现在对不同手机类型的不同品牌实现操作编程(比如:开机、关机、上网,打电话等),如图:
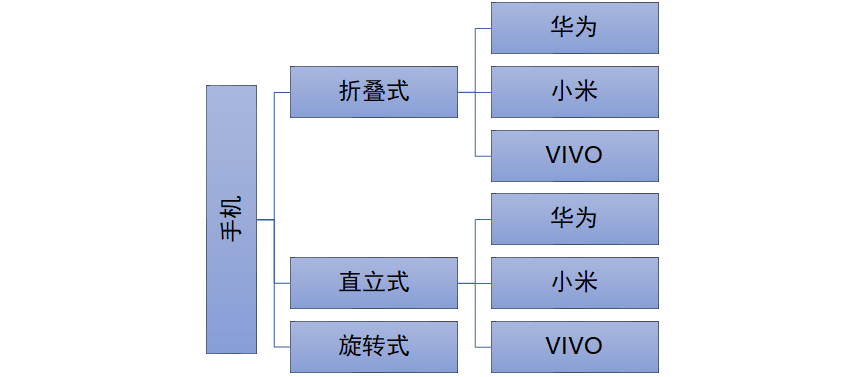
传统方法对应的类图
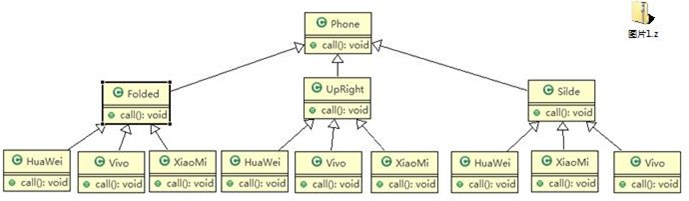
解决方案-使用桥接模式
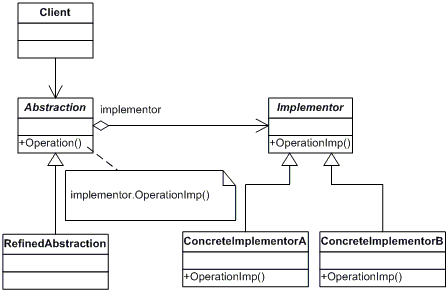
桥接模式(Bridge 模式)是指:将实现与抽象放在两个不同的类层次中,使两个层次可以独立改变。
是一种结构型设计模式
Bridge 模式基于类的最小设计原则,通过使用封装、聚合及继承等行为让不同的类承担不同的职责。它的主要特点是把抽象(Abstraction)与行为实现(Implementation)分离开来,从而可以保持各部分的独立性以及应对他们的功能扩展
上图做了说明
使用桥接模式改进传统方式,让程序具有搞好的扩展性,利用程序维护
应用实例说明(和前面要求一样)
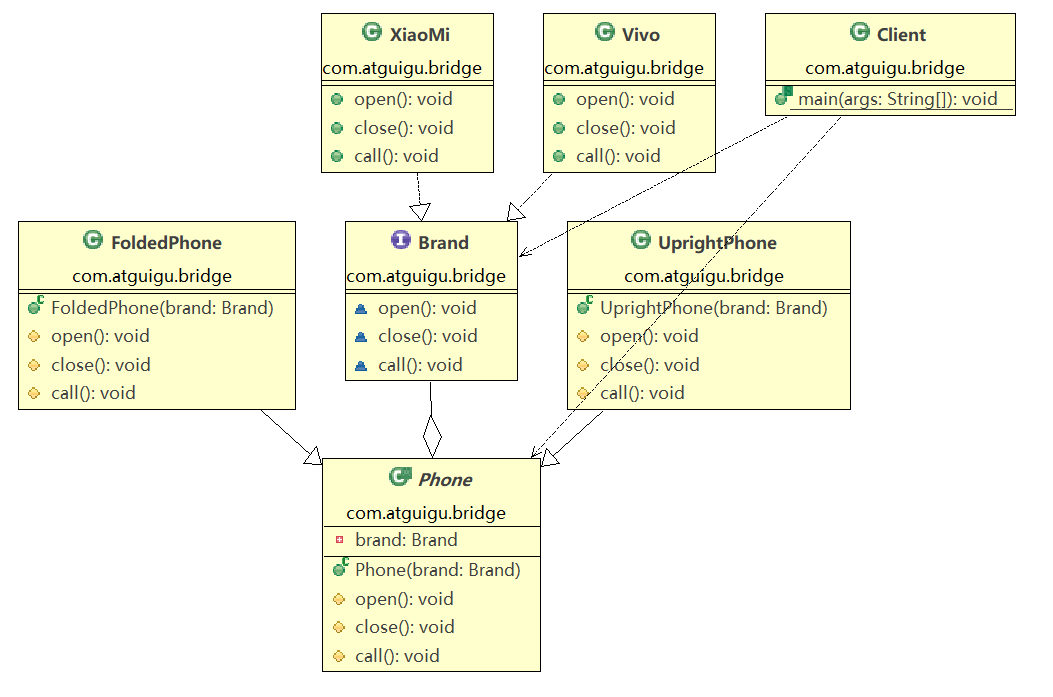
使用桥接模式对应的类图
package com.atguigu.bridge;
/**
* 接口
*
* @author Lenovo
*
*/
public interface Brand {
void open();
void close();
void call();
}
package com.atguigu.bridge;
/**
* @author Lenovo
*
*/
public class Client {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 获取折叠式手机(样式+拼配)
Phone phone1 = new FoldedPhone(new XiaoMi());
phone1.open();
phone1.call();
phone1.close();
Phone phone2 = new FoldedPhone(new Vivo());
phone2.open();
phone2.call();
phone2.close();
}
}
package com.atguigu.bridge;
/**
* @author Lenovo
*
*/
public abstract class Phone {
/**
* 组合品牌
*/
private Brand brand;
/**
* 构造器
*
* @param brand
*/
public Phone(Brand brand) {
super();
this.brand = brand;
}
protected void open() {
this.brand.open();
}
protected void close() {
this.brand.close();
}
protected void call() {
this.brand.call();
}
}
package com.atguigu.bridge;
/**
* @author Lenovo
*
*/
public class UprightPhone extends Phone {
/**
* @param brand
*/
public UprightPhone(Brand brand) {
super(brand);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
protected void open() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.open();
System.out.println("直立样式手机");
}
@Override
protected void close() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.close();
System.out.println("直立样式手机");
}
@Override
protected void call() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.call();
System.out.println("直立样式手机");
}
}
package com.atguigu.bridge;
/**
* @author Lenovo
*
*/
public class Vivo implements Brand {
@Override
public void open() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Vivo手机开机");
}
@Override
public void close() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Vivo手机关机");
}
@Override
public void call() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Vivo手机打电话");
}
}
package com.atguigu.bridge;
/**
* @author Lenovo
*
*/
public class XiaoMi implements Brand {
@Override
