这题很奇怪,一样的解法在中国区力扣就一直超时,在美国账号上就能accept,但就是时间复杂度不怎么好看。
You are given an n x n binary matrix grid. You are allowed to change at most one 0 to be 1.
Return the size of the largest island in grid after applying this operation.
An island is a 4-directionally connected group of 1s.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[1,0],[0,1]] Output: 3 Explanation: Change one 0 to 1 and connect two 1s, then we get an island with area = 3.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,1],[1,0]] Output: 4 Explanation: Change the 0 to 1 and make the island bigger, only one island with area = 4.
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,1],[1,1]] Output: 4 Explanation: Can‘t change any 0 to 1, only one island with area = 4.
Constraints:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500grid[i][j] is either 0 or 1.题意:给一个矩阵,由0和1组成,问最多可以将一个0翻成1,形成岛屿最大面积是多少。
思路:1, 用DFS来做
2, 遍历矩阵,找到所有连通块,并用负整数r记录是否访问过
3, 用hashmap来存每个连通块的面积
4,遍历到每个位置0时,查询与其连通的连通块总面积,trick: 可能与同一个“0”位置相连的是同一个连通块,因此要用一个unordered_set来去重
5,取最大值。
6,时间复杂度为O(4*M*N),不明白为什么中国区力扣会超时,北美区的就不会。
以图为证:
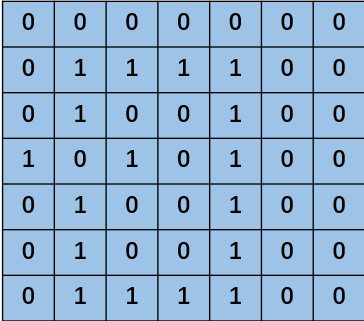
1,原始矩阵:
2, 遍历后的矩阵
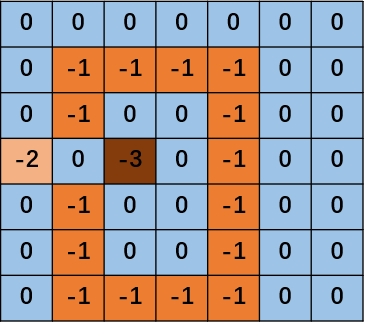
其中hashmap中记录:m[-1] = 16, m[-2] = 1, m[-3] = 1
3,遍历到grid[3][2]的时候,深搜到grid[3][1](即下图红色块)时发现有两个连通块与其相连(next to it),记录其面积和为next = m[-1]+m[-2]=17
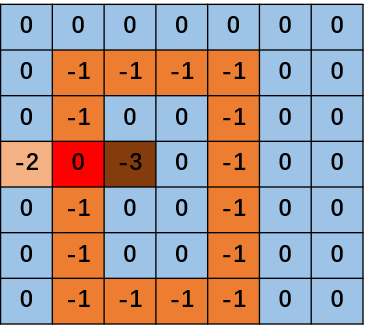
4,因此计算与红色块0连通的面积为1+17=18.
代码:
class Solution {
private:
unordered_map<int, int> m;
vector<vector<int>> dir = {{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
public:
void addNext(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int i, int j, unordered_set<int>& s, int& n){
if(i<0 || i==grid.size() || j<0 || j==grid[0].size() || grid[i][j] >= 0 || s.count(grid[i][j])) return;
s.insert(grid[i][j]);
n += m[grid[i][j]];
}
void DFS(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int& r, int i,int j, int& cur, int& next){
if(i<0 || i==grid.size() || j<0 || j==grid[0].size() || grid[i][j] < 0) return;
if(grid[i][j] == 0){
unordered_set<int> s;
int n = 0;
for(auto d : dir) addNext(grid, i+d[0], j+d[1], s, n);
next = max(next, n);
} else {
grid[i][j] = r;
cur++;
for(auto d : dir) DFS(grid, r, i+d[0], j+d[1], cur, next);
}
}
int largestIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int res = 1, r = 0, size = grid.size()*grid[0].size();
for(int i=0; i<grid.size(); i++){
for(int j=0; j<grid[0].size(); j++){
if(grid[i][j] != 1) continue;
int cur = 0, next = 0;
DFS(grid, --r, i, j, cur, next);
res = max(res, cur+next+1);
m[r] = cur;
}
}
return min(res, size);
}
};
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/boligongzhu/p/14586332.html