关于在Spring 容器 初始化和销毁 bean 前所做的操作有三种方式定义:
第一种:通过@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 方法 实现初始化后和销毁bean之前进行的操作
第三种:通过 在xml中配置init-method 和 destory-method方法,或者 配置@Bean(initMethod = "initMethod", destroyMethod = "destroyMethod") 注解
执行顺序:@PostConstruct -> InitializingBean -> 配置initMethod -> @PreDestroy -> DisposableBean -> 配置destroyMethod
本章介绍第一种
1 public class BeanPerson { 2 3 public void say(String word) { 4 System.out.println("Hello, " + word); 5 } 6 7 public BeanPerson() { 8 System.out.println("BeanPerson() "); 9 } 10 11 // 初始化方法 12 @PostConstruct 13 public void postConstruct(){ 14 System.out.println("postConstruct()...."); 15 } 16 17 // 销毁方法 18 @PreDestroy 19 public void preDestroy(){ 20 System.out.println("preDestroy()....."); 21 } 22 23 }
在对应的方法上加上@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 注解即可
实现是通过Bean后置处理器来实现的
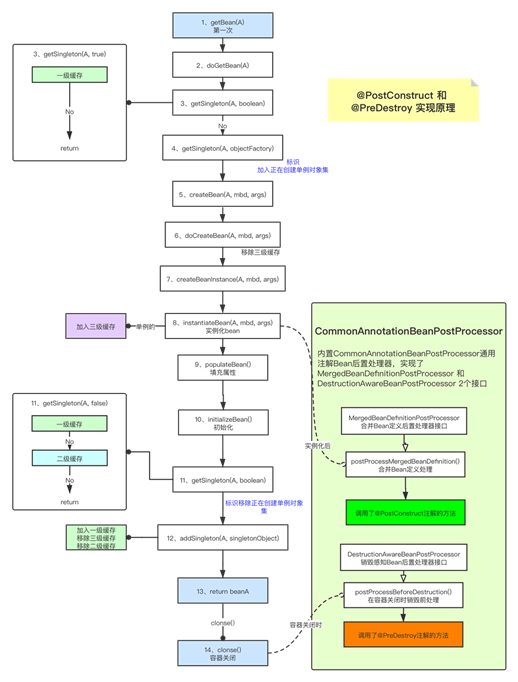
1、在初始化bean的时候,会调用doCreateBean(),方法中代码,支持合并Bean定义后置处理器,由于Spring内置类CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后置处理器,所以调用了CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后置处理器,进行合并Bean定义后置处理
2、调用CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition()方法
1 // 后置处理合并Bean定义 2 @Override 3 public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) { 4 // 后置处理合并Bean定义 5 // 主要是:查找或构建一个生命周期元数据对象,父类postProcessMergedBeanDefinition()方法调用了findLifecycleMetadata() 6 super.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(beanDefinition, beanType, beanName); 7 // 查找或构建一个资源元数据对象(注入信息元数据对象) 8 InjectionMetadata metadata = findResourceMetadata(beanName, beanType, null); 9 metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition); 10 }
3、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor父类InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition()
1 // 后置处理合并Bean定义 2 @Override 3 public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) { 4 // 查找或构建一个生命周期元数据对象 5 LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(beanType); 6 metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition); 7 }
4、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor父类InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的findLifecycleMetadata()方法,查找bean的生命周期元数据对象,没有的话,调用buildLifecycleMetadata(),构建了一个LifecycleMetadata对象(生命周期元数据对象)
1 /** 2 * 查找bean的生命周期元数据对象,没有的话,调用buildLifecycleMetadata(),构建了一个 3 * @param clazz 4 * @return 5 */ 6 private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) { 7 if (this.lifecycleMetadataCache == null) { 8 // Happens after deserialization, during destruction... 9 return buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz); 10 } 11 // Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking. 12 LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz); 13 if (metadata == null) { 14 synchronized (this.lifecycleMetadataCache) { 15 // 根据clazz,构建了一个bean的生命周期元数据对象 16 metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz); 17 if (metadata == null) { 18 metadata = buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz); 19 this.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata); 20 } 21 return metadata; 22 } 23 } 24 return metadata; 25 }
5、调用buildLifecycleMetadata(),构建了一个
1 /** 2 * 构建了一个bean的生命周期元数据对象 3 * 即获得了一个Bean的 初始化方法集合 和 销毁方法集合 4 * @param clazz 5 * @return 6 */ 7 private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) { 8 if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, Arrays.asList(this.initAnnotationType, this.destroyAnnotationType))) { 9 return this.emptyLifecycleMetadata; 10 } 11 12 // 初始化方法集合 13 List<LifecycleElement> initMethods = new ArrayList<>(); 14 // 销毁方法集合 15 List<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new ArrayList<>(); 16 Class<?> targetClass = clazz; 17 18 do { 19 20 final List<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new ArrayList<>(); 21 22 final List<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new ArrayList<>(); 23 24 // 利用反射获取对象方法,进行处理 25 ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> { 26 // 是否是@PostConstruct注解 27 // initAnnotationType这个值在 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor()构造方法中设置 28 if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) { 29 LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method); 30 currInitMethods.add(element); 31 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 32 logger.trace("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method); 33 } 34 } 35 36 // 是否是@PreDestroy 37 if (this.destroyAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.destroyAnnotationType)) { 38 currDestroyMethods.add(new LifecycleElement(method)); 39 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 40 logger.trace("Found destroy method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method); 41 } 42 } 43 }); 44 // 初始化方法集合 45 initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods); 46 // 销毁方法集合 47 destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods); 48 targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass(); 49 } 50 while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class); 51 52 return (initMethods.isEmpty() && destroyMethods.isEmpty() ? this.emptyLifecycleMetadata : 53 new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods)); 54 }
