach 元素的功能是非常强大的,它允许你指定一个集合,声明可以用在元素体内的集合项和索引变量。它也允许你指定开闭匹配的字符串以及在迭代中间放置分隔符。这个元素是很智能的,因此它不会偶然地附加多余的分隔符。
<select id="queryBlogForeach" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from mybatis.blog
where id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="(" close=")" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</select>
SqlSession sqlSession = Utils.getSqlSession();
BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Blog blog1=mapper.getBlog(1);
System.out.println(blog1);
Blog blog2=mapper.getBlog(1);
System.out.println(blog2);
sqlSession.close();
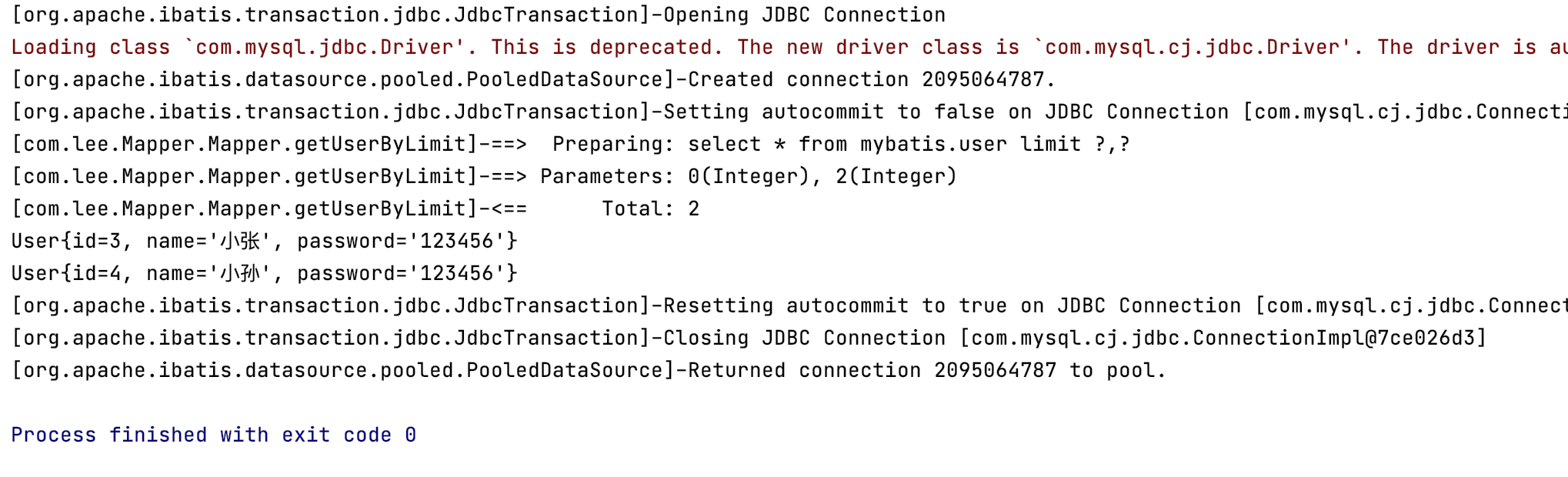
结果: 查询相同数据两次只连接了一次数据库。第二次查询是从缓存当中查询。可以分析日志的到。
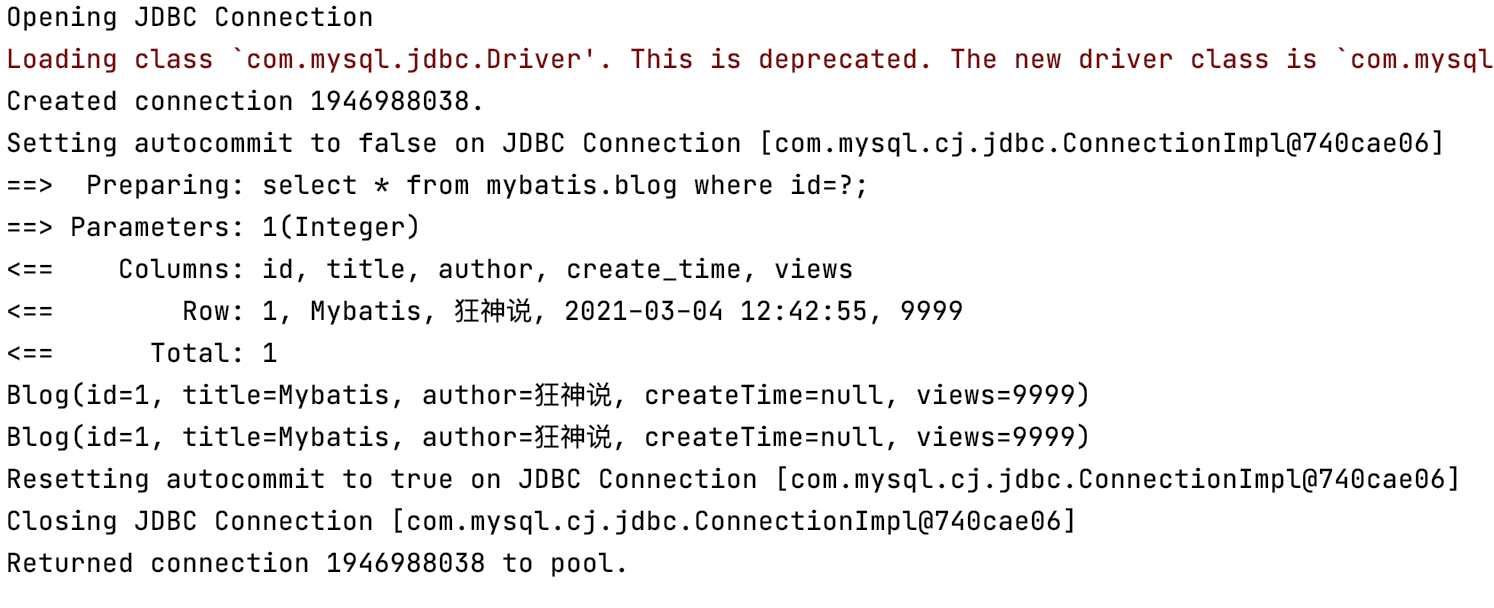
小结:一级缓存默认是开启的,只在一次sqlsession中有效,也就是拿到连接到关闭连接!
二级缓存也叫全局缓存,因为一级缓存作用域太低了,所以就有了二级缓存,它是基于namespace级别的缓存,一个名称空间对应一个二级缓存。


原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Jeson-Sun/p/14490490.html