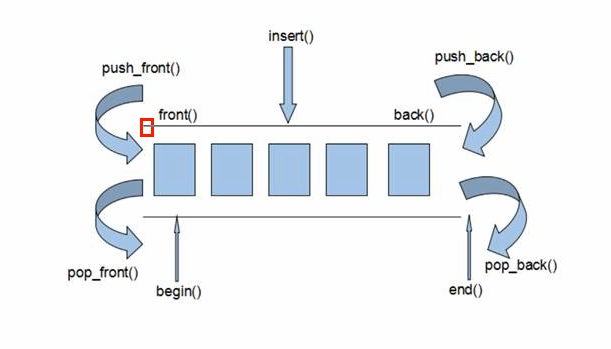
双端数组,可以对头端进行插入删除操作

deque头插比vector要高效得多。
vector访问速度比deque更快
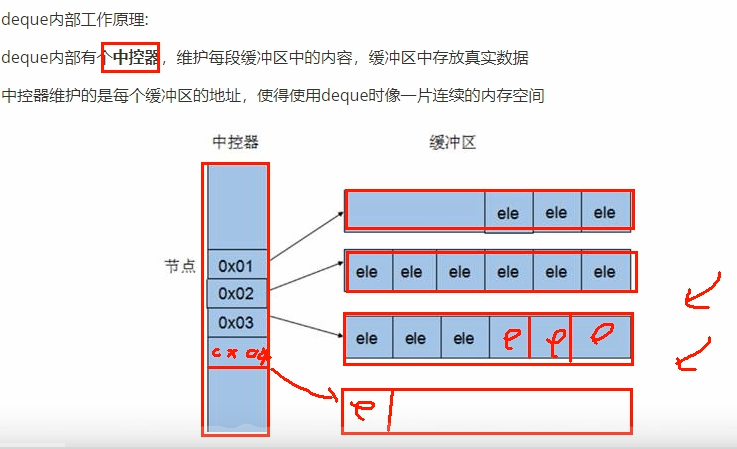
内部工作原理:
deque迭代器也支持随机访问

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<deque> 4 5 6 7 //deque容器 构造函数 8 9 void printDeque(const deque<int>&d) 10 { 11 for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) 12 { 13 //*it = 100; //容器中的数据不可以修改了 14 cout << *it << " "; 15 } 16 cout << endl; 17 } 18 19 void test01() 20 { 21 deque<int>d1; 22 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 23 { 24 d1.push_back(i); 25 } 26 printDeque(d1); 27 28 deque<int> d2(d1.begin(), d1.end()); 29 printDeque(d2); 30 31 deque<int>d3(10, 100); 32 printDeque(d3); 33 34 deque<int>d4(d3); 35 printDeque(d4); 36 37 38 } 39 40 int main() 41 { 42 test01(); 43 44 45 46 return 0; 47 }
deque容器和vector容器构造方式基本是一样的


1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<deque> 4 5 void printDeque(const deque<int>&d) 6 { 7 for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) 8 { 9 cout << *it << " "; 10 } 11 cout << endl; 12 } 13 14 //deque容器 赋值操作 15 void test01() 16 { 17 deque<int>d1; 18 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 19 { 20 d1.push_back(i); 21 } 22 printDeque(d1); 23 24 //operator=赋值 25 deque<int>d2; 26 d2 = d1; 27 printDeque(d2); 28 29 //assign赋值 30 deque<int>d3; 31 d3.assign(d1.begin(), d1.end()); 32 printDeque(d3); 33 34 deque<int>d4; 35 d4.assign(10, 100); 36 printDeque(d4); 37 } 38 39 40 int main() 41 { 42 test01(); 43 44 45 return 0; 46 }
3.3.4deque大小操作

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<deque> 4 5 //deque容器大小操作 6 void printDeque(const deque<int>&d) 7 { 8 for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) 9 { 10 cout << *it << " "; 11 } 12 cout << endl; 13 } 14 15 void test01() 16 { 17 deque<int>d1; 18 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 19 { 20 d1.push_back(i); 21 } 22 printDeque(d1); 23 24 if (d1.empty()) 25 { 26 cout << "d1为空" << endl; 27 } 28 else 29 { 30 cout << "d1不为空" << endl; 31 cout << "d1的大小为:" << d1.size() << endl; 32 33 //deque容器没有容量概念 34 } 35 36 //重新指定大小 37 //d1.resize(15); 38 d1.resize(15,1); 39 printDeque(d1); 40 41 d1.resize(5); 42 printDeque(d1); 43 44 } 45 46 47 int main() 48 { 49 test01(); 50 51 52 return 0; 53 }
3.3.5deque插入和删除
两端——任意位置

