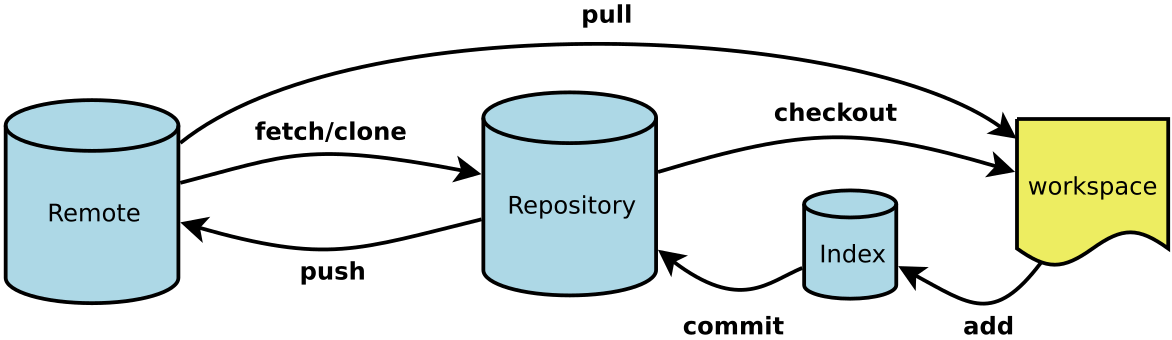
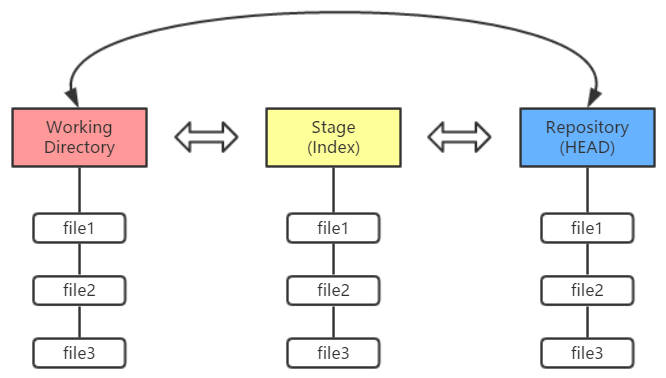
首先:关联“远程库”
git remote add [起一个名字,默认为origin] [你的远程库地址,eg:github地址]
SYNOPSIS
git remote [-v | --verbose]
//查看远程库有哪些,-v | --verbose 列出详细信息,在每一个名字后面列出其远程url
git remote add [-t <branch>] [-m <master>] [-f] [--[no-]tags] [--mirror=<fetch|push>] <name> <url>
git remote rename <old> <new>
//更改远程库的名字,eg: origin--->origin2
git remote remove <name>
//移除远程库
git remote set-head <name> (-a | -d | <branch>)
//
git remote set-branches [--add] <name> <branch>...
git remote set-url [--push] <name> <newurl> [<oldurl>]
git remote set-url --add [--push] <name> <newurl>
git remote set-url --delete [--push] <name> <url>
git remote [-v | --verbose] show [-n] <name>...
//显示远程仓库name的详细信息
git remote prune [-n | --dry-run] <name>...
在你经常使用的命令当中有一个git remote -v show 用来查看所有的分支,包括本地和远程的。但是时间长了你会发现有些分支在远程其实早就被删除了,但是在你本地依然可以看见这些被删除的分支。git remote prune 移除这个分支(也就是说你可以刷新本地仓库与远程仓库的保持这些改动的同步,清除本地缓存)
git remote [-v | --verbose] update [-p | --prune] [(<group> | <remote>)...]
有时会遇到git branch -a时总是不出现新的分支或者远程已经没有的分支在本地还有,这时就需要更新下本地的git分支保持和远程分支一致,使用下面命令即可:
# git remote update origin --prune
用法:
git push <远程主机名><本地分支名>:<远端分支名>
git push origin master
如果远程分支被省略,如上则表示将本地分支推送到与之存在追踪关系的远程分支(通常两者同名),如果该远程分支不存在,则会被新建
git push origin :master
如果省略本地分支名,则表示删除指定的远程分支,因为这等同于推送一个空的本地分支到远程分支,等同于 git push origin --delete master
git push origin
如果当前分支与远程分支存在追踪关系,则本地分支和远程分支都可以省略,将当前分支推送到origin主机的对应分支
git push --all origin
将本地的所有分支都推送到远程主机,当遇到这种情况就是不管是否存在对应的远程分支,这时需要 -all 选项
git push --force origin
git push的时候需要本地先git pull更新到跟服务器版本一致,如果本地版本库比远程服务器上的低,那么一般会提示你git pull更新,如果一定要提交,那么可以使用这个命令。
? 当前有2个分支master和dev2,当执行git clone的时候会clone下来远程分支到本地远程分支,并且默认本地分支显示master分支,使用git branche可以看到的本地分支只有master,git branch -r可以看到远程2个分支。当使用git checkout dev2 的时候,就会把本地远程分支加入到本地分支中,使用git branch就可以看到本地有2个分支。
[root@VM-0-4-centos _data]# git fetch -h
usage:
git fetch [<options>] [<repository> [<refspec>...]]
or: git fetch [<options>] <group>
or: git fetch --multiple [<options>] [(<repository> | <group>)...]
