SpringSecurity采用的是责任链的设计模式,它有一条很长的过滤器链。现在对这条过滤器链的15个过滤器进行说明
Spring Security采取过滤链实现认证与授权,只有当前过滤器通过,才能进入下一个过滤器
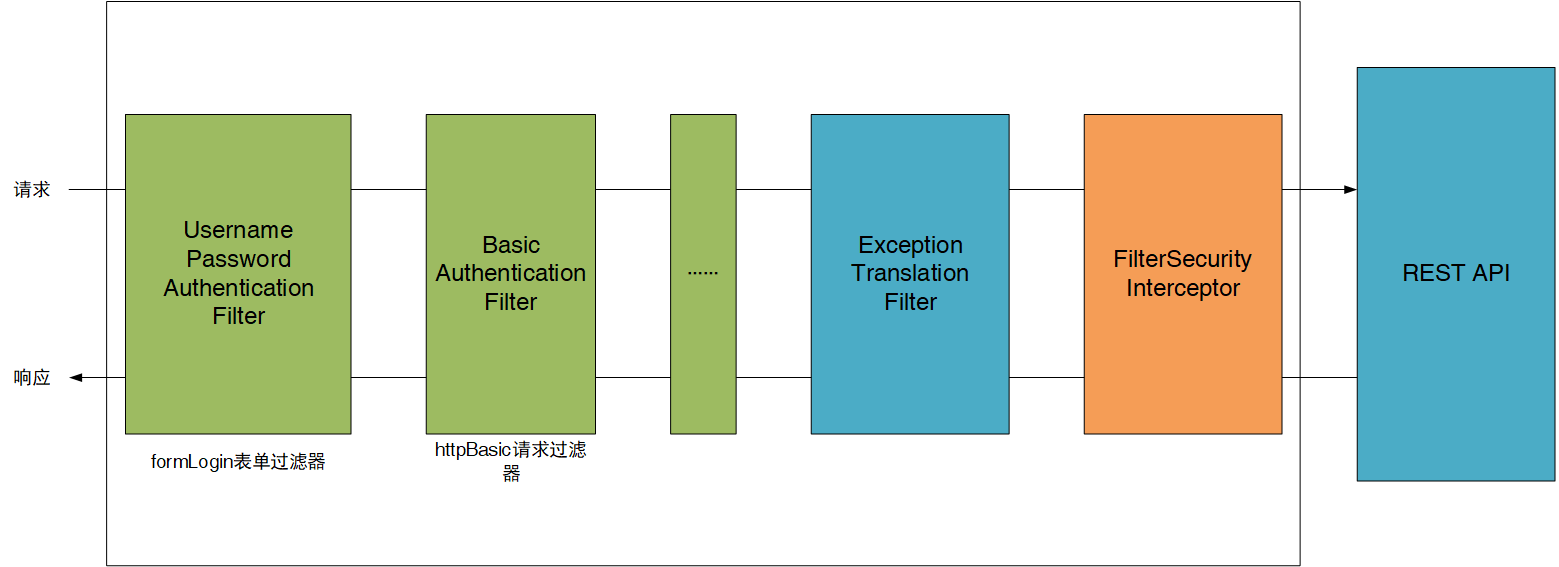
绿色部分是认证过滤器,需要我们自己配置,可以配置多个认证过滤器。认证过滤器可以使用Spring Security提供的认证过滤器,也可以自定义过滤器(例如:短信验证)。认证过滤器要在configure(HttpSecurity http)方法中配置,没有配置不生效。下面会重点介绍以下三个过滤器:
认证流程是在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器中处理的,具体流程如下所示:
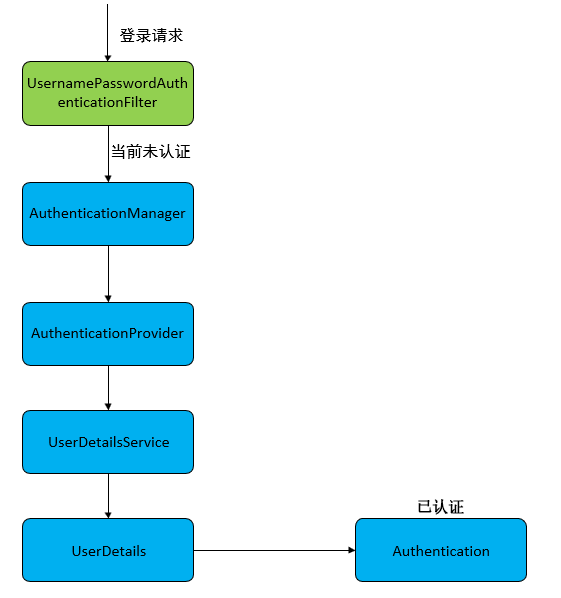
当前端提交的是一个POST 方式的登录表单请求,就会被该过滤器拦截,并进行身份认证。
该过滤器的doFilter() 方法实现首先在其抽象父类AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter中,查看相关源码:
/**
* Invokes the
* {@link #requiresAuthentication(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse)
* requiresAuthentication} method to determine whether the request is for
* authentication and should be handled by this filter. If it is an authentication
* request, the
* {@link #attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse)
* attemptAuthentication} will be invoked to perform the authentication. There are
* then three possible outcomes:
* <ol>
* <li>An <tt>Authentication</tt> object is returned. The configured
* {@link SessionAuthenticationStrategy} will be invoked (to handle any
* session-related behaviour such as creating a new session to protect against
* session-fixation attacks) followed by the invocation of
* {@link #successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, FilterChain, Authentication)}
* method</li>
* <li>An <tt>AuthenticationException</tt> occurs during authentication. The
* {@link #unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, AuthenticationException)
* unsuccessfulAuthentication} method will be invoked</li>
* <li>Null is returned, indicating that the authentication process is incomplete. The
* method will then return immediately, assuming that the subclass has done any
* necessary work (such as redirects) to continue the authentication process. The
* assumption is that a later request will be received by this method where the
* returned <tt>Authentication</tt> object is not null.
* </ol>
*/
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Request is to process authentication");
}
Authentication authResult;
try {
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn‘t completed
// authentication
return;
}
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
logger.error(
"An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.",
failed);
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
// Authentication success