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<deque> 4 5 //deque容器的插入和删除 6 7 void printDeque(const deque<int> &d) 8 { 9 for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) 10 { 11 cout << *it << " "; 12 } 13 cout << endl; 14 } 15 16 //两端操作 17 void test01() 18 { 19 deque<int> d1; 20 21 //尾插 22 d1.push_back(10); 23 d1.push_back(20); 24 25 //头插 26 d1.push_front(100); 27 d1.push_front(200); 28 29 //200 100 10 20 30 printDeque(d1); 31 32 //尾删 33 d1.pop_back(); 34 printDeque(d1); 35 36 //头删 37 d1.pop_front(); 38 printDeque(d1); 39 40 } 41 42 void test02() 43 { 44 deque<int>d1; 45 d1.push_back(10); 46 d1.push_back(20); 47 d1.push_front(100); 48 d1.push_front(200); 49 50 //200 100 10 20 51 printDeque(d1); 52 53 //insert插入 54 d1.insert(d1.begin(), 1000); 55 //1000 200 100 10 20 56 printDeque(d1); 57 58 d1.insert(d1.begin(), 2,10000); 59 //10000 10000 1000 200 100 10 20 60 printDeque(d1); 61 62 //按照区间来进行插入 63 deque<int>d2; 64 d2.push_back(1); 65 d2.push_back(2); 66 d2.push_back(3); 67 68 d1.insert(d1.begin(), d2.begin(), d2.end()); 69 //1 2 3 10000 10000 1000 200 100 10 20 70 printDeque(d1); 71 72 } 73 74 void test03() 75 { 76 deque<int>d1; 77 d1.push_back(10); 78 d1.push_back(20); 79 d1.push_front(100); 80 d1.push_front(200); 81 82 //删除 83 deque<int>::iterator it = d1.begin(); 84 it++; 85 d1.erase(it); 86 //200 10 20 87 printDeque(d1); 88 89 //按区间方式删除 90 //d1.erase(d1.begin(), d1.end()); 91 //printDeque(d1); 92 93 //清空 94 d1.clear(); 95 printDeque(d1); 96 97 98 } 99 100 101 int main() 102 { 103 //test01(); 104 //test02(); 105 test03(); 106 107 return 0; 108 }

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<deque> 4 5 //deque数据存取 6 void test01() 7 { 8 deque<int>d; 9 d.push_back(10); 10 d.push_back(20); 11 d.push_back(30); 12 13 d.push_front(100); 14 d.push_front(200); 15 d.push_front(300); 16 17 //通过[]方式访问元素 18 //300 200 100 10 20 30 19 for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++) 20 { 21 cout << d[i] << " "; 22 } 23 cout << endl; 24 25 //通过at方式访问元素 26 for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++) 27 { 28 cout << d.at(i) << " "; 29 } 30 cout << endl; 31 32 cout << "第一个元素为:" << d.front() << endl; 33 cout << "最后一个元素为:" << d.back() << endl; 34 35 36 37 } 38 39 40 41 42 int main() 43 { 44 test01(); 45 46 47 48 return 0; 49 }
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<deque> 4 #include<algorithm> //标准算法头文件 5 6 7 void printDeque(const deque<int> &d) 8 { 9 for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) 10 { 11 cout << *it << " "; 12 } 13 cout << endl; 14 15 16 } 17 //deque容器 排序 18 void test01() 19 { 20 deque<int>d; 21 d.push_back(10); 22 d.push_back(20); 23 d.push_back(30); 24 d.push_front(100); 25 d.push_front(200); 26 d.push_front(300); 27 28 //300 200 100 10 20 30 29 printDeque(d); 30 31 //排序 默认排序规则 从小到大 升序 32 //对于支持随机访问的迭代器的容器,都可以利用sort算法直接对其进行排序 33 //vector容器也可以利用 sort进行排序 34 sort(d.begin(), d.end()); 35 cout << "排序后:" << endl; 36 printDeque(d); 37 38 39 } 40 41 42 int main() 43 { 44 test01(); 45 46 return 0; 47 }

