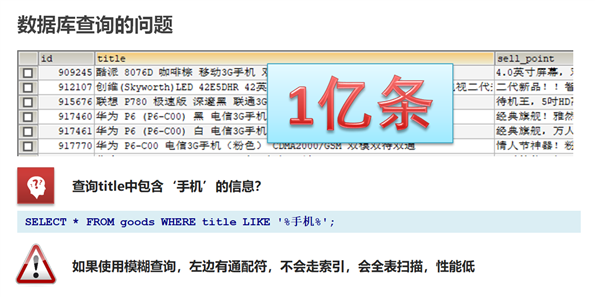
数据库查询存在的问题:
性能低:使用模糊查询,左边有通配符,不会走索引,会全表扫描,性能低
功能弱:
对于如下的数据如果以”华为手机“作为条件,查询不出来数据
select * from goods where title like ‘%华为手机%‘
华为手机需要拆分成华为和手机两个词然后分别查询,但是MySQL等关系型数据库没有拆分词语的功能
select * from goods where title like ‘%华为%‘ or title like ‘%手机%‘
Es通过倒排索引解决这些问题,比如京东的商品信息就保存在ElasticSearch中,可以很快速的得到搜索结果
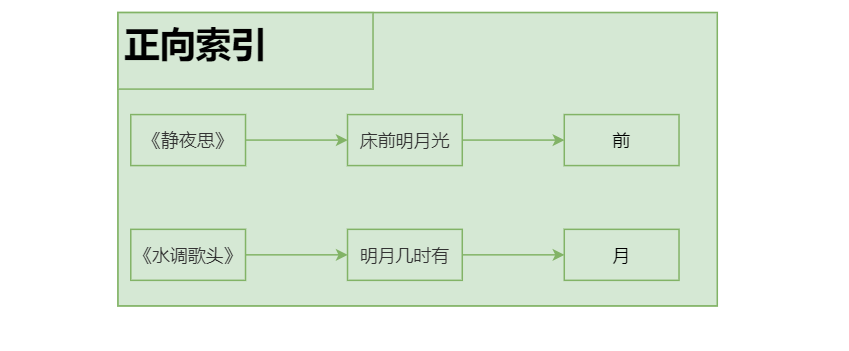
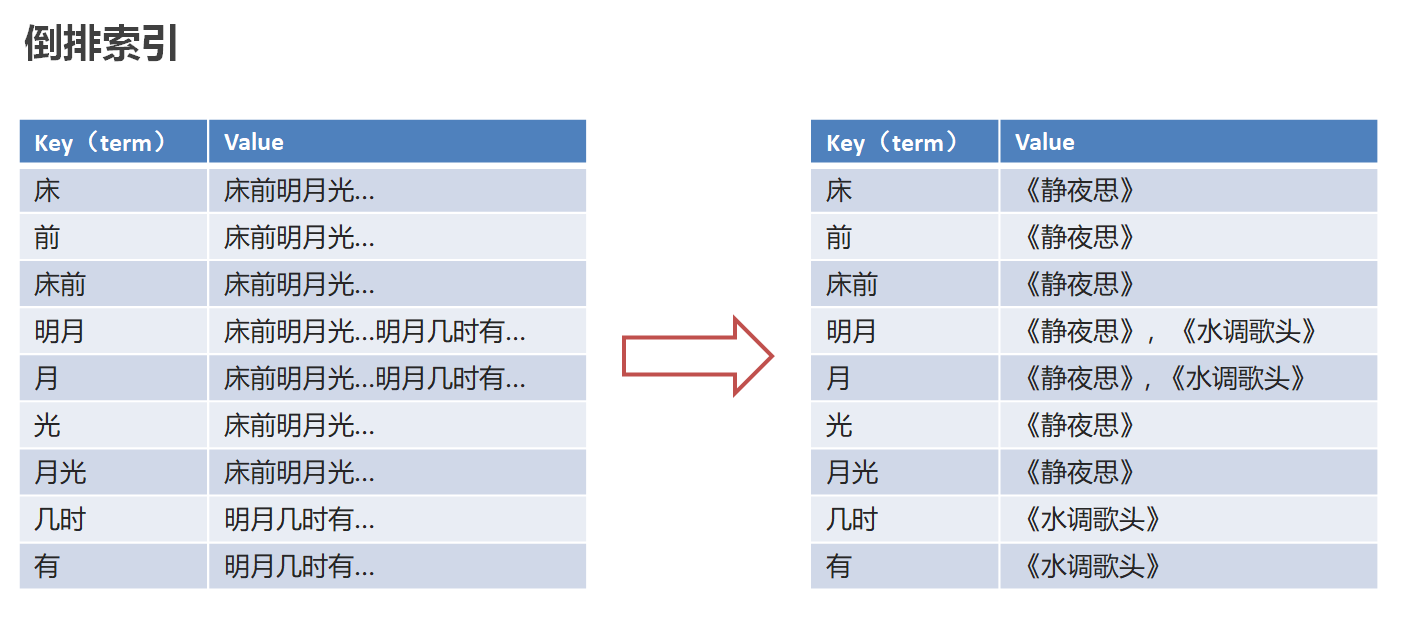
正向索引:由《静夜思》-->床前明月光--->“前”字
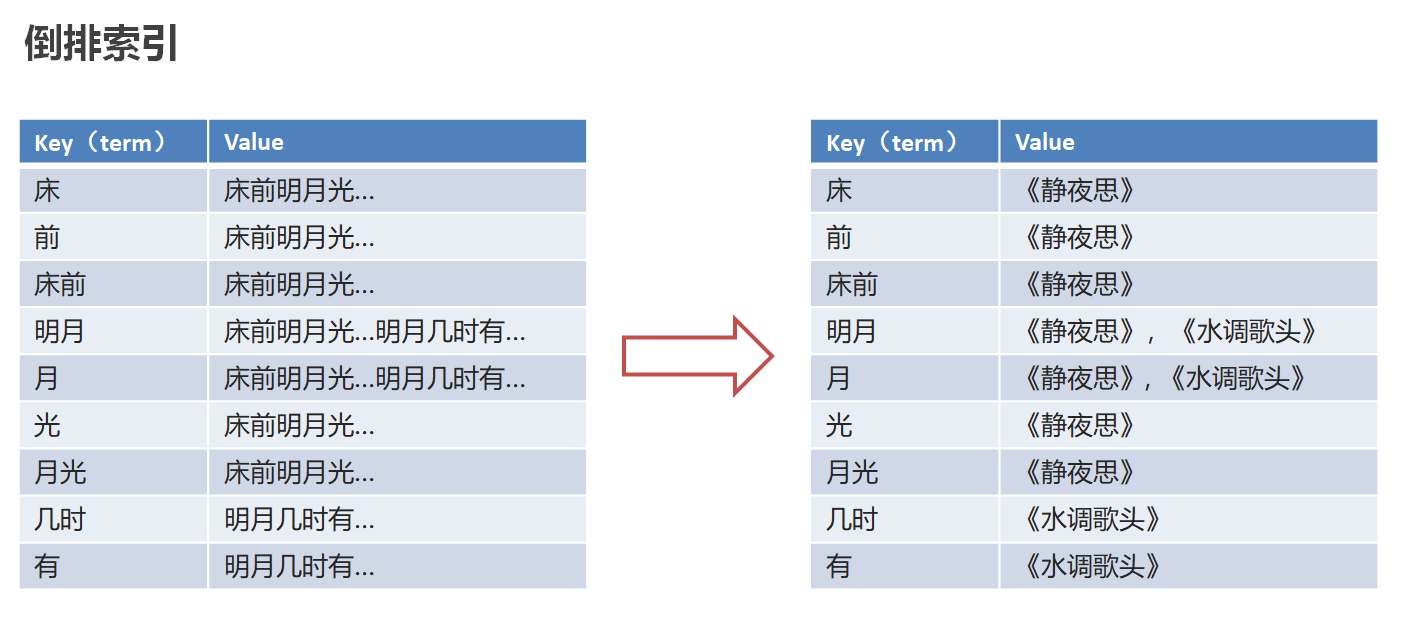
分词:将华为手机拆分成华为和手机两个词,这个动作简称为分词
倒排索引(反向索引):将文档进行分词,形成词条和id的对应关系即为反向索引。
先对“床前明月光”--> 分词