6、创建CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,通用Bean后置处理器的时候,设置了初始化注解、销毁注解
1 // CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor()构造方法, 2 // 初始化了2个值@PostConstruct,@PreDestroy 3 public CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() { 4 setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 3); 5 setInitAnnotationType(PostConstruct.class); 6 setDestroyAnnotationType(PreDestroy.class); 7 ignoreResourceType("javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext"); 8 }
7、doCreateBean(),方法中,支持初始化前bean的后置处理器
调用了CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后置处理器,进行初始化前后置处理
8、调用CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法
1 @Override 2 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 3 // 查找或构建一个生命周期元数据对象(同上) 4 LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass()); 5 try { 6 // 调用初始化方法 7 metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName); 8 } 9 catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { 10 throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex.getTargetException()); 11 } 12 catch (Throwable ex) { 13 throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Failed to invoke init method", ex); 14 } 15 return bean; 16 }
9、调用初始化方法
1 // 调用初始化方法 2 public void invokeInitMethods(Object target, String beanName) throws Throwable { 3 // 获取后置处理器检查过的初始化方法集合 4 Collection<LifecycleElement> checkedInitMethods = this.checkedInitMethods; 5 Collection<LifecycleElement> initMethodsToIterate = 6 (checkedInitMethods != null ? checkedInitMethods : this.initMethods); 7 if (!initMethodsToIterate.isEmpty()) { 8 // 遍历 9 for (LifecycleElement element : initMethodsToIterate) { 10 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 11 logger.trace("Invoking init method on bean ‘" + beanName + "‘: " + element.getMethod()); 12 } 13 // 调用对应的初始化方法 14 element.invoke(target); 15 } 16 } 17 }
和@PostConstruct原理一样只是最后出触发条件不一样,当调用容器close()方法销毁时,会调用doClose(),然后destroy()
7、destroy(),方法中,支持销毁前bean的后置处理器,调用了CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后置处理器,进行销毁前后置处理
1 @Override 2 public void destroy() { 3 if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.beanPostProcessors)) { 4 for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : this.beanPostProcessors) { 5 // 进行销毁前后置处理 6 processor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(this.bean, this.beanName); 7 } 8 } 9 }
8、调调用CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeDestruction()方法
1 // 用销毁前bean的后置处理器方法 2 @Override 3 public void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 4 // 查找或构建一个生命周期元数据对象 5 LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass()); 6 try { 7 // 调用销毁方法 8 metadata.invokeDestroyMethods(bean, beanName); 9 } 10 catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { 11 String msg = "Destroy method on bean with name ‘" + beanName + "‘ threw an exception"; 12 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 13 logger.warn(msg, ex.getTargetException()); 14 } 15 else { 16 logger.warn(msg + ": " + ex.getTargetException()); 17 } 18 } 19 catch (Throwable ex) { 20 logger.warn("Failed to invoke destroy method on bean with name ‘" + beanName + "‘", ex); 21 } 22 }
9、调用销毁方法
1 public void invokeDestroyMethods(Object target, String beanName) throws Throwable { 2 // 获取后置处理器检查过的销毁方法集合 3 Collection<LifecycleElement> checkedDestroyMethods = this.checkedDestroyMethods; 4 Collection<LifecycleElement> destroyMethodsToUse = 5 (checkedDestroyMethods != null ? checkedDestroyMethods : this.destroyMethods); 6 if (!destroyMethodsToUse.isEmpty()) { 7 for (LifecycleElement element : destroyMethodsToUse) { 8 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 9 logger.trace("Invoking destroy method on bean ‘" + beanName + "‘: " + element.getMethod()); 10 } 11 // 调用对应的销毁方法 12 element.invoke(target); 13 } 14 } 15 }
【Spring】@PostConstruct 与 @PreDestroy 的实现原理(五)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/h--d/p/14656012.html