代码实现:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<string> 4 #include<vector> 5 #include<deque> 6 #include<algorithm> 7 #include<ctime> 8 9 //需求: 10 11 class Person 12 { 13 public: 14 Person(string name, int score) 15 { 16 this->m_Name = name; 17 this->m_Score = score; 18 } 19 20 string m_Name; //姓名 21 int m_Score; //平均分 22 23 }; 24 25 void createPerson(vector<Person>&v) 26 { 27 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 28 { 29 string nameSeed = "ABCDE"; 30 string name = "选手"; 31 name += nameSeed[i]; 32 33 int score = 0; 34 Person p(name, score); 35 36 //将创建的Person对象 放入到容器中 37 v.push_back(p); 38 } 39 } 40 41 //打分 42 void setScore(vector<Person> &v) 43 { 44 for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 45 { 46 //将评委的分数 放入到deque容器中 47 deque<int>d; 48 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 49 { 50 //int score = rand() % 40 + 60; //0-39 加60 //60~100区间随机数 51 int score = rand() % 41 + 60; //0-40 加60 //60~100区间随机数 52 d.push_back(score); 53 } 54 55 //cout << "选手:" << it->m_Name << " 打分:" << endl; 56 57 //for (deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++) 58 //{ 59 // cout << *dit<< " "; //累加每个评委的分数 60 //} 61 //cout << endl; 62 63 //排序 64 sort(d.begin(), d.end()); 65 66 //去除最高和最低分 67 d.pop_back(); 68 d.pop_front(); 69 70 //取平均分 71 int sum = 0; 72 for (deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++) 73 { 74 sum += *dit; //累加每个评委的分数 75 } 76 77 int avg = sum / d.size(); 78 79 //将平均分 赋值给选手身上 80 it->m_Score = avg; 81 82 } 83 } 84 85 //打印分数 86 void showScore(vector<Person>&v) 87 { 88 for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 89 { 90 cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name 91 << " 平局分" << it->m_Score 92 << endl; 93 } 94 } 95 96 int main() 97 { 98 //随机数种子 99 srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); 100 101 //1、创建5名选手 102 vector<Person>v; //存放选手的容器 103 createPerson(v); 104 105 //测试 106 //for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 107 //{ 108 // cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name 109 // << " 分数:" << (*it).m_Score << endl; 110 //} 111 112 //2、给5名选手打分 113 setScore(v); 114 115 //3、显示最后得分 116 showScore(v); 117 118 return 0; 119 }
先进后出,只有一个出口
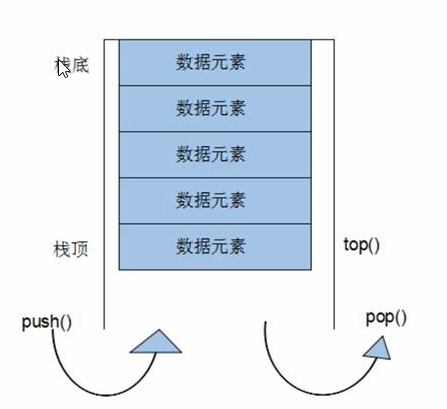
栈中只有栈顶元素才能被外界使用,因此,栈不能被遍历 。

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<stack> 4 5 //栈stack容器 6 7 void test01() 8 { 9 //特点:符合先进后出的数据结构 10 stack<int>s; 11 12 //入栈 13 s.push(10); 14 s.push(20); 15 s.push(30); 16 s.push(40); 17 18 cout << "栈的大小:" << s.size() << endl; 19 20 21 //只要栈不为空,查看栈顶并且执行出栈操作 22 while (!s.empty()) 23 { 24 //查看栈顶元素 25 cout << "栈顶元素为:" << s.top() << endl; 26 27 //出栈 28 s.pop(); //就向蒸包子 29 } 30 31 cout << "栈的大小:" << s.size() << endl; 32 33 34 } 35 36 37 int main() 38 { 39 test01(); 40 41 42 43 return 0; 44 }
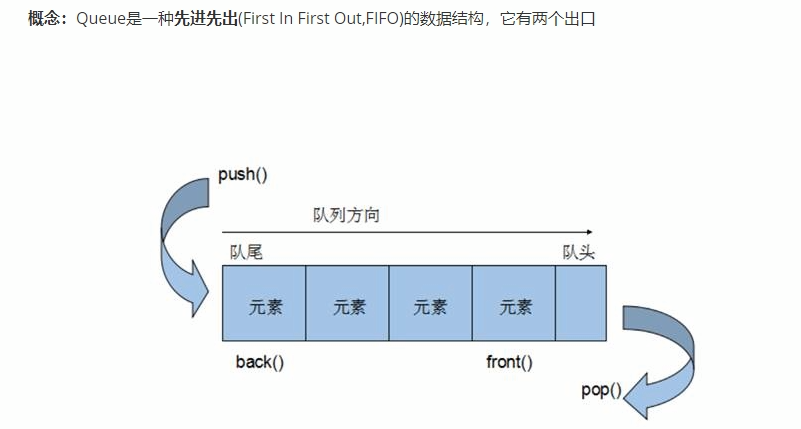

