关于在Spring 容器 初始化和销毁 bean 前所做的操作有三种方式定义:
第一种:通过@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 方法 实现初始化后和销毁bean之前进行的操作
第二种:通过bean实现InitializingBean和 DisposableBean接口
第三种:通过 在xml中配置init-method 和 destory-method方法,或者 配置@Bean(initMethod = "initMethod", destroyMethod = "destroyMethod") 注解
执行顺序:@PostConstruct -> InitializingBean -> 配置initMethod -> @PreDestroy -> DisposableBean -> 配置destroyMethod
本章介绍第二种
第一种见:【Spring】@PostConstruct 与 @PreDestroy 的实现原理(五)
1 public class BeanPerson implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean { 2 3 public void say(String word) { 4 System.out.println("Hello, " + word); 5 } 6 7 public BeanPerson() { 8 System.out.println("BeanPerson() "); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { 13 System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet()......"); 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public void destroy() throws Exception { 18 System.out.println("destroy()......"); 19 } 20 21 }
实现原理是通过代码逻辑判断bean的类型,是否实现的对应的接口
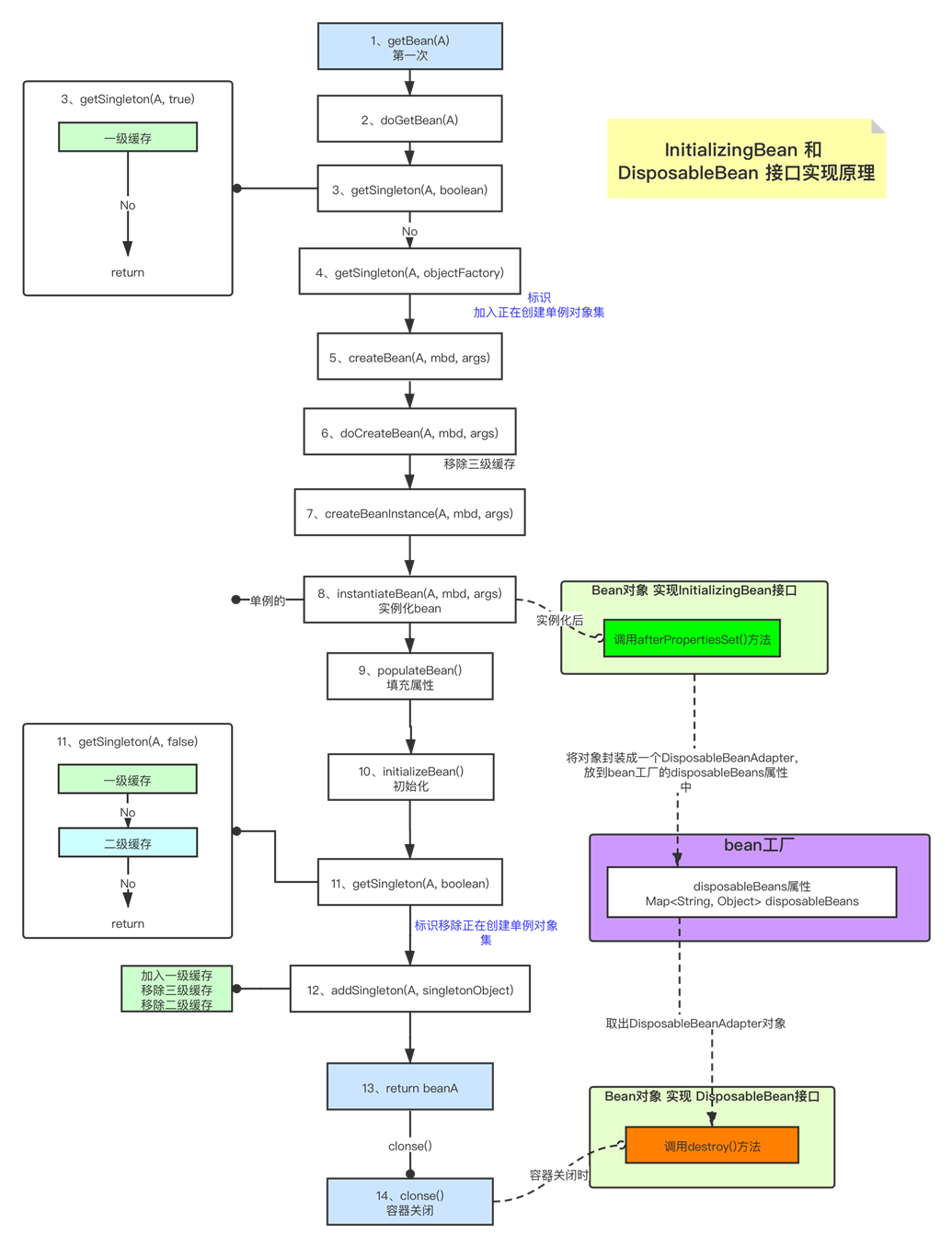
1、实例化bean时,createBeat()->doCreateBeat()->initializeBean()
初始化 initializeBean() 方法如下:
1 protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { 2 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { 3 AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { 4 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); 5 return null; 6 }, getAccessControlContext()); 7 } else { 8 // 若bean实现了XXXAware接口进行方法的回调 9 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); 10 } 11 12 Object wrappedBean = bean; 13 if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { 14 // 支持初始化前bean的后置处理器 15 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); 16 } 17 18 try { 19 // 调用初始化方法 20 invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); 21 } catch (Throwable ex) { 22 throw new BeanCreationException( 23 (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), 24 beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); 25 } 26 if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { 27 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); 28 } 29 30 return wrappedBean; 31 }
2、调用了初始化方法 invokeInitMethods() ,如下:
1 protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) 2 throws Throwable { 3 // 判断容器中是否实现了InitializingBean接口 4 boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean); 5 if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) { 6 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 7 logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name ‘" + beanName + "‘"); 8 } 9 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { 10 try { 11 AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> { 12 ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); 13 return null; 14 }, getAccessControlContext()); 15 } catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) { 16 throw pae.getException(); 17 } 18 } else { 19 // 回调实现InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet()方法 20 ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); 21 } 22 } 23 24 if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) { 25 // bean定义中看是否有配置的init方法 26 String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName(); 27 // 判断自定义的init方法名称不叫afterPropertiesSet 28 if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) && 29 !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) && 30 !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) { 31 // 调用配置的初始化方法 32 invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd); 33 } 34 } 35 }
其中,判断类bean是否属于InitializingBean接口,然后调用了afterPropertiesSet()方法
1、在容器关闭时,调用方法链:context.clonse() -> doClose() -> destroyBeans() -> destroySingletons() ->destroySingleton()
销毁单例方法 destroySingleton() 如下:
1 public void destroySingleton(String beanName) { 2 // Remove a registered singleton of the given name, if any. 3 // 移除缓存 4 removeSingleton(beanName); 5 6 // Destroy the corresponding DisposableBean instance. 7 DisposableBean disposableBean; 8 // 加锁 9 synchronized (this.disposableBeans) { 10 // 根据名称,从需要销毁的是实例集合移除实例,得到disposableBean 11 disposableBean = (DisposableBean) this.disposableBeans.remove(beanName); 12 } 13 // 销毁bean 14 destroyBean(beanName, disposableBean); 15 }
