难度 medium
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器类BSTIterator ,表示一个按中序遍历二叉搜索树(BST)的迭代器:
BSTIterator(TreeNode root) 初始化 BSTIterator 类的一个对象。BST 的根节点 root 会作为构造函数的一部分给出。指针应初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,且该数字小于 BST 中的任何元素。
boolean hasNext() 如果向指针右侧遍历存在数字,则返回 true ;否则返回 false 。
int next()将指针向右移动,然后返回指针处的数字。
注意,指针初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,所以对 next() 的首次调用将返回 BST 中的最小元素。
你可以假设 next() 调用总是有效的,也就是说,当调用 next() 时,BST 的中序遍历中至少存在一个下一个数字。
示例:
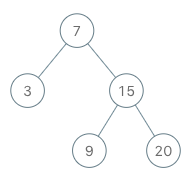
输入
["BSTIterator", "next", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext"]
[[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []]
输出
[null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false]
解释
BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]);
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 3
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 7
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 9
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 15
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 20
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 False
提示:
树中节点的数目在范围 [1, 105] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 106
最多调用 105 次 hasNext 和 next 操作
解题思路:这道题我用了栈来解决,首先初始化的时候先把根节点压入栈,然后一直往左深入遍历,不断把节点压入栈,这样栈中就保留了最左边的所有节点,next操作就是把栈顶的节点弹出,如果该节点有右子节点,那么当前就应该从这个右子节点开始,继续往左深入遍历,并不断把节点压入栈,这样栈顶保留的始终是中序遍历需要访问的下一个节点元素,而hasNext操作则判断stack是否为空即可。
代码 t10 s29 java
class BSTIterator {
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
st = new Stack<>();
TreeNode t = root;
while(t!=null){
st.push(t);
t = t.left;
}
}
public int next() {
TreeNode cur = st.pop();
if(cur.right!=null){
TreeNode t = cur.right;
while(t!=null){
st.push(t);
t = t.left;
}
}
return cur.val;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return !st.isEmpty();
}
private Stack<TreeNode> st;
}
参考资料
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhengxch/p/14587769.html