public void open() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("小米手机开机");
}
@Override
public void close() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("小米手机关机");
}
@Override
public void call() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("小米手机打电话");
}
}
桥接模式在 JDBC 的源码剖析
Jdbc 的 Driver 接口,如果从桥接模式来看,Driver 就是一个接口,下面可以有 MySQL 的 Driver,Oracle 的Driver,这些就可以当做实现接口类
代码分析+Debug 源码
/**
* The Java SQL framework allows for multiple database drivers. Each driver
* should supply a class that implements the Driver interface
*
* <p>
* The DriverManager will try to load as many drivers as it can find and then
* for any given connection request, it will ask each driver in turn to try to
* connect to the target URL.
*
* <p>
* It is strongly recommended that each Driver class should be small and
* standalone so that the Driver class can be loaded and queried without
* bringing in vast quantities of supporting code.
*
* <p>
* When a Driver class is loaded, it should create an instance of itself and
* register it with the DriverManager. This means that a user can load and
* register a driver by doing Class.forName("foo.bah.Driver")
*
* @see org.gjt.mm.mysql.Connection
* @see java.sql.Driver
* @author Mark Matthews
* @version $Id$
*/
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
// ~ Static fields/initializers
// ---------------------------------------------
//
// Register ourselves with the DriverManager
//
static {
try {
java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException E) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can‘t register driver!");
}
}
// ~ Constructors
// -----------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Construct a new driver and register it with DriverManager
*
* @throws SQLException
* if a database error occurs.
*/
public Driver() throws SQLException {
// Required for Class.forName().newInstance()
}
}
对 jdbc 源码分析的类图
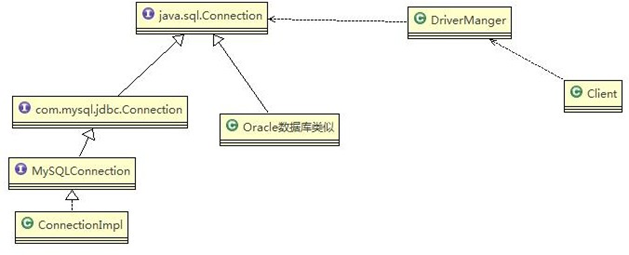
实现了抽象和实现部分的分离,从而极大的提供了系统的灵活性,让抽象部分和实现部分独立开来,这有助于系统进行分层设计,从而产生更好的结构化系统。
对于系统的高层部分,只需要知道抽象部分和实现部分的接口就可以了,其它的部分由具体业务来完成。
桥接模式替代多层继承方案,可以减少子类的个数,降低系统的管理和维护成本。
桥接模式的引入增加了系统的理解和设计难度,由于聚合关联关系建立在抽象层,要求开发者针对抽象进行设计和编程
桥接模式要求正确识别出系统中两个独立变化的维度(抽象、和实现),因此其使用范围有一定的局限性,即需要有这样的应用场景。
桥接模式其它应用场景:对于那些不希望使用继承或因为多层次继承导致系统类的个数急剧增加的系统,桥接模式尤为适用.
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/iamfatotaku/p/14607967.html