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
判断一个请求是否要再这层filter进行处理
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
调用子类 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 重写的方法进行身份认证,返回的 authResult 对象封装认证后的用户信息
Authentication 是用来存储用户认证信息的类,后续会进行详细介绍
Authentication authResult;
try {
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn‘t completed
// authentication
return;
}
Session 策略处理(如果配置了用户 Session 最大并发数,就是在此处进行判断并处理)
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
认证失败,调用认证失败的处理器
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
logger.error(
"An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.",
failed);
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
/**
* Default behaviour for unsuccessful authentication.
* <ol>
* <li>Clears the {@link SecurityContextHolder}</li>
* <li>Stores the exception in the session (if it exists or
* <tt>allowSesssionCreation</tt> is set to <tt>true</tt>)</li>
* <li>Informs the configured <tt>RememberMeServices</tt> of the failed login</li>
* <li>Delegates additional behaviour to the {@link AuthenticationFailureHandler}.</li>
* </ol>
*/
protected void unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException failed)
throws IOException, ServletException {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication request failed: " + failed.toString(), failed);
logger.debug("Updated SecurityContextHolder to contain null Authentication");
logger.debug("Delegating to authentication failure handler " + failureHandler);
}
rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, failed);
}
认证成功的处理
默认的 continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication为 false,所以认证成功之后不进入下一个过滤器
调用认证成功的处理器
// Authentication success
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
上述的第二过程调用了UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter的attemptAuthentication() 方法,源码如下:
/**
* Processes an authentication form submission. Called
* {@code AuthenticationProcessingFilter} prior to Spring Security 3.0.
* <p>
* Login forms must present two parameters to this filter: a username and password. The
* default parameter names to use are contained in the static fields
* {@link #SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY} and
* {@link #SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY}. The parameter names can also be changed by
* setting the {@code usernameParameter} and {@code passwordParameter} properties.
* <p>
* This filter by default responds to the URL {@code /login}.