和栈一样,队列也没有遍历行为
队列的常用接口:

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<queue> 4 #include<string> 5 6 //队列queue 7 8 class Person 9 { 10 public: 11 Person(string name, int age) 12 { 13 this->m_Name = name; 14 this->m_Age = age; 15 } 16 17 string m_Name; 18 int m_Age; 19 20 }; 21 22 void test01() 23 { 24 //创建队列 25 queue<Person> q; 26 27 //准备数据 28 Person p1("唐僧", 30); 29 Person p2("孙悟空", 1000); 30 Person p3("猪八戒", 900); 31 Person p4("沙僧", 800); 32 33 //入队 34 q.push(p1); 35 q.push(p2); 36 q.push(p3); 37 q.push(p4); 38 39 cout << "队列大小为:" << q.size() << endl; 40 41 42 //判断只要队列不为空,查看队头,查看队尾,出队 43 while (!q.empty()) 44 { 45 //查看队头 46 cout << "队头元素——姓名:" 47 << q.front().m_Name 48 << " 年龄:" << q.front().m_Age << endl; 49 50 //查看队尾 51 cout << "队尾元素——姓名:" 52 << q.back().m_Name 53 << " 年龄:" << q.back().m_Age << endl; 54 55 //出队 56 q.pop(); 57 } 58 cout << "队列大小为:" << q.size() << endl; 59 60 61 } 62 63 int main() 64 { 65 test01(); 66 67 68 return 0; 69 }

图解:
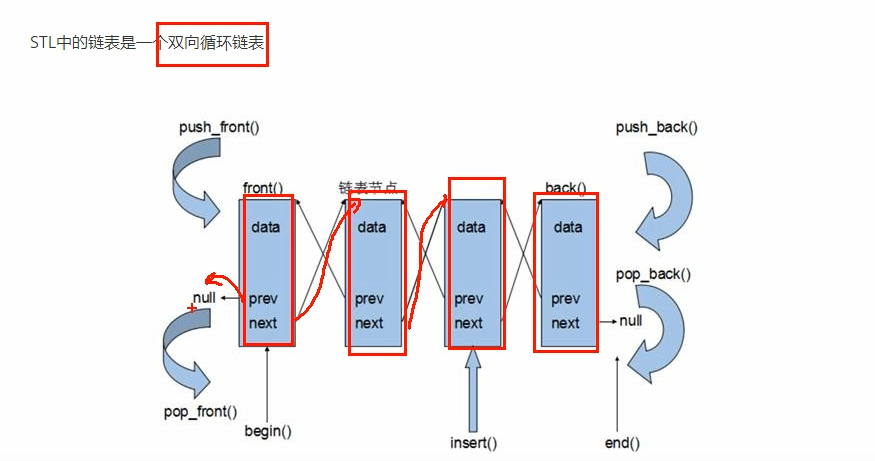
链表的迭代器只能前移和后移,属于双向迭代器。
优点:
动态内存分配,不会造成内存溢出和浪费;插入和删除高效。