将一段文本按照一定的规则,拆分为不同的词条(每一个词条被称为term)
所有的分词结果都记录对应的诗句内容
反向索引的实现就是对诗句进行分词,分成单个的词或字,由词推句,即为反向索引
需要解决数据库查询存在的问题:
性能低:使用模糊查询,左边有通配符,不会走索引,会全表扫描,性能低
功能弱:对于如下的数据如果以”华为手机“作为条件,查询不出来数据
存储和查询原理:
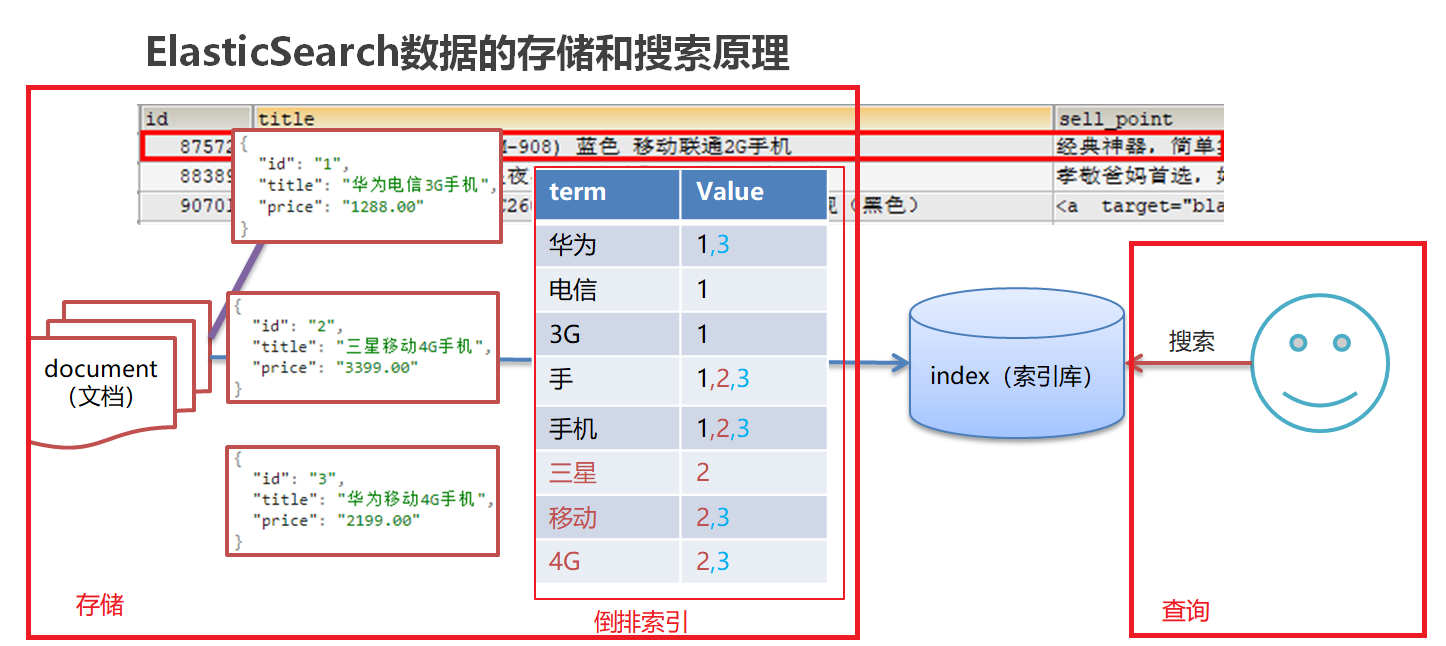
存储
对存储数据中的title进行分词,记录每个词语和数据id的对应关系(倒排索引)
搜索:使用倒排索引,自定将对title进行分词(“华为”,“手机”),找到所有的匹配:1,2,3
使用“华为手机”作为关键字查询
华为:1,3
手机:1,2,3
?MySQL有事务性,而ElasticSearch没有事务性,所以你删了的数据是无法恢复的。
?ElasticSearch没有物理外键这个特性,,如果你的数据强一致性要求比较高,还是建议慎用
?ElasticSearch和MySql分工不同,MySQL负责存储(增删改)数据,ElasticSearch负责搜索数据。
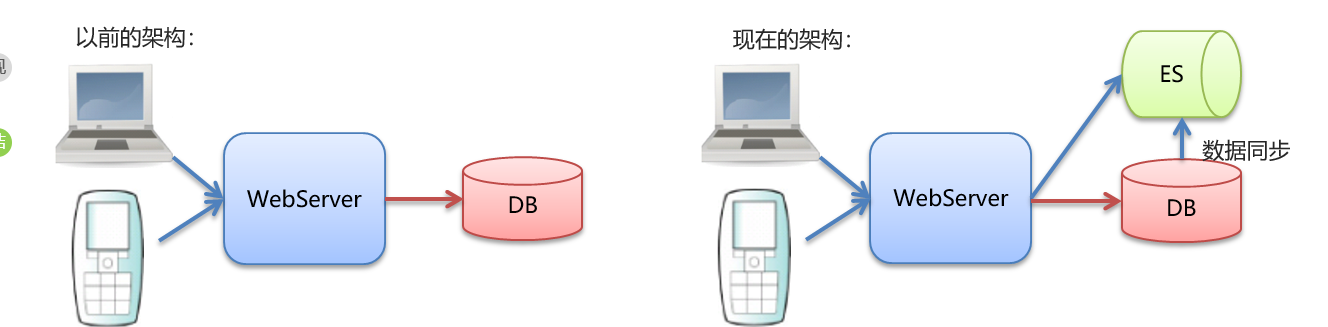
