导入相关库,编写作图函数
"""
已知分布的随机抽样
2020.11.10
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
import matplotlib
from scipy import optimize
matplotlib.rcParams[‘font.sans-serif‘] = [‘SimHei‘] #将默认字体font...改为黑体
matplotlib.rcParams[‘axes.unicode_minus‘] = False #有负号不正常显示,使负号不显示
def plot_hist(arr, bins, title):
plt.hist(arr, bins)
plt.title(title)
plt.xlabel(‘抽样值‘)
plt.ylabel(‘频数‘)
plt.savefig(title+‘.jpg‘)
plt.show()


time1 = time.process_time_ns()
‘‘‘题一‘‘‘
time1 = time.process_time_ns()
‘‘‘题一‘‘‘
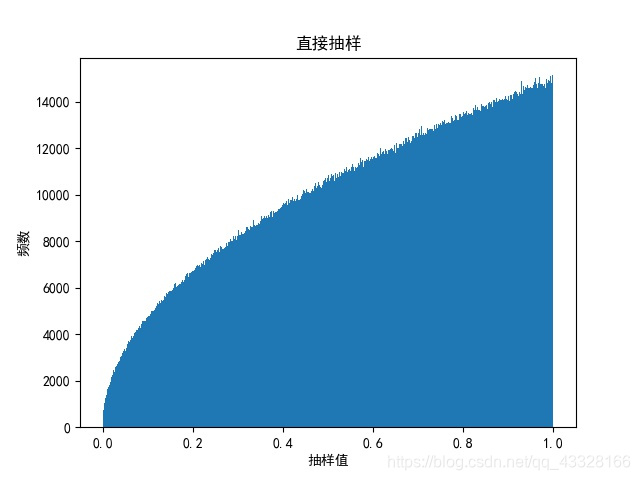
# 直接抽样
arr = np.random.uniform(size=(3, 10000000))**2 # 抽样得到随机数s的平方
arr = arr.max(axis=0) # 对每一列的三个随机数s做max(s1,s2,s3)
plot_hist(arr, np.linspace(0, 1, 1000),‘题一:直接抽样‘) # 作图
time2 = time.process_time_ns()
print(‘直接抽样运行时间: ‘, (time2-time1)*10**-6, ‘毫秒, 抽样个数为:‘, arr.size)
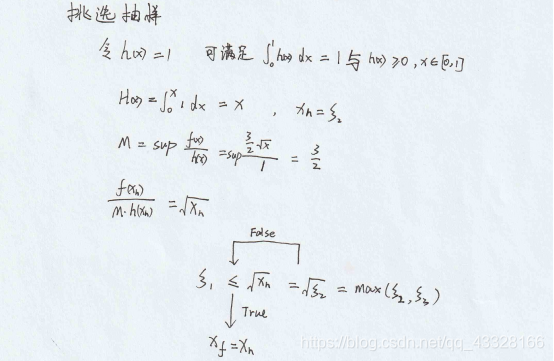

# 挑选抽样
xf = np.array([])
for i in range(100000):
s1 = np.random.uniform() # 抽取s1
s2 = np.random.uniform() # 抽取s2
if np.sqrt(s2)>s1:
xf = np.append(xf,s2)
plot_hist(xf,np.linspace(0,1,300),‘题一:挑选抽样‘)
# 方法二
s1 = np.random.uniform(size=100000)
