有\(n\)个蹦床,每个蹦床都有一个权值\(S_{i}\),每次在蹦床上可以跳到\(i+S_{i}\)的位置,当你跳到一个蹦床上时,蹦床的权值会变成\(max(S_{i}-1,1)\),如果跳跃以后没有超出蹦床的范围,则可以继续跳跃。可以选择任意一个位置开始起跳,询问最后将蹦床的所有权值变为\(1\)的最少跳跃次数。
首先,我们从任意位置起跳都不会影响最终的结果,证明如下:
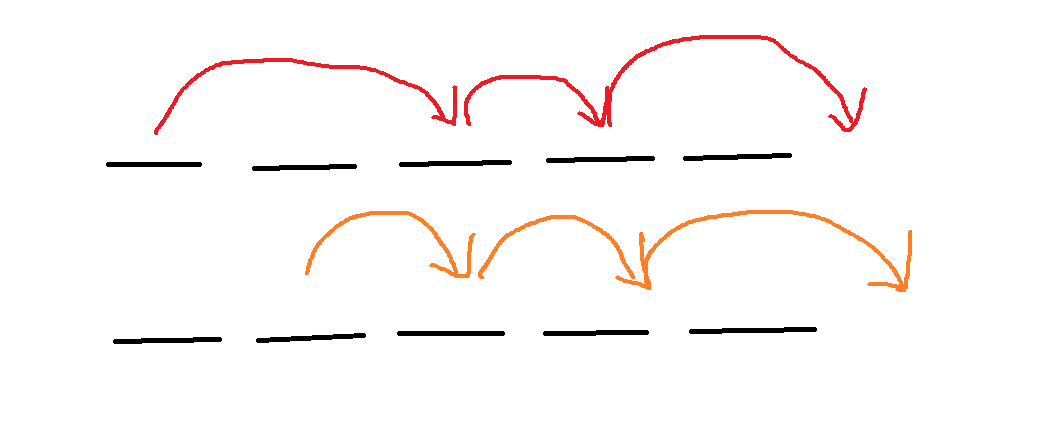
交换上下图中的第一个箭头后
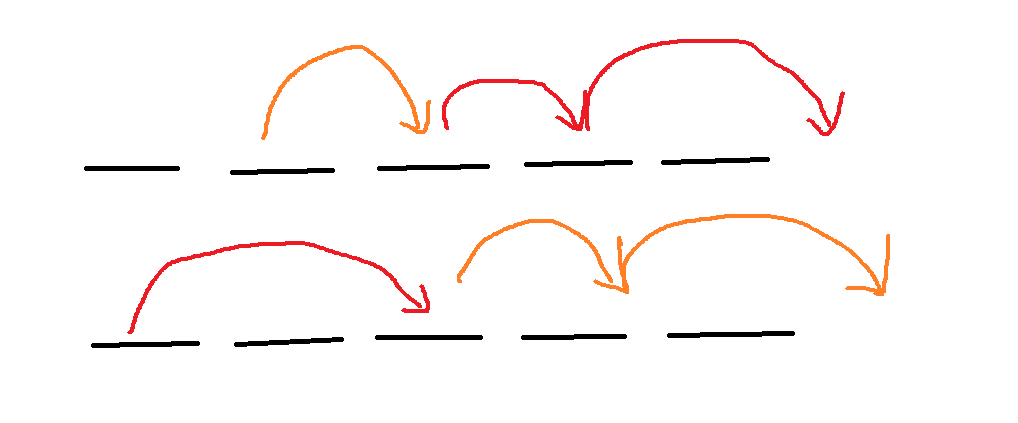
发现并不会影响结果,证毕。
由于每张蹦床的权值只能由它左边的蹦床蹦到,所以我们每次选择从左边开始权值不为\(1\)的蹦床开始跳,使用一个数组\(cnt\)来表示这个蹦床被蹦到的次数,如果\(cnt[i]>=a[i]-1\),则表示该蹦床的权值已经为\(1\),同时将多余的次数转移到下一个蹦床上。在纸上模拟后发现,每个蹦床的跳跃区间为\([i+2,min(i+a[i],n)]\),所以如果\(i+2<=n\)时,还要将跳跃区间内的\(cnt[i]\)加一。
#include "iostream"
#include "cstring"
#include "string"
#include "vector"
#include "cmath"
#include "algorithm"
#include "map"
#include "set"
#include "queue"
#include "stack"
#include "cassert"
#include "unordered_map"
#include "sstream"
#include "cstdio"
using namespace std;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define PB push_back
#define mst(x,a) memset(x,a,sizeof(x))
#define all(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define rep(x,l,u) for(ll x=l;x<u;x++)
#define rrep(x,l,u) for(ll x=l;x>=u;x--)
#define sz(x) x.size()
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);
#define seteps(N) setprecision(N)
#define uni(x) sort(all(x)), x.erase(unique(all(x)), x.end())
#define lson (ind<<1)
#define rson (ind<<1|1)
#define endl ‘\n‘
#define dbg(x) cerr << #x " = " << (x) << endl
#define mp make_pair
//#define LOCAL
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef __int128 lll;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef pair<char,char> PCC;
typedef pair<double,double> PDD;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PLL;
typedef pair<int,PII> PIII;
struct Scanner {
bool hasNext = 1;
bool hasRead = 1;
int nextInt() {
hasRead = 0;
int res = 0;
char flag = 1, ch = getchar();
while(ch != EOF && !isdigit(ch)) {
hasRead = 1;
flag = (ch == ‘-‘) ? -flag : flag;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch != EOF && isdigit(ch)) {
hasRead = 1;
res = res * 10 + (ch - ‘0‘);
ch = getchar();
}
if(ch == EOF)
hasNext = 0;
return res * flag;
}
ll nextLL() {
hasRead = 0;
ll res = 0;
char flag = 1, ch = getchar();
while(ch != EOF && !isdigit(ch)) {
hasRead = 1;
flag = (ch == ‘-‘) ? -flag : flag;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch != EOF && isdigit(ch)) {
hasRead = 1;
res = res * 10 + (ch - ‘0‘);
ch = getchar();
}
if(ch == EOF)
hasNext = 0;
return res * flag;
}
char nextChar() {
hasRead = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch != EOF && isspace(ch)) {
hasRead = 1;