MySQL同步数据到ES常用工具:
通过JavaAPI写入ES
logstash, es官方推荐的
canal, 阿里开源的
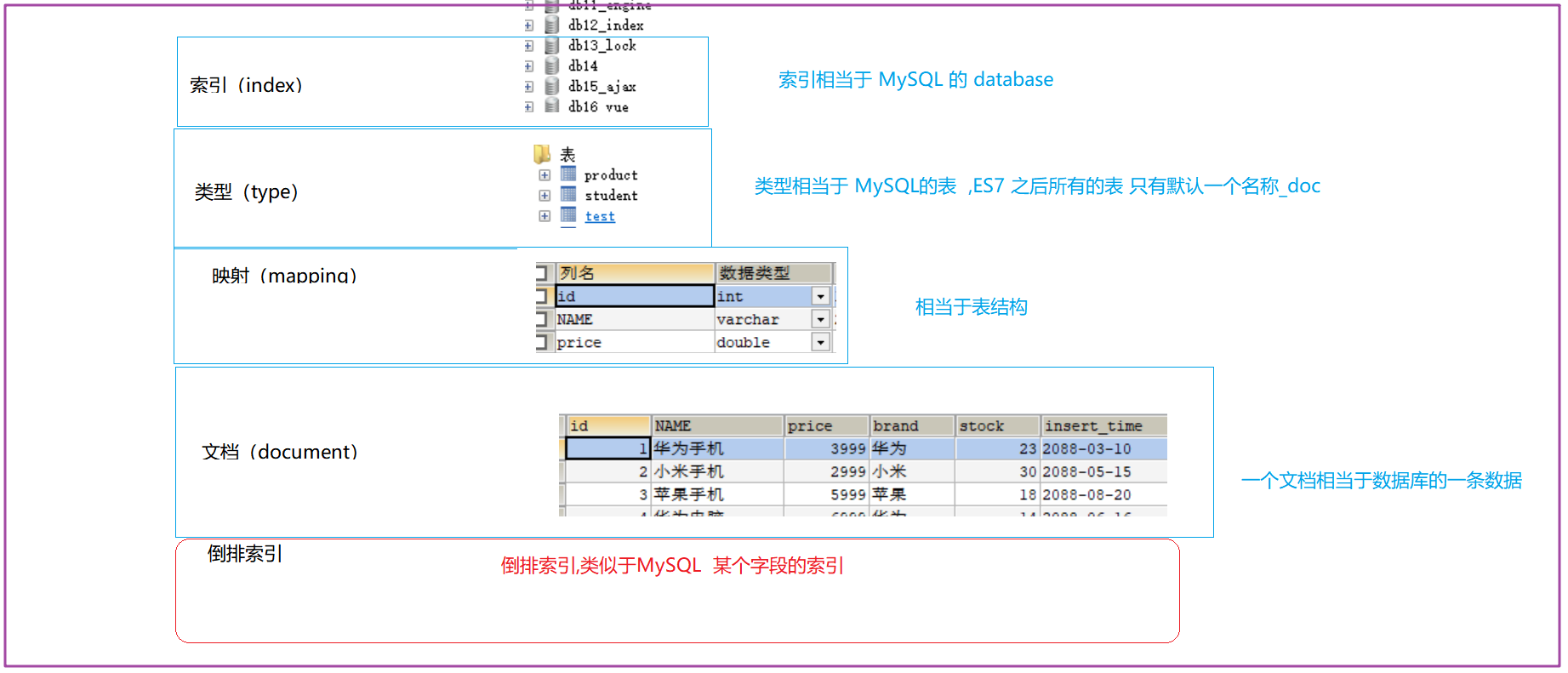
mapping定义了每个字段的类型、字段所使用的分词器等。相当于关系型数据库中的表结构。
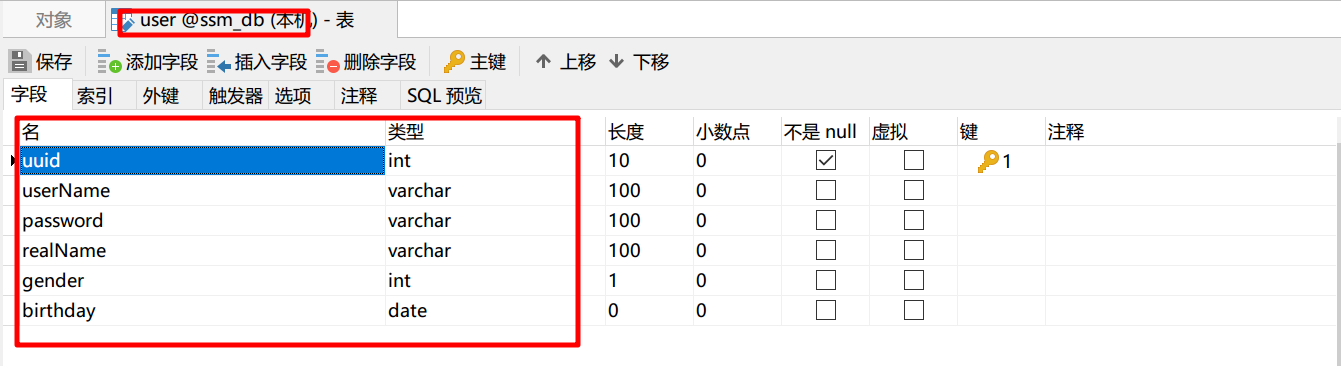
Elasticsearch中的最小数据单元,常以json格式显示。一个document相当于MySQL数据库中的一行数据。
一个倒排索引由文档中所有不重复词的列表构成,对于其中每个词,对应一个包含它的文档id列表。
1.REST(Representational State Transfer),表述性状态转移,是一组架构约束条件和原则。满足这些约束条件和原则的应用程序或设计就是RESTful。就是一种定义接口的规范。
2.基于HTTP。
3.使用XML格式定义或JSON格式定义。
4.每一个URI代表一种资源。
5.客户端使用GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 4个表示操作方式的动词对服务端资源进行操作:
GET:用来获取资源(查询)
POST:用来新建资源(新增)
PUT:用来更新资源(修改)