s2 = np.sqrt(np.random.uniform(size=100000))
xf = np.array([])
for s1,s2 in zip(s1,s2):
if (s2)>s1:
xf = np.append(xf,s2)
xf = xf**2 # 千万要注意,判断时用"根号s",取值时用s 。所以要平方回来
plot_hist(xf,np.linspace(0,1,100),‘题一:挑选抽样1‘)
# 方法三
s1arr = np.random.uniform(size=100000)
s2arr = np.random.uniform(size=100000)
s3arr = np.random.uniform(size=100000)
xf = np.array([])
for s1,s2,s3 in zip(s1arr,s2arr,s3arr):
s2 = np.max([s2,s3])
if s2>s1:
xf = np.append(xf,s2**2)
plot_hist(xf,np.linspace(0,1,100),‘题一:挑选抽样1‘)
time1 = time.process_time_ns()
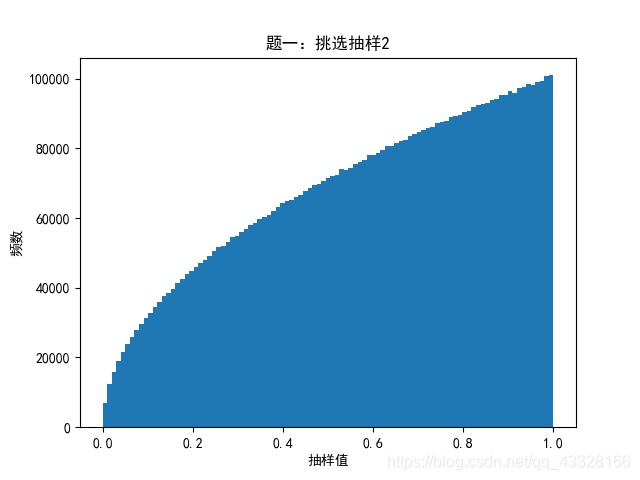
# 方法四:快速矩阵方法
s1 = np.random.uniform(size=10000000)
s2 = np.max(np.random.uniform(size=10000000*2).reshape(2,10000000),axis=0)
a = (s2-s1)
a[a<0] = 0
a[a>0] = 1
s2=s2*a # 相当于选取了符合挑选条件s1<s2的部分
s2 = s2[s2>0] # 清洗掉0项
s2 = s2**2 # max相当于开根号,现在平方回来
plot_hist(s2,np.linspace(0,1,100),‘题一:挑选抽样2‘)
time2 = time.process_time_ns()
print(‘直接抽样运行时间: ‘, (time2-time1)*10**-9, ‘秒, 抽样次数为:‘, s1.size)
抽样分布如图:

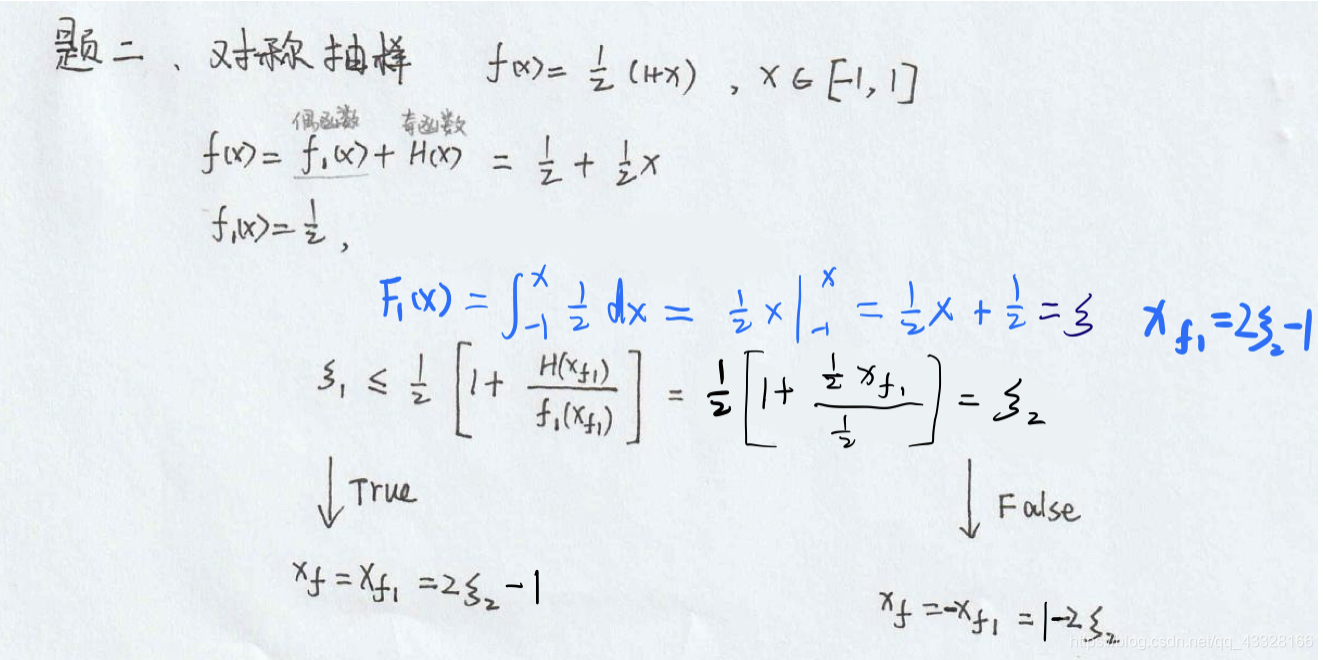
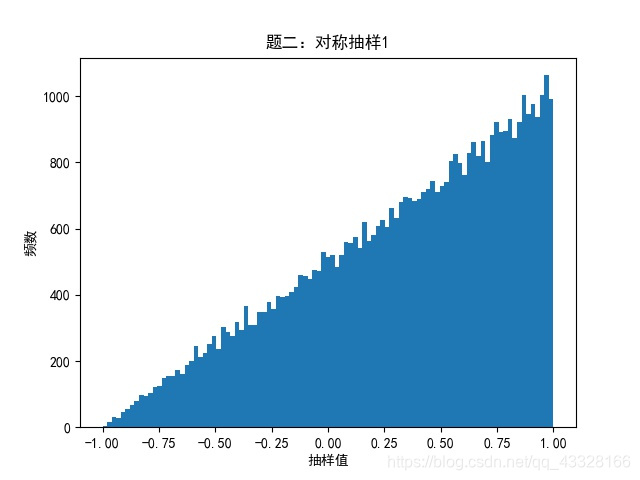
‘‘‘题二 对称抽样‘‘‘
xf = np.array([])
for i in range(100000):