*
* @author Ben Alex
* @author Colin Sampaleanu
* @author Luke Taylor
* @since 3.0
*/
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
// ~ Static fields/initializers
// =====================================================================================
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY = "username";
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY = "password";
private String usernameParameter = SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY;
private String passwordParameter = SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY;
private boolean postOnly = true;
// ~ Constructors
// ===================================================================================================
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter() {
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/login", "POST"));
}
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
上述的 doFilter()方法调用此 attenptAuthentication()方法进行身份认证
默认情况下,如果请求方式不是 POST,会抛出异常
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
获取请求携带的 usernane 和 password
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
使用前端传入的 username、password 构造 Authent1cation 对象,标记该对象未认证
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
将请求中的一些属性信息设置到 Authentication 对象中,如:remoteAddress、sessionId
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
调用 ProviderManager 类的 authenticate()方法进行身份认证
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
上述的(3)过程创建的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken是Authentication 接口的实现类,该类有两个构造器,一个用于封装前端请求传入的未认证的用户信息,一个用于封装认证成功后的用户信息:
/**
* An {@link org.springframework.security.core.Authentication} implementation that is
* designed for simple presentation of a username and password.
* <p>
* The <code>principal</code> and <code>credentials</code> should be set with an
* <code>Object</code> that provides the respective property via its
* <code>Object.toString()</code> method. The simplest such <code>Object</code> to use is
* <code>String</code>.
*
* @author Ben Alex
*/
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
private static final long serialVersionUID = SpringSecurityCoreVersion.SERIAL_VERSION_UID;
// ~ Instance fields
// ================================================================================================
private final Object principal;
private Object credentials;
// ~ Constructors
// ===================================================================================================
/**
* This constructor can be safely used by any code that wishes to create a
* <code>UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken</code>, as the {@link #isAuthenticated()}
* will return <code>false</code>.
* 用于封装前端请求传入的未认证的用户信息,前面的 authRequest 对象就是调用该构造器进行构造的
*/
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials) {
super(null); // 用户权限为 null
this.principal = principal; // 前端传入的用户名
this.credentials = credentials; // 前端传入的密码
setAuthenticated(false); // 标记未认证
}
/**
* This constructor should only be used by <code>AuthenticationManager</code> or
* <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> implementations that are satisfied with
* producing a trusted (i.e. {@link #isAuthenticated()} = <code>true</code>)
* authentication token.
* 用于封装认证成功后的用户信息
*
* @param principal
* @param credentials
* @param authorities
*/
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials,
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities); // 用户权限集合
this.principal = principal; // 封装认证用户信息的UserDetails对象,不再是用户名
this.credentials = credentials; // 前端传入的密码
super.setAuthenticated(true); // 标记认证成功
}
Authentication 接口的实现类用于存储用户认证信息,查看该接口具体定义:
/**
* Represents the token for an authentication request or for an authenticated principal
* once the request has been processed by the
* {@link AuthenticationManager#authenticate(Authentication)} method.
* <p>
* Once the request has been authenticated, the <tt>Authentication</tt> will usually be
* stored in a thread-local <tt>SecurityContext</tt> managed by the
* {@link SecurityContextHolder} by the authentication mechanism which is being used. An
* explicit authentication can be achieved, without using one of Spring Security‘s
* authentication mechanisms, by creating an <tt>Authentication</tt> instance and using
* the code:
*
* <pre>
* SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(anAuthentication);
* </pre>
*
* Note that unless the <tt>Authentication</tt> has the <tt>authenticated</tt> property
* set to <tt>true</tt>, it will still be authenticated by any security interceptor (for
* method or web invocations) which encounters it.
* <p>
* In most cases, the framework transparently takes care of managing the security context
* and authentication objects for you.
*
* @author Ben Alex
*/
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
// ~ Methods
// ========================================================================================================
/**
* Set by an <code>AuthenticationManager</code> to indicate the authorities that the
* principal has been granted. Note that classes should not rely on this value as
* being valid unless it has been set by a trusted <code>AuthenticationManager</code>.
* <p>
* Implementations should ensure that modifications to the returned collection array
* do not affect the state of the Authentication object, or use an unmodifiable
* instance.
* </p>
*
* @return the authorities granted to the principal, or an empty collection if the
* token has not been authenticated. Never null.