DELETE:用来删除资源(删除)
使用Kibana操作ES:http://192.168.52.128:5601/app/kibana#/dev_tools/console?_g=()
kibana是操作ES的WEB客户端,相当于操作MySQL数据库的sqlyog
# 创建索引
PUT person
# 查看索引
GET person
# 删除索引(同时会删除其所有数据,相当于mysql的drop database)
DELETE person
# 查询所有索引
GET _all
?
delete /c* (通配符删除c 开头的索引)
简单数据类型
字符串
text:会分词,不支持聚合
keyword:不会分词,将全部内容作为一个词条,支持聚合
数值:long.inteter,double等
布尔:boolean
日期:date
二进制:binary
范围类型
integer_range, float_range, long_range, double_range, date_range
复杂数据类型

数组:[ ] Nested: nested (for arrays of JSON objects 数组类型的JSON对象)
对象:{ } Object: object(for single JSON objects 单个JSON对象)
注意: 字段类型没有修改功能
# 删除索引(同时会删除其所有数据,相当于mysql的drop database)
DELETE person
?
# 创建索引
PUT person
?
# 查看索引
GET person
?
# 添加映射(相当于添加表字段)
PUT /person/_mapping
{
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"text"
},
"age":{
"type":"integer"
}
}
}
# 仅查看映射(查看表结构)
GET person/_mapping
# 仅查看索引,会自动显示表结构(查看表结构)
GET person
# 创建索引并添加映射(相当于建立数据库时,(因为只有一张表type=_doc)同时制定表字段)
PUT /person
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
# 指定id,如果id=1数据不存在,则添加(insert)数据;否则是修改(update)
PUT /person/_doc/1
{
"name":"张三",
"age":18,
"address":"北京海淀区"
}
?