3.7.2构造函数

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<list> 4 5 //list容器的构造 6 7 void printList(const list<int> &L) 8 { 9 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 10 { 11 cout << *it << " "; 12 } 13 cout << endl; 14 } 15 16 void test01() 17 { 18 //创建list容器 19 list<int>L1; 20 21 //添加数据 22 L1.push_back(10); 23 L1.push_back(20); 24 L1.push_back(30); 25 L1.push_back(40); 26 27 //遍历容器 28 printList(L1); 29 30 //区间方式构造 31 list<int> L2(L1.begin(), L1.end()); 32 printList(L2); 33 34 //拷贝构造 35 list<int>L3(L2); 36 printList(L3); 37 38 //n个elem 39 list<int>L4(10, 1000); 40 printList(L4); 41 42 43 44 } 45 46 int main() 47 { 48 test01(); 49 50 51 52 return 0; 53 }
基本一样。

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<list> 4 5 //list容器赋值和交换 6 void printList(const list<int> &L) 7 { 8 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 9 { 10 cout << *it << " "; 11 } 12 cout << endl; 13 14 } 15 16 //赋值 17 void test01() 18 { 19 list<int>L1; 20 21 L1.push_back(10); 22 L1.push_back(20); 23 L1.push_back(30); 24 L1.push_back(40); 25 26 printList(L1); 27 28 list<int>L2; 29 L2 = L1; //operator=赋值 30 printList(L2); 31 32 list<int>L3; 33 L3.assign(L2.begin(), L2.end()); 34 printList(L3); 35 36 list<int>L4; 37 L4.assign(10, 100); 38 printList(L4); 39 40 41 } 42 43 //交换 44 void test02() 45 { 46 list<int>L1; 47 48 L1.push_back(10); 49 L1.push_back(20); 50 L1.push_back(30); 51 L1.push_back(40); 52 53 list<int>L2; 54 L2.assign(10, 100); 55 56 cout << "交换前:" << endl; 57 printList(L1); 58 printList(L2); 59 60 cout << "交换后:" << endl; 61 L1.swap(L2); 62 printList(L1); 63 printList(L2); 64 65 66 67 68 } 69 70 int main() 71 { 72 //test01(); 73 test02(); 74 75 76 return 0; 77 }

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<list> 4 5 //list容器大小操作 6 void printList(const list<int>&L) 7 { 8 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 9 { 10 cout << *it << " "; 11 } 12 cout << endl; 13 14 } 15 16 void test01() 17 { 18 list<int>L1; 19 L1.push_back(10); 20 L1.push_back(20); 21 L1.push_back(30); 22 L1.push_back(40); 23 24 printList(L1); 25 26 //判断容器是否为空 27 if (L1.empty()) 28 { 29 cout << "L1为空" << endl; 30 } 31 else 32 { 33 cout << "L1不为空" << endl; 34 cout << "L1的元素个数为:" << L1.size() << endl; 35 } 36 37 //重新指定大小 38 L1.resize(10,10000); 39 printList(L1); 40 41 L1.resize(2); 42 printList(L1); 43 44 45 } 46 47 int main() 48 { 49 test01(); 50 51 52 return 0; 53 }

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<list> 4 5 //list容器插入和删除 6 7 void printList(const list<int>&L) 8 { 9 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 10 { 11 cout << *it << " "; 12 } 13 cout << endl; 14 } 15 16 17 void test01() 18 { 19 list<int>L; 20 21 //尾插 22 L.push_back(10); 23 L.push_back(20); 24 L.push_back(30); 25 26 //头插 27 L.push_front(100); 28 L.push_front(200); 29 L.push_front(300); 30 31 //300 200 100 10 20 30 32 printList(L); 33 34 //尾删 35 L.pop_back(); 36 //300 200 100 10 20 37 printList(L); 38 39 //头删 40 L.pop_front(); 41 //200 100 10 20 42 printList(L); 43 44 //insert插入 45 list<int>::iterator it = L.begin(); 46 L.insert(++it, 1000); 47 //200 1000 100 10 20 48 printList(L); 49 50 //删除 51 it = L.begin(); 52 L.erase(++it); 53 //200 100 10 20 54 55 printList(L); 56 57 //移除 58 L.push_back(10000); 59 L.push_back(10000); 60 L.push_back(10000); 61 L.push_back(10000); 62 63 printList(L); 64 65 L.remove(10000); 66 printList(L); 67 68 //清空 69 L.clear(); 70 printList(L); 71 72 73 74 } 75 76 77 78 int main() 79 { 80 test01(); 81 82 83 84 return 0; 85 }
头、尾操作;insert和erase;remove;clear。