or: git fetch --all [<options>]
-v, --verbose be more verbose
-q, --quiet be more quiet
--all fetch from all remotes
-a, --append append to .git/FETCH_HEAD instead of overwriting
--upload-pack <path> path to upload pack on remote end
-f, --force force overwrite of local branch
-m, --multiple fetch from multiple remotes
-t, --tags fetch all tags and associated objects
-n do not fetch all tags (--no-tags)
-p, --prune prune remote-tracking branches no longer on remote
--recurse-submodules[=<on-demand>]
control recursive fetching of submodules
--dry-run dry run
-k, --keep keep downloaded pack
-u, --update-head-ok allow updating of HEAD ref
--progress force progress reporting
--depth <depth> deepen history of shallow clone
--unshallow convert to a complete repository
git fetch
一旦远程主机的版本库有了更新(Git术语叫做commit),需要将这些更新取回本地,这时就要用到git fetch命令。
$ git fetch <远程主机名>
上面命令将某个远程主机的更新,全部取回本地。
git fetch命令通常用来查看其他人的进程,因为它取回的代码对你本地的开发代码没有影响。
默认情况下,git fetch取回所有分支(branch)的更新。如果只想取回特定分支的更新,可以指定分支名。
$ git fetch <远程主机名> <分支名>
比如,取回origin主机的master分支。
$ git fetch origin master
所取回的更新,在本地主机上要用"远程主机名/分支名"的形式读取。比如origin主机的master,就要用origin/master读取。
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「YPL_ZML」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/YPL_ZML/article/details/90781737
git branch命令的-r选项,可以用来查看远程分支,-a选项查看所有分支。
usage: git clone [options] [--] <repo> [<dir>]
-v, --verbose be more verbose
-q, --quiet be more quiet
--progress force progress reporting
-n, --no-checkout don‘t create a checkout
--bare create a bare repository
--mirror create a mirror repository (implies bare)
-l, --local to clone from a local repository
--no-hardlinks don‘t use local hardlinks, always copy
-s, --shared setup as shared repository
--recursive initialize submodules in the clone
--recurse-submodules initialize submodules in the clone
--template <template-directory>
directory from which templates will be used
--reference <repo> reference repository
-o, --origin <name> use <name> instead of ‘origin‘ to track upstream
-b, --branch <branch>
checkout <branch> instead of the remote‘s HEAD
-u, --upload-pack <path>
path to git-upload-pack on the remote
--depth <depth> create a shallow clone of that depth
--single-branch clone only one branch, HEAD or --branch
--separate-git-dir <gitdir>
separate git dir from working tree
-c, --config <key=value>
set config inside the new repository
git clone git@?/xxx.git 会在当前目录下创建一个xxx目录,xxx/.git是本地仓库,clone 完毕一般需要接一句 cd xxx 进入当前项目
git clone git@?/xxx.git yyy 会在当前目录下创建一个 yyy 目录,clone 完毕一般需要接一句 cd yyy 进入当前项目
git clone git@?/xxx.git . 最后一个字符是点,注意有空格,不会新建目录,使用当前目录容纳代码和 .git,当前目录一开始最好是个空目录
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「yingjieweb」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Marker__/article/details/105710471
git checkout -h
usage: git checkout [options] <branch>
or: git checkout [options] [<branch>] -- <file>...
-q, --quiet suppress progress reporting
-b <branch> create and checkout a new branch
-B <branch> create/reset and checkout a branch #如果存在,就重置
-l create reflog for new branch
--detach detach the HEAD at named commit
-t, --track set upstream info for new branch
--orphan <new branch>
new unparented branch
-2, --ours checkout our version for unmerged files
-3, --theirs checkout their version for unmerged files
-f, --force force checkout (throw away local modifications)
-m, --merge perform a 3-way merge with the new branch
--overwrite-ignore update ignored files (default)
--conflict <style> conflict style (merge or diff3)
-p, --patch select hunks interactively
--ignore-skip-worktree-bits
do not limit pathspecs to sparse entries only
创建分支和切换分支,也可以称为检出分支。
A:
问题:线上分支出现了一个问题,急需要修复。
步骤:
1. 需要创建一个hotfix分支,参考语法:
git checkout -b|-B <new_branch> [<start point>]
1
实际语句:
git checkout -b hotfix-1.2.1 master
1
这个时候分支是本地分支,并没有提交到服务器上去,如果这个分支已经被创建,这个命令会失败,这个时候,如果想要重置这个分支,需要使用-B参数。
2. 查看分支:git branch -av
3. 进行修改工作
4. ……
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「IT老兵驿站」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/chaiyu2002/article/details/81086865
B:
git checkout -- <file> 拉取暂存区文件 并将其替换成工作区文件(就是工作区文件乱了,暂存区文件完好,将暂存区的东西覆盖工作区某一个文件)
usage: git merge [options] [<commit>...]
or: git merge [options] <msg> HEAD <commit>
or: git merge --abort
-n do not show a diffstat at the end of the merge
--stat show a diffstat at the end of the merge
--summary (synonym to --stat)
--log[=<n>] add (at most <n>) entries from shortlog to merge commit message
--squash create a single commit instead of doing a merge
--commit perform a commit if the merge succeeds (default)
-e, --edit edit message before committing
--ff allow fast-forward (default)
--ff-only abort if fast-forward is not possible
--rerere-autoupdate update the index with reused conflict resolution if possible
--verify-signatures Verify that the named commit has a valid GPG signature
-s, --strategy <strategy>
merge strategy to use
-X, --strategy-option <option=value>
option for selected merge strategy
-m, --message <message>
merge commit message (for a non-fast-forward merge)
-v, --verbose be more verbose
-q, --quiet be more quiet
--abort abort the current in-progress merge
--progress force progress reporting
-S, --gpg-sign[=<key id>]
GPG sign commit
--overwrite-ignore update ignored files (default)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/getonechao/p/14503014.html