# 添加文档,不指定id
POST /person/_doc/
{
"name":"王五",
"age":18,
"address":"北京"
}
# 根据id 查看
GET /person1/_doc/1
# 查看所有(无条件查询)
GET /person1/_search
# 删除指定id文档
DELETE /person1/_doc/1
中文分词器
?IKAnalyzer是一个开源的,基于java语言开发的轻量级的中文分词工具包
?是一个基于Maven构建的项目
?具有60万字/秒的高速处理能力
?支持用户词典扩展定义
?下载地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/archive/v7.4.0.zip
参见 ik分词器安装.md
IK分词器有两种分词模式:ik_max_word和ik_smart模式
1、ik_max_word
# 方式一ik_max_word
# 会将文本做最细粒度的拆分,比如会将“乒乓球明年总冠军”拆分为“乒乓球、乒乓、球、明年、总冠军、冠军。
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "乒乓球明年总冠军"
}
ik_max_word分词器执行如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "乒乓球",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "乒乓",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "球",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "明年",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "总冠军",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "冠军",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 5
}
]
}
2、ik_smart
# 方式二ik_smart
# 会做最粗粒度的拆分,比如会将“乒乓球明年总冠军”拆分为乒乓球、明年、总冠军。
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"text": "乒乓球明年总冠军"
}
ik_smart分词器执行如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "乒乓球",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "明年",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "总冠军",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 2
}
]
}
由此可见:使用ik_smart可以将文本"text": "乒乓球明年总冠军"分成了【乒乓球】【明年】【总冠军】
这样看的话,这样的分词效果更智能一些,达到了我们的要求。
1.创建索引,添加映射,并指定分词器为ik分词器
# 如果有删除
DELETE person
?
# 添加映射_指定分词器(相当于添加表字段)
PUT person
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword" // keyword 类型 不会分词
},
"address": {
"type": "text", // text 类型 会分词, 但不能进行聚合查询(类似SQL group by/sum函数)
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
?
GET person
2.添加文档
# 添加几条数据备用
# 指定id
POST /person/_doc/1
{
"name":"张三",
"age":18,
"address":"北京海淀区"
}
?
POST /person/_doc/2
{
"name":"李四",
"age":18,
"address":"北京朝阳区"
}
?
POST /person/_doc/3
{
"name":"王五",
"age":18,
"address":"北京昌平区"
}
?
POST /person/_doc/4
{
"name":"李雷",
"age":18,
"address":"华为5G手机"
}
3.查询映射数据
GET /person/_search
4.查看分词效果
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "北京昌平区"
}
词条查询:term,不会将查询条件拆分
使用“北京”做为查询条件:
# 可以查询到3条数据
GET /person/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"address": {
"value": "北京"
}
}
}
}
使用“北京昌平”做为查询条件:
# 查询不到数据,因为没有一个叫“北京昌平”的词条
GET /person/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"address": {
"value": "北京昌平"
}
}
}
}
全文查询:match
match查询会对查询条件进行分词,先将查询条件进行分词,然后查询,求并集(or)
# 1.对查询条件“北京昌平”进行分词: 北京,昌平
# 2.根据分词结果逐个查询
?
GET /person/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "北京昌平"
}
}
}
结果会把所有address中有北京和昌平的都查询出来:
词条查询:term(关键词查询)
term查询不会对查询条件进行分词,只有当词条和查询字符串完全匹配时才匹配搜索
全文查询:match(全文查询)
match查询会对查询条件进行分词,先将查询条件进行分词,然后查询,求并集(or)
①搭建SpringBoot工程
②引入ElasticSearch相关坐标:7.4.0
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
?
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
?
<!--引入es的坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-client</artifactId>
<version>7.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>7.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
?
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.4</version>
</dependency>
?
</dependencies>
③测试
编写配置类ElasticSearchConfig
package com.itheima.elasticsearchdemo.config;
?
import lombok.Data;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
?
配置es信息: resources\application.yml
elasticsearch
编写单元测试类:ElasticsearchDay01ApplicationTests
注意:使用@Autowired注入RestHighLevelClient 如果报红线,则是因为配置类所在的包和测试类所在的包,包名不一致造成的
package com.itheima.elasticsearchdemo;
?
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
?
在ElasticsearchDemoApplicationTests单元测试类中进行如下练习:
1.添加索引
# 注意导包:org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest
/**
* 添加索引
*/
添加索引,并添加映射
/**
* 添加索引,并添加映射
*/
查询索引
/**
* 查询索引
*/
删除索引
/**
* 删除索引
*/
索引是否存在
/**
* 索引是否存在
*/
1.添加文档,使用map作为数据
/**
* 添加文档,使用map作为数据
*/
2.添加文档,使用对象作为数据
检查是否添加fastjson和lombok的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
?