2、从bean工厂的 disposableBeans 中,获取移除对象,而这个 disposableBeans 销毁对象集合中的对象是从注册的时候来的
查看bean创建逻辑: createBeat()->doCreateBeat(),在 doCreateBeat() 调用了registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary() 方法
1 protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args) 2 throws BeanCreationException { 3 4 // Instantiate the bean. 5 // 实例化的bean会封装成一个BeanWrapper对象 6 // BeanWrapper是对Bean的包装,其接口中所定义的功能很简单包括设置获取被包装的对象,获取被包装bean的属性描述器, 7 // 由于BeanWrapper接口是PropertyAccessor的子接口,因此其也可以设置以及访问被包装对象的属性值。 8 BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; 9 if (mbd.isSingleton()) { 10 // 移除工厂bean实例缓存,并获取 11 instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); 12 } 13 if (instanceWrapper == null) { 14 // 使用合适的实例化策略来创建新的实例:工厂方法、构造函数自动注入、简单初始化 该方法很复杂也很重要 15 instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); 16 } 17 // 获取包装Bean中的bean实例 18 final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance(); 19 // 获取包装Bean中的bean的类clazz对象 20 Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass(); 21 if (beanType != NullBean.class) { 22 // 在bean定义中设置类clazz对象类型 23 mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType; 24 } 25 26 ...... 27 28 // Initialize the bean instance. 29 // 早起暴露的对象 30 Object exposedObject = bean; 31 try { 32 // 给的属性进行赋值(调用set方法进行赋值) 33 populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); 34 // 进行对象初始化操作(在这里可能生成代理对象),调用init方法 35 exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); 36 } catch (Throwable ex) { 37 if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) { 38 throw (BeanCreationException) ex; 39 } else { 40 throw new BeanCreationException( 41 mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex); 42 } 43 } 44 45 ...... 46 47 // Register bean as disposable. 48 try { 49 // 注册销毁对象 50 // 将给定Bean添加到该工厂中的可丢弃Bean列表中,注册器可丢弃Bean接口 和/或 51 // 在工厂关闭 时调用给定销毁方法(如果适用)。只适用单例 52 registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd); 53 } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { 54 throw new BeanCreationException( 55 mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex); 56 } 57 58 return exposedObject; 59 }
3、注册销毁对象方法:registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary()
1 protected void registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { 2 // 如果有安全管理器器,获取其访问控制上下文 3 AccessControlContext acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null ? getAccessControlContext() : null); 4 // 判断是否是非多例 && 是否需要在关闭时销毁 5 if (!mbd.isPrototype() && requiresDestruction(bean, mbd)) { 6 if (mbd.isSingleton()) { 7 // Register a DisposableBean implementation that performs all destruction 8 // work for the given bean: DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors, 9 // DisposableBean interface, custom destroy method. 10 // 注册一个一次性Bean实现来执行给定Bean的销毁工作:DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors 一次性Bean接口, 11 // 自定义销毁方法。 12 // DisposableBeanAdapter:实际一次性Bean和可运行接口适配器,对给定Bean实例执行各种销毁步骤 13 // 构建Bean对应的DisposableBeanAdapter对象,与beanName绑定到 注册中心的一次性Bean列表中 14 registerDisposableBean(beanName, 15 new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc)); 16 } 17 else { 18 // A bean with a custom scope... 19 Scope scope = this.scopes.get(mbd.getScope()); 20 if (scope == null) { 21 throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name ‘" + mbd.getScope() + "‘"); 22 } 23 scope.registerDestructionCallback(beanName, 24 new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc)); 25 } 26 } 27 }
4、其中调用了registerDisposableBean() 方法,并且把原对象和一些其他信息封装成了一个DisposableBeanAdapter对象,放入了工厂的 disposableBeans 集合中
1 // 注册需要销毁的是实例 2 public void registerDisposableBean(String beanName, DisposableBean bean) { 3 synchronized (this.disposableBeans) { 4 this.disposableBeans.put(beanName, bean); 5 } 6 }
5、销毁时,从disposableBeans 获取对象,继续从1步骤的 destroyBean() 方法,往下走