*/
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
/**
* The credentials that prove the principal is correct. This is usually a password,
* but could be anything relevant to the <code>AuthenticationManager</code>. Callers
* are expected to populate the credentials.
*
* @return the credentials that prove the identity of the <code>Principal</code>
*/
Object getCredentials();
/**
* Stores additional details about the authentication request. These might be an IP
* address, certificate serial number etc.
*
* @return additional details about the authentication request, or <code>null</code>
* if not used
*/
Object getDetails();
/**
* The identity of the principal being authenticated. In the case of an authentication
* request with username and password, this would be the username. Callers are
* expected to populate the principal for an authentication request.
* <p>
* The <tt>AuthenticationManager</tt> implementation will often return an
* <tt>Authentication</tt> containing richer information as the principal for use by
* the application. Many of the authentication providers will create a
* {@code UserDetails} object as the principal.
*
* @return the <code>Principal</code> being authenticated or the authenticated
* principal after authentication.
*/
Object getPrincipal();
/**
* Used to indicate to {@code AbstractSecurityInterceptor} whether it should present
* the authentication token to the <code>AuthenticationManager</code>. Typically an
* <code>AuthenticationManager</code> (or, more often, one of its
* <code>AuthenticationProvider</code>s) will return an immutable authentication token
* after successful authentication, in which case that token can safely return
* <code>true</code> to this method. Returning <code>true</code> will improve
* performance, as calling the <code>AuthenticationManager</code> for every request
* will no longer be necessary.
* <p>
* For security reasons, implementations of this interface should be very careful
* about returning <code>true</code> from this method unless they are either
* immutable, or have some way of ensuring the properties have not been changed since
* original creation.
*
* @return true if the token has been authenticated and the
* <code>AbstractSecurityInterceptor</code> does not need to present the token to the
* <code>AuthenticationManager</code> again for re-authentication.
*/
boolean isAuthenticated();
/**
* See {@link #isAuthenticated()} for a full description.
* <p>
* Implementations should <b>always</b> allow this method to be called with a
* <code>false</code> parameter, as this is used by various classes to specify the
* authentication token should not be trusted. If an implementation wishes to reject
* an invocation with a <code>true</code> parameter (which would indicate the
* authentication token is trusted - a potential security risk) the implementation
* should throw an {@link IllegalArgumentException}.
*
* @param isAuthenticated <code>true</code> if the token should be trusted (which may
* result in an exception) or <code>false</code> if the token should not be trusted
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if an attempt to make the authentication token
* trusted (by passing <code>true</code> as the argument) is rejected due to the
* implementation being immutable or implementing its own alternative approach to
* {@link #isAuthenticated()}
*/
void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
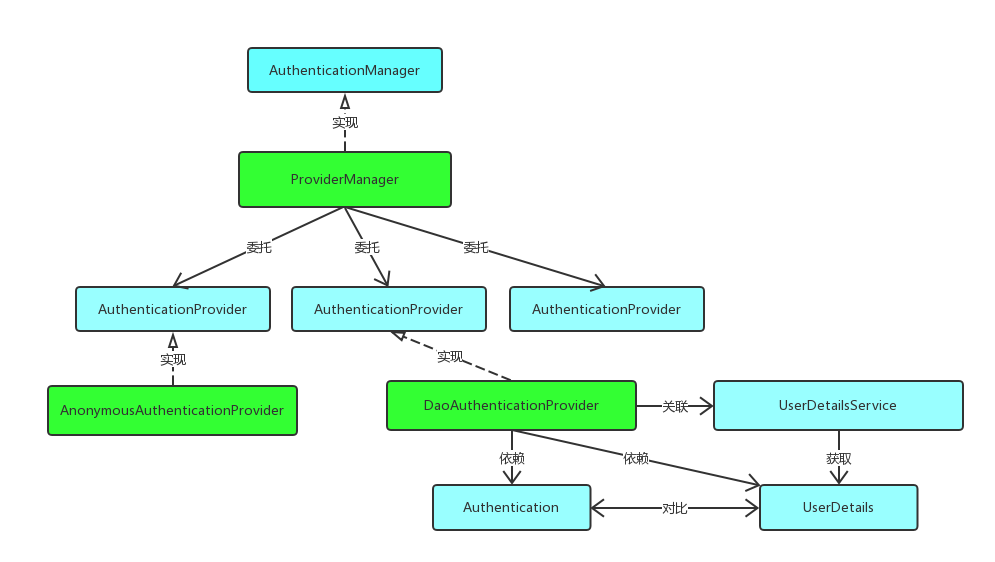
上述过程中,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器的attemptAuthentication() 方法的(5)过程将未认证的Authentication 对象传入ProviderManager 类的authenticate() 方法进行身份认证。
ProviderManager 是AuthenticationManager 接口的实现类,该接口是认证相关的核心接口,也是认证的入口。在实际开发中,我们可能有多种不同的认证方式,例如:用户名+密码、邮箱+密码、手机号+验证码等,而这些认证方式的入口始终只有一个,那就是AuthenticationManager。在该接口的常用实现类ProviderManager 内部会维护一个List
/**
* Attempts to authenticate the passed {@link Authentication} object.