<!--fastjson依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.4</version>
</dependency>
创建Person类:使用lombok提供的@Data注解来完成setter, getter,toString等方法
package com.itheima.domain;
?
import lombok.Data;
?
通过fastjson将Java对象转换成JSON字符串:
//将对象转为json
String data = JSON.toJSONString(p);
/**
* 添加文档,使用对象作为数据
*/
1.修改文档:添加文档时,如果id存在则修改,id不存在则添加
/**
* 修改文档:添加文档时,如果id存在则修改,id不存在则添加
*/
2.根据id查询文档
/**
* 根据id查询文档
*/
3.根据id删除文档
/**
* 根据id删除文档
*/
新增或修改:
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("index_name").id("")
client.index()
查询
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("index_name").id("")
client.get()
删除
DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest("index_name").id("")
client.delete()
配置es连接地址:application.yml
elasticsearch
在单元测试类中编写批量操作代码
3.验证执行结果
GET person/_doc/1
GET person/_doc/3
GET person/_doc/6
应用场景:
公司之前做的电子商城项目,查询使用的是MySQL数据库;后期发现太慢,需要用ES进行搜索,所以要将原来存储在MySQL的数据全部拿到ES中。
PUT goods
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"price": {
"type": "double"
},
"createTime": {
"type": "date"
},
"categoryName": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"brandName": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"spec": {
"type": "object"
},
"saleNum": {
"type": "integer"
},
"stock": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
title:商品标题
price:商品价格
createTime:创建时间
categoryName:分类名称。如:家电,手机
brandName:品牌名称。如:华为,小米
spec: 商品规格。如: spec:{"屏幕尺寸","5寸","内存大小","128G"}
saleNum:销量
stock:库存量
检查数据库配置和表是否创建
添加mybatis,mysql,fastjson依赖
<!--mybatis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
?
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
?
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.4</version>
</dependency>
执行代码
/**
* 批量导入
*/
验证执行结果:
GET goods/_search
查询所有商品信息
# 发现只能查询出10条数据
GET goods/_search
ES中分页查询:分页的参数 和MySQL中的 limit 一致
SELECT * FROM user limit 0, 10;
# 默认情况下,es一次展示10条数据,通过from和size来控制分页
GET goods/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0, // 从第几条开始,索引从 0 开始
"size": 100 // 查询多少条
}
/**
* 查询所有
* 1. matchAll
* 2. 将查询结果封装为Goods对象,装载到List中
* 3. 分页。默认显示10条
*/
term Query为精确查询,在搜索时会整体匹配关键字,不再将关键字分词。
GET goods/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"title": {
"value": "华为手机" // 根据"华为手机"这个词 去ES库 中 的title 的倒排索引中找(完全匹配)
}
}
}
}
term查询,查询text类型字段时,只有其中的单词相匹配都会查到,text字段会对数据进行分词
QueryBuilder query = QueryBuilders.termQuery("title", "华为");//term词条查询
?
//keyword:完全匹配
//QueryBuilder query = QueryBuilders.termQuery("categoryName", "电视");//term词条查询
/**
* termQuery:词条查询
*/
match Query即全文检索,它的搜索方式是先将搜索字符串分词,再使用各各词条从索引中搜索。
会对查询条件进行分词。
然后将分词后的查询条件和词条进行等值匹配
默认取并集(or 并集)
例如:华为手机,会分词为 “华为”,“手机” 只要出现其中一个词条都会搜索到
# match查询
GET goods/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "华为手机" // 先把 华为手机 分词, 然后再去倒排索引中找
}
},
"size": 500
}
match的 and(交集) 搜索
例如:华为手机,会分词为 “华为”,“手机” 但要求“华为”,和“手机”同时出现在词条中
# match查询 and
GET goods/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": {
"query": "华为手机",
"operator": "and"
}
}
},
"size": 500
}
MatchQueryBuilder query = QueryBuilders.matchQuery("title", "华为手机");
query.operator(Operator.AND);//求交集
/**
* matchQuery:词条分词查询
*/
term query会去倒排索引中寻找确切的term,它并不知道分词器的存在。这种查询适合keyword 、numeric、date
match query知道分词器的存在。并且理解是如何被分词的
//通配符查询
WildcardQueryBuilder query = QueryBuilders.wildcardQuery("title", "华*");//华后多个字符
//正则查询
RegexpQueryBuilder query = QueryBuilders.regexpQuery("title", "\\w+(.)*");
//前缀查询,针对类型为keyword的字符串
PrefixQueryBuilder query = QueryBuilders.prefixQuery("brandName", "三");
完整代码:
/**
* 通配符查询:WildcardQuery
*/
范围查询:查找指定字段在指定范围内包含值:gte大于等于,lte 小于等于
gte: greater than or equal 大于等于
lte: less than or equal 小于等于
?