1 protected void destroyBean(String beanName, @Nullable DisposableBean bean) { 2 // Trigger destruction of dependent beans first... 3 Set<String> dependencies; 4 // 移除依赖 5 synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) { 6 // Within full synchronization in order to guarantee a disconnected Set 7 dependencies = this.dependentBeanMap.remove(beanName); 8 } 9 if (dependencies != null) { 10 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 11 logger.trace("Retrieved dependent beans for bean ‘" + beanName + "‘: " + dependencies); 12 } 13 for (String dependentBeanName : dependencies) { 14 destroySingleton(dependentBeanName); 15 } 16 } 17 18 // Actually destroy the bean now... 19 // 现在真正销毁 20 if (bean != null) { 21 try { 22 // 调用销毁方法 23 bean.destroy(); 24 } 25 catch (Throwable ex) { 26 if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { 27 logger.warn("Destruction of bean with name ‘" + beanName + "‘ threw an exception", ex); 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 32 // Trigger destruction of contained beans... 33 Set<String> containedBeans; 34 synchronized (this.containedBeanMap) { 35 // Within full synchronization in order to guarantee a disconnected Set 36 containedBeans = this.containedBeanMap.remove(beanName); 37 } 38 if (containedBeans != null) { 39 for (String containedBeanName : containedBeans) { 40 destroySingleton(containedBeanName); 41 } 42 } 43 44 // Remove destroyed bean from other beans‘ dependencies. 45 synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) { 46 for (Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Set<String>>> it = this.dependentBeanMap.entrySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();) { 47 Map.Entry<String, Set<String>> entry = it.next(); 48 Set<String> dependenciesToClean = entry.getValue(); 49 dependenciesToClean.remove(beanName); 50 if (dependenciesToClean.isEmpty()) { 51 it.remove(); 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 56 // Remove destroyed bean‘s prepared dependency information. 57 // 移除依赖关系集中对象 58 this.dependenciesForBeanMap.remove(beanName); 59 }
6、bean.destroy() 方法, 这里的bean对象是 DisposableBeanAdapter对象 如下:
1 // 销毁 2 @Override 3 public void destroy() { 4 if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.beanPostProcessors)) { 5 for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : this.beanPostProcessors) { 6 // 调持销毁前bean的后置处理器 7 processor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(this.bean, this.beanName); 8 } 9 } 10 11 // 判断是否实现DisposableBean接口 12 if (this.invokeDisposableBean) { 13 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 14 logger.trace("Invoking destroy() on bean with name ‘" + this.beanName + "‘"); 15 } 16 try { 17 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { 18 AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> { 19 ((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy(); 20 return null; 21 }, this.acc); 22 } 23 else { 24 // 强转,调用destroy()方法 25 ((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy(); 26 } 27 } 28 catch (Throwable ex) { 29 String msg = "Invocation of destroy method failed on bean with name ‘" + this.beanName + "‘"; 30 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 31 logger.warn(msg, ex); 32 } 33 else { 34 logger.warn(msg + ": " + ex); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 39 if (this.destroyMethod != null) { 40 // 调用配置的销毁方法 41 invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod); 42 } 43 else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) { 44 Method methodToInvoke = determineDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethodName); 45 if (methodToInvoke != null) { 46 // 调用配置的销毁方法 47 invokeCustomDestroyMethod(ClassUtils.getInterfaceMethodIfPossible(methodToInvoke)); 48 } 49 } 50 }
可以看到其中,判断是否实现DisposableBean接口,然后调用了 ((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();
this.bean 即是封装前原实例对象,即调用了原实例对象的 destroy() 方法
【Spring】InitializingBean与 DisposableBean 接口的实现原理(六)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/h--d/p/14656057.html