list不支持at和operator[]访问。不是连续的内存空间,迭代器不支持随机访问,是双向迭代器,只能前移和后移。
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<list> 4 5 //list容器 数据存取 6 void test01() 7 { 8 list<int>L1; 9 L1.push_back(10); 10 L1.push_back(20); 11 L1.push_back(30); 12 L1.push_back(40); 13 14 //L1[0]; 不可以用[]访问list容器中的元素 15 //L1.at(0);不可以用at方式访问list容器中的元素 16 17 //原因是list本质是链表,不是用连续的线性空间存储数据 18 //迭代器也是不支持随机访问的 19 20 cout << "第一个元素为:" << L1.front() << endl; 21 cout << "最后一个元素为:" << L1.back() << endl; 22 23 //验证迭代器是不支持随机访问的 24 list<int> ::iterator it = L1.begin(); 25 26 it++;//支持双向 27 it--; 28 //it = it + 1;//不支持随机访问 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 } 36 37 38 int main() 39 { 40 test01(); 41 42 return 0; 43 }
3.7.7list反转和排序

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<list> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 6 7 //list容器的反转和排序 8 9 void printList(const list<int>&L) 10 { 11 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 12 { 13 cout << *it << " "; 14 } 15 cout << endl; 16 } 17 18 19 void test01() 20 { 21 //反转 22 list<int>L1; 23 L1.push_back(20); 24 L1.push_back(10); 25 L1.push_back(50); 26 L1.push_back(40); 27 L1.push_back(30); 28 29 cout << "反转前:" << endl; 30 printList(L1); 31 32 //反转后 33 cout << "反转后:" << endl; 34 35 L1.reverse(); 36 printList(L1); 37 } 38 39 40 bool myCompare(int v1, int v2) 41 { 42 //降序 就让第一个数>第二个数 43 return v1 > v2; 44 } 45 46 //排序 47 void test02() 48 { 49 list<int>L1; 50 L1.push_back(20); 51 L1.push_back(10); 52 L1.push_back(50); 53 L1.push_back(40); 54 L1.push_back(30); 55 56 //排序 57 cout << "排序前:" << endl; 58 printList(L1); 59 60 61 //所有不支持随机访问迭代器的容器,不可以用标准的算法 62 //不支持随机访问迭代器的容器内部会提供对应的一些算法 63 64 //sort(L1.begin(), L1.end()); 65 66 L1.sort(); //默认排序规则 从小到大 升序 67 cout << "排序后:" << endl; 68 printList(L1); 69 70 L1.sort(myCompare); 71 printList(L1); 72 73 } 74 75 76 77 int main() 78 { 79 //test01(); 80 test02(); 81 82 return 0; 83 }

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<list> 4 #include<string> 5 6 7 //list容器 排序案例 对自定义数据类型 做排序 8 9 //按照年龄升序,年龄相同的按身高降序 10 11 class Person 12 { 13 14 public: 15 Person(string name, int age, int height) 16 { 17 this->m_Name = name; 18 this->m_Age = age; 19 this->m_Height = height; 20 } 21 22 string m_Name;//姓名 23 int m_Age;//年龄 24 int m_Height;//身高 25 }; 26 27 28 //指定排序规则 29 bool comparePerson(Person &p1, Person &p2) 30 { 31 //按照年龄 升序 32 if (p1.m_Age == p2.m_Age) 33 { 34 //年龄相同 按照身高降序 35 return p1.m_Height > p2.m_Height; 36 } 37 return p1.m_Age < p2.m_Age; 38 39 } 40 41 void test01() 42 { 43 list<Person>L; //创建容器 44 45 //准备容器 46 Person p1("刘备", 35, 175); 47 Person p2("曹操", 45, 180); 48 Person p3("孙权", 40, 170); 49 Person p4("赵云", 25, 190); 50 Person p5("张飞", 35, 160); 51 Person p6("关羽", 35, 200); 52 53 //插入数据 54 L.push_back(p1); 55 L.push_back(p2); 56 L.push_back(p3); 57 L.push_back(p4); 58 L.push_back(p5); 59 L.push_back(p6); 60 61 for (list<Person>::iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 62 { 63 cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name 64 << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age 65 << " 身高:" << it->m_Height << endl; 66 } 67 68 //排序 69 cout << "-------------------" << endl; 70 cout << "排序后:" << endl; 71 72 L.sort(comparePerson); 73 for (list<Person>::iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 74 { 75 cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name 76 << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age 77 << " 身高:" << it->m_Height << endl; 78 } 79 80 81 82 83 } 84 85 int main() 86 { 87 test01(); 88 return 0; 89 }
3.8.1set基本概念