排序查询:desc 降序,asc 升序
# 范围查询
GET goods/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 2000,
"lte": 3000
}
}
},
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
JavaAPI:
//范围查询 以price 价格为条件
RangeQueryBuilder query = QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price");
?
//指定下限
query.gte(2000);
//指定上限
query.lte(3000);
?
sourceBuilder.query(query);
?
//排序 价格 降序排列
sourceBuilder.sort("price",SortOrder.DESC);
SELECT
*
FROM
goods
WHERE
title LIKE ‘%华为%手机‘
OR brandName LIKE ‘%华为%手机‘
OR categoryName LIKE ‘%华为%手机‘
queryString 多条件查询,可以让字符串中包含关键词
?会对查询条件进行分词。
?然后将分词后的查询条件和词条进行等值匹配
?默认取并集(OR)
?可以指定多个查询字段
query_string:识别query中的连接符(or 、and),可以使用有default_operator连接符的脚本
# queryString
GET goods/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"fields": ["title","categoryName","brandName"],
"query": "华为手机"
, "default_operator": "AND"
}
}
}
simple_query_string:不识别query中的连接符(or 、and),查询时会将 “华为”、"and"、“手机”分别进行查询
GET goods/_search
{
"query": {
"simple_query_string": {
"fields": ["title","categoryName","brandName"],
"query": "华为 AND 手机" //不识别or, and
// , "default_operator": "AND"
}
}
}
Java代码
//queryString
QueryStringQueryBuilder query =
QueryBuilders.queryStringQuery("华为手机")
.field("title").field("categoryName").field("brandName")
.defaultOperator(Operator.AND);
SELECT
*
FROM
goods
WHERE
title LIKE ‘%手机%‘
OR brandName LIKE ‘%华为%‘
boolQuery:对多个查询条件连接。
must(and):条件必须成立
must_not(not):条件必须不成立
should(or):条件可以成立
?
?
filter:条件必须成立,性能比must高。不会计算得分
得分:即条件匹配度,匹配度越高,得分越高
# boolquery
# must和filter配合使用时,max_score(得分)是显示的
# must 默认数组形式
GET goods/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"brandName": {
"value": "华为"
}
}
}
],
"filter":[
{
"term": {
"title": "手机"
}
},
{
"range":{
"price": {
"gte": 2000,
"lte": 3000
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
布尔查询:boolQuery
查询品牌名称为:华为
查询标题包含:手机
查询价格在:2000-3000
其中must 、filter为连接方式;term、match为不同的查询方式
//1.构建boolQuery
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
?
//2.构建各个查询条件
//2.1 查询品牌名称为:华为
TermQueryBuilder termQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.termQuery("brandName", "华为");
boolQuery.must(termQueryBuilder);
?
//2.2. 查询标题包含:手机
MatchQueryBuilder matchQuery = QueryBuilders.matchQuery("title", "手机");
boolQuery.filter(matchQuery);
?
//2.3 查询价格在:2000-3000
RangeQueryBuilder rangeQuery = QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price");
rangeQuery.gte(2000);
rangeQuery.lte(3000);
boolQuery.filter(rangeQuery);
?
sourceBuilder.query(boolQuery);
聚合查询:桶聚合,分组查询
查询title包含手机的数据
查询品牌列表
/**
* 聚合查询:桶聚合,分组查询
* 1. 查询title包含手机的数据
* 2. 查询品牌列表
*/
高亮显示可以将搜索结果一个或多个字突出显示,以便向用户展示匹配关键字的位置。
高亮三要素:
?高亮字段
?前缀
?后缀
默认前后缀 :
<em>手机</em>
替换默认高亮前后缀为:更改字体颜色为red
GET goods/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "电视"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"title": {
"pre_tags": "<font color=‘red‘>",
"post_tags": "</font>"
}
}
}
}
设置高亮
高亮字段
前缀
后缀
将高亮后的字段数据,替换原有数据
/**
*
* 高亮查询:
* 1. 设置高亮
* * 高亮字段
* * 前缀
* * 后缀
* 2. 将高亮了的字段数据,替换原有数据
*/
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunhao410526/p/14587038.html