Angular 中的一个常见模式就是在父组件和一个或多个子组件之间共享数据。可以用 @Input() 和 @Output() 来实现这个模式:
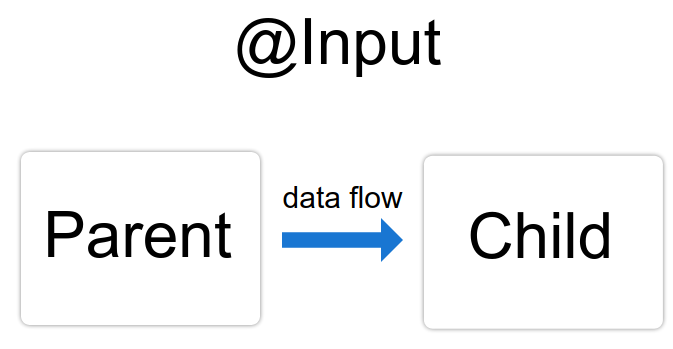
1、父传子 : @Input() 装饰器允许父组件更新子组件中的数据。
2、子传父 : @Output() 装饰器允许子组件传数据给父组件。
3、模板:
<parent-component> <child-component></child-component> </parent-component>
一、父传子 :
1、配置子组件:
child.ts
import { Component, Input } from ‘@angular/core‘; // First, import Input
export class ItemDetailComponent {
//但 @Input() 属性可以是任意类型,比如 number、string、boolean 或 object。item 的值来自父组件
@Input() item: string; // decorate the property with @Input()
}
child.html
<p>
Today‘s item: {{item}}
</p>
2、配置父组件:
parent.ts
export class AppComponent {
//在父组件类中,为 currentItem 指定一个值
currentItem = ‘Television‘;
}
parent.html
// 在父组件的模板中绑定该属性
<app-child [item]="currentItem"></app-child>
3、通过 @Input(),Angular 把 currentItem 的值传给子组件,以便 item 渲染为 Television
4、要想监视 @Input() 属性的变化,你可以使用 Angular 的生命周期钩子OnChanges 。
二、子传父 :
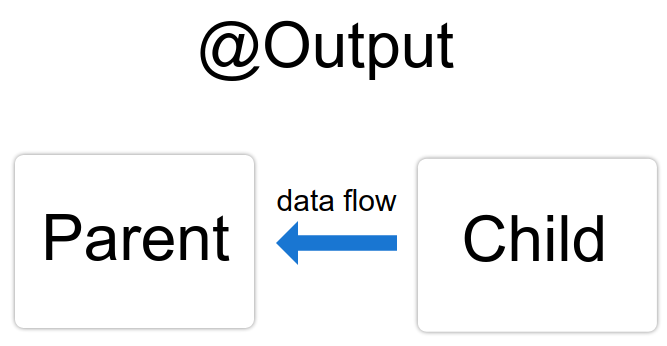
子组件使用 @Output() 属性来引发事件,以通知父组件这一变化。为了引发事件,@Output() 必须是 EventEmitter 类型,它是 @angular/core 中用来发出自定义事件的类
1、配置子组件:
child.ts
在子组件类中导入Output和EventEmitter
import { Output, EventEmitter } from ‘@angular/core‘;
export class ItemDetailComponent {
// 下面的例子中newItemEvent这个@Output()的类型为EventEmitter,这意味着它是一个事件
@Output() newItemEvent = new EventEmitter<string>();
//创建一个addNewItem()方法:
addNewItem(value: string) {
this.newItemEvent.emit(value);
};
}
child.html
//用户可在其中输入条目名称。 #newItem 变量的 value 属性存储了用户输入到 <input> 中的值
<label>Add an item: <input #newItem></label>
//addNewItem() 方法接受一个 #newItem.value 属性的值作为参数
<button (click)="addNewItem(newItem.value)">Add to parent‘s list</button>
2、配置父组件:
parent.ts
export class AppComponent {
items = [‘item1‘, ‘item2‘, ‘item3‘, ‘item4‘];
//addItem() 方法接受一个字符串形式的参数,然后把该字符串添加到 items 数组中。
addItem(newItem: string) {
this.items.push(newItem);
}
}
parent.html
在父模板中,把父组件的方法绑定到子组件的事件上。
把子组件选择器(<app-item-output>)放在父组件的模板 app.component.html 中 。 <app-child (newItemEvent)="addItem($event)"></app-child>
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/a1-top/p/14554617.html