3.8.2set构造和赋值

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<set> 4 5 //set容器构造和赋值 6 void printSet(const set<int> &s) 7 { 8 for (set<int>::const_iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) 9 { 10 cout << *it << " "; 11 } 12 cout << endl; 13 } 14 15 void test01() 16 { 17 set<int>s1; 18 19 //插入数据只有insert方式 20 21 s1.insert(10); 22 s1.insert(40); 23 s1.insert(30); 24 s1.insert(20); 25 s1.insert(30); 26 27 //遍历容器 28 //set容器特点:所有元素在插入的时候回自动排序 29 //set容器不允许插入重复的值 30 printSet(s1); 31 32 //拷贝构造 33 set<int>s2(s1); 34 printSet(s2); 35 36 //赋值 37 set<int>s3; 38 s3 = s2; 39 printSet(s3); 40 41 42 } 43 44 int main() 45 { 46 test01(); 47 48 49 return 0; 50 }

不能重新指定大小
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<set> 4 5 //set容器 大小和交换 6 void printSet(set<int>&s) 7 { 8 for (set<int>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) 9 { 10 cout << *it << " "; 11 } 12 cout << endl; 13 } 14 15 16 //大小 17 void test01() 18 { 19 set<int>s1; 20 21 //插入数据 22 s1.insert(10); 23 s1.insert(30); 24 25 s1.insert(20); 26 s1.insert(40); 27 28 //打印容器 29 printSet(s1); 30 31 //判断是否为空 32 if (s1.empty()) 33 { 34 cout << "s1为空" << endl; 35 } 36 else 37 { 38 cout << "s1不为空" << endl; 39 cout << "s1的大小为:" << s1.size() << endl; 40 } 41 42 } 43 44 //交换 45 void test02() 46 { 47 set<int>s1; 48 49 //插入数据 50 s1.insert(10); 51 s1.insert(30); 52 53 s1.insert(20); 54 s1.insert(40); 55 56 set<int>s2; 57 58 //插入数据 59 s2.insert(100); 60 s2.insert(300); 61 62 s2.insert(200); 63 s2.insert(400); 64 65 cout << "交换前:" << endl; 66 printSet(s1); 67 printSet(s2); 68 69 cout << "交换后:" << endl; 70 s1.swap(s2); 71 printSet(s1); 72 printSet(s2); 73 74 75 76 } 77 78 int main() 79 { 80 //test01(); 81 test02(); 82 83 84 85 return 0; 86 }

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<set> 4 5 //set容器 插入和删除 6 7 void printSet(set<int>&s) 8 { 9 for (set<int>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) 10 { 11 cout << *it << " "; 12 } 13 cout << endl; 14 } 15 16 void test01() 17 { 18 set<int>s1; 19 20 //插入 21 s1.insert(30); 22 23 s1.insert(10); 24 s1.insert(20); 25 s1.insert(40); 26 27 //遍历 28 printSet(s1); 29 30 //删除 看的不是 插入顺序 31 s1.erase(s1.begin()); 32 printSet(s1); 33 34 //删除重载版本 35 s1.erase(30); 36 printSet(s1); 37 38 //清空 39 //s1.erase(s1.begin(), s1.end()); 40 41 s1.clear(); 42 printSet(s1); 43 44 45 46 } 47 48 int main() 49 { 50 test01(); 51 52 53 return 0; 54 }

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<set> 4 5 //set容器 查找和统计 6 7 void test01() 8 { 9 //查找 10 set<int>s1; 11 12 //插入数据 13 s1.insert(10); 14 s1.insert(20); 15 s1.insert(30); 16 s1.insert(40); 17 18 set<int>::iterator pos = s1.find(300); 19 if (pos != s1.end()) 20 { 21 //找到了 22 cout << "找到元素:" << *pos << endl; 23 } 24 else 25 { 26 cout << "未找到元素" << endl; 27 } 28 29 30 31 32 33 } 34 35 36 //统计 37 void test02() 38 { 39 set<int>s1; 40 41 //插入数据 42 s1.insert(10); 43 s1.insert(20); 44 s1.insert(30); 45 s1.insert(40); 46 47 48 //统计30的个数 49 int num = s1.count(30); 50 //对于set而言 统计结果 要么是0 要么是1 51 cout << "num = " << num << endl; 52 53 } 54 55 int main() 56 { 57 //test01(); 58 test02(); 59 60 61 return 0; 62 }
find和count