s1 = np.random.uniform()
s2 = np.random.uniform()
if s1<=0.5*(1+2*s2-1):
xf = np.append(xf, 2*s2-1)
else:
xf = np.append(xf, 1-2*s2)
plot_hist(xf,np.linspace(-1,1,300),‘题二:对称抽样‘)
# 矩阵方法
s1 = np.random.uniform(size=100000)
s2 = np.random.uniform(size=100000)
a = 0.5*(1+2*s2-1)-s1
a[a>0] = 1
a[a<0] = -1
xf = (2*s2-1)*a
plot_hist(xf,np.linspace(-1,1,100),‘题二:对称抽样2‘)

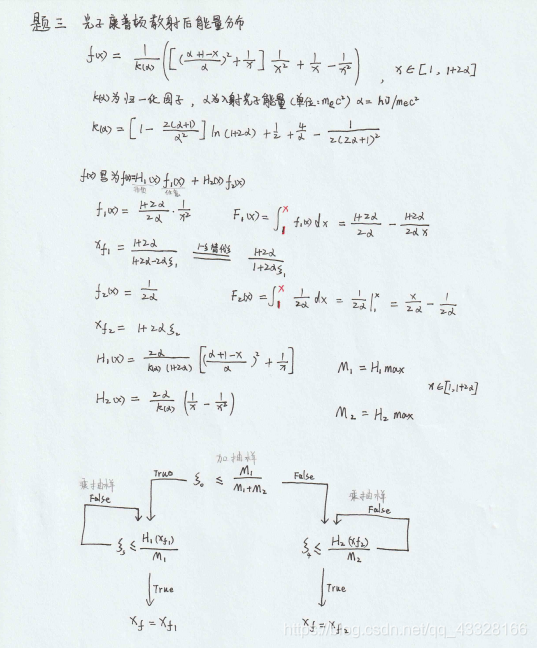
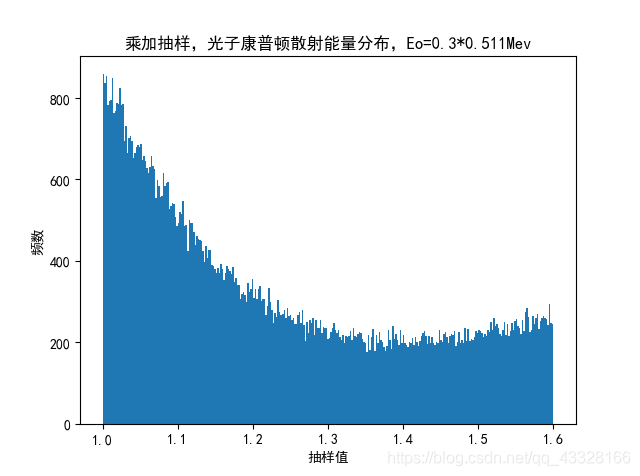
‘‘‘题三:乘加抽样,光子康普顿散射能量分布‘‘‘
# 入射粒子能量,单位(mc**2)
a = 0.3
k = (1-(2*a+2)/a**2)*np.log(1+2*a)+0.5+4/a - 1/(2*(2*a+1)**2)
def H1(x):
z = -( 2*a/(k+2*k*a) * ((a+1-x)**2)/a**2 + 1/x )
return z
result1 = optimize.fminbound(H1,1,5,full_output=True)
m1 = -result1[1]
print(‘最小值计算结果:‘,result1,‘, 最大值为:‘,m1)
def H2(x):
z = -( 2*a/k * (1/x - 1/x**2) )
return z
result2 = optimize.fminbound(H2,1 ,5, full_output=True)
m2 = -result2[1]
print(‘最小值计算结果:‘,result2,‘, 最大值为:‘,m2)
line = m1/(m1+m2)
print(‘加抽样部分判断条件:‘,line)
xf = np.array([])
for i in range(100000):
s1 = np.random.uniform()
if s1 <= line:
condition=True
while condition:
xf1 = (1+2*a) / (1+2*a-2*a*np.random.uniform())