* <p>
* The list of {@link AuthenticationProvider}s will be successively tried until an
* <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> indicates it is capable of authenticating the
* type of <code>Authentication</code> object passed. Authentication will then be
* attempted with that <code>AuthenticationProvider</code>.
* <p>
* If more than one <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> supports the passed
* <code>Authentication</code> object, the first one able to successfully
* authenticate the <code>Authentication</code> object determines the
* <code>result</code>, overriding any possible <code>AuthenticationException</code>
* thrown by earlier supporting <code>AuthenticationProvider</code>s.
* On successful authentication, no subsequent <code>AuthenticationProvider</code>s
* will be tried.
* If authentication was not successful by any supporting
* <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> the last thrown
* <code>AuthenticationException</code> will be rethrown.
*
* @param authentication the authentication request object.
*
* @return a fully authenticated object including credentials.
*
* @throws AuthenticationException if authentication fails.
*/
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
AuthenticationException parentException = null;
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using "
+ provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException | InternalAuthenticationServiceException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
// SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to
// invalid account status
throw e;
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
}
}
if (result == null && parent != null) {
// Allow the parent to try.
try {
result = parentResult = parent.authenticate(authentication);
}
catch (ProviderNotFoundException e) {
// ignore as we will throw below if no other exception occurred prior to
// calling parent and the parent
// may throw ProviderNotFound even though a provider in the child already
// handled the request
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = parentException = e;
}
}
if (result != null) {
if (eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication
&& (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
// Authentication is complete. Remove credentials and other secret data
// from authentication
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
// If the parent AuthenticationManager was attempted and successful then it will publish an AuthenticationSuccessEvent
// This check prevents a duplicate AuthenticationSuccessEvent if the parent AuthenticationManager already published it
if (parentResult == null) {
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
}
return result;
}
// Parent was null, or didn‘t authenticate (or throw an exception).
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(messages.getMessage(
"ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() },
"No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
// If the parent AuthenticationManager was attempted and failed then it will publish an AbstractAuthenticationFailureEvent
// This check prevents a duplicate AbstractAuthenticationFailureEvent if the parent AuthenticationManager already published it
if (parentException == null) {
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
}
throw lastException;
}
获取传入的 Authentication 类型,即 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
循环迭代
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
判断当前 AuthenticationProvider是否适用UsernanePasswordAuthenticationToken.class类型的
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
成功找到适配当前认证方式的 AuthenticationProvider,此处为 DaoAuthenticationProvider
调用 DaoAuthenticationProvider的 authenticate()方法进行认证。如果认证成功,会返回一个标记已认证的 Authent1cation 对象
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
认证成功后,将传入的 Authentication对象中的 deta1ls 信息拷贝到已认证的 Authentication对象
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
认证成功之后,去除 result 的敏感信息,要求相关类实现CredentialsContainer 接口
去除过程就是调用 CredentialsContainer 接口的 eraseCredentials()方法
if (eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication
&& (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
// Authentication is complete. Remove credentials and other secret data
// from authentication
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
发布认证成功的事件
// If the parent AuthenticationManager was attempted and successful then it will publish an AuthenticationSuccessEvent
// This check prevents a duplicate AuthenticationSuccessEvent if the parent AuthenticationManager already published it
if (parentResult == null) {
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
}
认证失败之后,抛出失败的异常信息
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(messages.getMessage(
"ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() },
"No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
// If the parent AuthenticationManager was attempted and failed then it will publish an AbstractAuthenticationFailureEvent
// This check prevents a duplicate AbstractAuthenticationFailureEvent if the parent AuthenticationManager already published it
if (parentException == null) {
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
}
上述认证成功之后的(6)过程,调用CredentialsContainer 接口定义的eraseCredentials() 方法去除敏感信息。查看UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 实现的eraseCredentials() 方法,该方法实现在其父类中:
父类实现了 CredentialsContainer 接口
/**
* Base class for <code>Authentication</code> objects.