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<set> 4 5 //set容器 和 multiset容器的区别 6 void test01() 7 { 8 set<int>s; 9 pair<set<int>::iterator,bool> ret = s.insert(10); 10 11 if (ret.second) 12 { 13 cout << "第一次插入成功" << endl; 14 } 15 else 16 { 17 cout << "第一次插入失败" << endl; 18 } 19 20 ret = s.insert(10); 21 22 if (ret.second) 23 { 24 cout << "第二次插入成功" << endl; 25 } 26 else 27 { 28 cout << "第二次插入失败" << endl; 29 } 30 31 32 33 multiset<int>ms; 34 //允许插入重复的值 35 ms.insert(10); 36 ms.insert(10); 37 ms.insert(10); 38 ms.insert(10); 39 40 41 for (multiset<int>::iterator it = ms.begin(); it != ms.end(); it++) 42 { 43 cout << *it << " "; 44 } 45 cout << endl; 46 } 47 48 int main() 49 { 50 test01(); 51 52 return 0; 53 }

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<string> 4 5 //pair对组的创建 6 void test01() 7 { 8 //第一种方式 9 pair<string, int> p("Tom", 20); 10 11 cout << "姓名:" << p.first 12 << " 年龄:" << p.second << endl; 13 14 //第二种方式 15 pair<string, int>p2 = make_pair("Jerry", 30); 16 cout << "姓名:" << p2.first 17 << " 年龄:" << p2.second << endl; 18 19 20 } 21 22 23 int main() 24 { 25 test01(); 26 27 28 return 0; 29 }

示例1存放内置数据类型
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<set> 4 5 //set容器排序 6 7 class MyCompare/**/ 8 { 9 public: 10 bool operator()/*要重载的符号是()*/ (int v1, int v2)/*指的是模板参数列表 11 */ 12 { 13 return v1 > v2; 14 } 15 }; 16 17 void test01() 18 { 19 set<int>s1; 20 21 s1.insert(10); 22 s1.insert(40); 23 s1.insert(20); 24 s1.insert(50); 25 s1.insert(30); 26 27 for (set<int>::iterator it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++) 28 29 { 30 cout << *it << " "; 31 } 32 cout << endl; 33 34 //指定排序规则为从大到小 35 set<int,MyCompare>s2; 36 37 s2.insert(10); 38 s2.insert(40); 39 s2.insert(20); 40 s2.insert(50); 41 s2.insert(30); 42 43 for (set<int>::iterator it = s2.begin(); it != s2.end(); it++) 44 { 45 cout << *it << " "; 46 } 47 cout<< endl; 48 } 49 50 51 int main() 52 { 53 test01(); 54 55 56 57 58 return 0; 59 }
实例2存放自定义数据类型
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<string> 4 #include<set> 5 6 //set容器排序,存放自定义数据类型 7 8 class Person 9 { 10 public: 11 Person(string name, int age) 12 { 13 this->m_Name = name; 14 this->m_Age = age; 15 } 16 17 string m_Name; 18 int m_Age; 19 }; 20 21 22 class comparePerson 23 { 24 public: 25 bool operator()(const Person &p1, const Person &p2) 26 { 27 //按照年龄降序 28 return p1.m_Age > p2.m_Age; 29 30 } 31 32 }; 33 34 void test01() 35 { 36 //自定义数据类型 都会制定排序规则 37 set<Person, comparePerson>s; 38 39 //创建Person对象 40 Person p1("刘备", 24); 41 Person p2("关羽", 28); 42 Person p3("张飞", 25); 43 Person p4("赵云", 21); 44 45 s.insert(p1); 46 s.insert(p2); 47 s.insert(p3); 48 s.insert(p4); 49 50 for (set<Person, comparePerson>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) 51 { 52 cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name 53 << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl; 54 } 55 56 57 } 58 59 int main() 60 { 61 test01(); 62 63 64 65 return 0; 66 }
存放自定义数据类型必须指定排序规则
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zlh-1024powr/p/14628843.html