ch = getchar();
}
if(ch == EOF)
hasNext = 0;
return ch;
}
int nextString(char *str) {
hasRead = 0;
int len = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch != EOF && isspace(ch)) {
hasRead = 1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch != EOF && !isspace(ch)) {
hasRead = 1;
str[++len] = ch;
ch = getchar();
}
str[len + 1] = 0;
if(ch == EOF)
hasNext = 0;
return len;
}
} sc;
ll rd() {
ll x = sc.nextLL();
return x;
}
void rd(int &x) {
x = sc.nextInt();
}
void rd(ll &x) {
x = sc.nextLL();
}
void rd(char &x) {
x = sc.nextChar();
}
void rd(char* x) {
sc.nextString(x);
}
template<typename T1, typename T2>
void rd(pair<T1, T2> &x) {
rd(x.first);
rd(x.second);
}
template<typename T>
void rd(T *x, int n) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
rd(x[i]);
}
template<typename T>
void rd(vector<T> &x,int n){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
rd(x[i]);
}
void printInt(int x) {
if(x < 0) {
putchar(‘-‘);
x = -x;
}
if(x >= 10)
printInt(x / 10);
putchar(‘0‘ + x % 10);
}
void printLL(ll x) {
if(x < 0) {
putchar(‘-‘);
x = -x;
}
if(x >= 10)
printLL(x / 10);
putchar(‘0‘ + x % 10);
}
void pr(int x, char ch = ‘\n‘) {
printInt(x);
putchar(ch);
}
void pr(ll x, char ch = ‘\n‘) {
printLL(x);
putchar(ch);
}
template<typename T1, typename T2>
void pr(pair<T1, T2> x, char ch = ‘\n‘) {
#ifdef LOCAL
putchar(‘<‘);
pr(x.first, ‘ ‘);
pr(x.second, ‘>‘);
putchar(ch);
return;
#endif //LOCAL
pr(x.first, ‘ ‘);
pr(x.second, ch);
}
template<typename T>
void pr(T *x, int n) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
pr(x[i], " \n"[i == n]);
}
template<typename T>
void pr(vector<T> &x) {
int n = x.size();
for(int i = 1; i <= n - 1; ++i)
pr(x[i], " \n"[i == n - 1]);
}
const int N=5005;
const int M=1<<12;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod=1e9+7;
const lll oone=1;
const double eps=1e-6;
const double pi=acos(-1);
int n,a[N];
ll cnt[N];
struct Solver
{
void InitOnce(){
}
void Read(){
rd(n);
rd(a,n);
}
void Solve(){
fill(cnt,cnt+1+n,0);
ll ans=0;
rep(i,1,n+1){
ll temp=cnt[i];
if(temp<a[i]-1){
ans+=a[i]-1-temp;
temp+=a[i]-1-temp;
}
cnt[i+1]+=temp-a[i]+1;
if(i+2<=n){
rep(j,i+2,min(n*1ll,i+a[i])+1) cnt[j]++;
}
}
pr(ans);
}
}solver;
int main(){
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in","r",stdin);
#endif LOCAL
solver.InitOnce();
int t=1;
t=sc.nextInt();
//t=INF;
while(t--){
solver.Read();
if(!sc.hasRead) break;
solver.Solve();
if(!sc.hasNext) break;
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/dejavuzz/p/14521724.html