s2 = np.random.uniform()
if s2 <= -H1(xf1) / m1:
xf = np.append(xf, xf1)
condition=False
else:
condition2 = True
while condition2:
xf2 = 1+2*a*np.random.uniform()
s2 = np.random.uniform()
if s2 <= -H2(xf2)/m2:
xf = np.append(xf,xf2)
condition2 = False
plot_hist(xf,np.linspace(1,1+2*a,300),‘乘加抽样,光子康普顿散射能量分布‘)

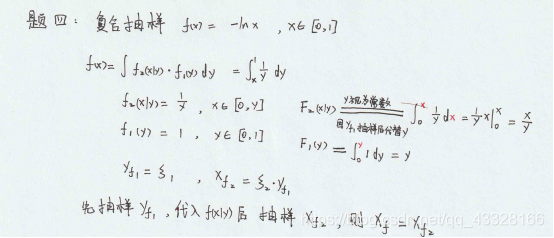
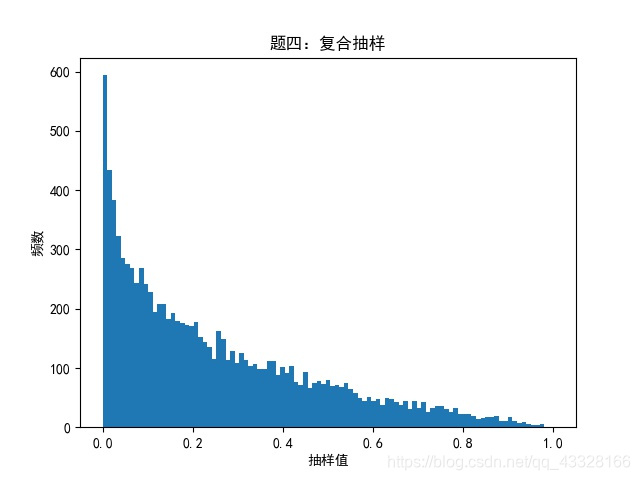
‘‘‘题四:复合抽样‘‘‘
xfarr = np.array([])
for i in range(10000):
yf = np.random.uniform()
xf = yf*np.random.uniform()
xfarr = np.append(xfarr,xf)
plot_hist(xfarr,np.linspace(0,1,100),‘题四:复合抽样‘)

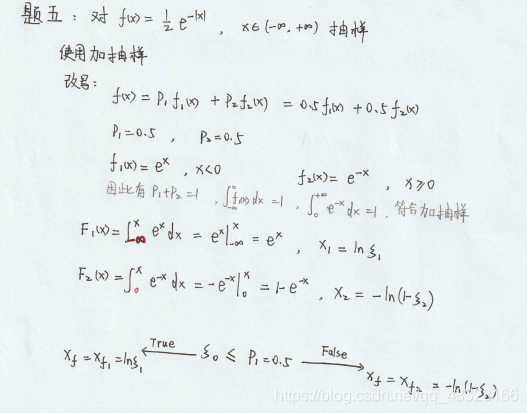
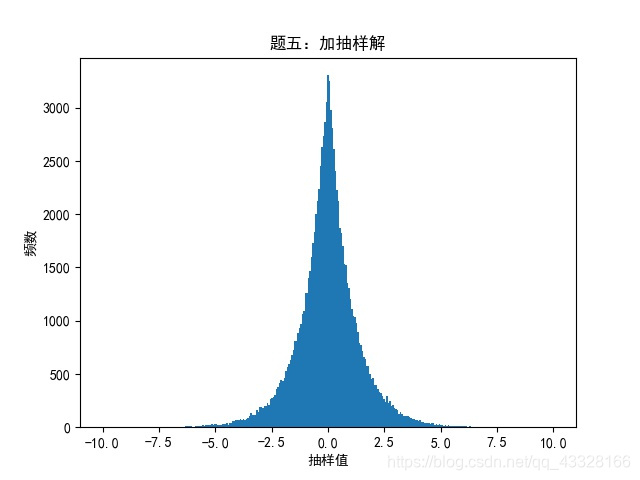
‘‘‘题五:自选-加抽样‘‘‘
xf = np.array([])
for i in range(100000):
s0 = np.random.uniform()
s1 = np.random.uniform()
s2 = np.random.uniform()
if s0 <= 0.5:
xf1 = np.log(s1)
xf = np.append(xf,xf1)
else:
xf2 = -1*np.log(1-s2)
xf = np.append(xf,xf2)
plot_hist(xf,np.linspace(-10,10,300),‘题五:加抽样解‘)
蒙特卡罗方法(二):各类分布的抽样方法(直接、挑选、对称、复合、加、乘加抽样)、光子康普顿散射后的能量分布
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/mayuhua/p/14589555.html