* <p>
* Implementations which use this class should be immutable.
*
* @author Ben Alex
* @author Luke Taylor
*/
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationToken implements Authentication,
CredentialsContainer {
/**
* Checks the {@code credentials}, {@code principal} and {@code details} objects,
* invoking the {@code eraseCredentials} method on any which implement
* {@link CredentialsContainer}.
*/
public void eraseCredentials() {
eraseSecret(getCredentials());
eraseSecret(getPrincipal());
eraseSecret(details);
}
private void eraseSecret(Object secret) {
if (secret instanceof CredentialsContainer) {
((CredentialsContainer) secret).eraseCredentials();
}
}
credentials(前端传入的密码)会置为 null
eraseSecret(getCredentials());
principal 在已认证的 Authentication 中是 UserDetails 实现类;如果该实现类想要去除敏感信息,需要实现 CredentialsContainer 接口的 eraseCredentials()方法;由于我们自定义的 user 类没有实现该接口,所以不进行任何操作。
eraseSecret(getPrincipal());
上述过程就是认证流程的最核心部分,接下来重新回到UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器的doFilter() 方法,查看认证成功/失败的处理
查看 successfulAuthentication()和unsuccessfulAuthentication()方法源码:
/**
* Default behaviour for successful authentication.
* <ol>
* <li>Sets the successful <tt>Authentication</tt> object on the
* {@link SecurityContextHolder}</li>
* <li>Informs the configured <tt>RememberMeServices</tt> of the successful login</li>
* <li>Fires an {@link InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent} via the configured
* <tt>ApplicationEventPublisher</tt></li>
* <li>Delegates additional behaviour to the {@link AuthenticationSuccessHandler}.</li>
* </ol>
*
* Subclasses can override this method to continue the {@link FilterChain} after
* successful authentication.
* @param request
* @param response
* @param chain
* @param authResult the object returned from the <tt>attemptAuthentication</tt>
* method.
* @throws IOException
* @throws ServletException
*/
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication success. Updating SecurityContextHolder to contain: "
+ authResult);
}
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
authResult, this.getClass()));
}
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}
认证成功后的处理:
将认证成功的用户信息对象Authentication封装进 SecurityContext 对象中,并存入 SecurityContext
SecurityContextHolder是对 ThreadLocal 的一个封装,后续会介绍
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
renenberMe 的处理
rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
发布认证成功的事件
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
authResult, this.getClass()));
}
调用认证成功处理器
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
/**
* Default behaviour for unsuccessful authentication.
* <ol>
* <li>Clears the {@link SecurityContextHolder}</li>
* <li>Stores the exception in the session (if it exists or
* <tt>allowSesssionCreation</tt> is set to <tt>true</tt>)</li>
* <li>Informs the configured <tt>RememberMeServices</tt> of the failed login</li>
* <li>Delegates additional behaviour to the {@link AuthenticationFailureHandler}.</li>
* </ol>
*/
protected void unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException failed)
throws IOException, ServletException {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication request failed: " + failed.toString(), failed);
logger.debug("Updated SecurityContextHolder to contain null Authentication");
logger.debug("Delegating to authentication failure handler " + failureHandler);
}
rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, failed);
}
认证失败后的处理:
清除该线程在 SecurityContextHolder 中对应的 SecurityContext 对象
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication request failed: " + failed.toString(), failed);
logger.debug("Updated SecurityContextHolder to contain null Authentication");
logger.debug("Delegating to authentication failure handler " + failureHandler);
}
remenberMe 的处理
rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
调用认证失败处理器
failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, failed);
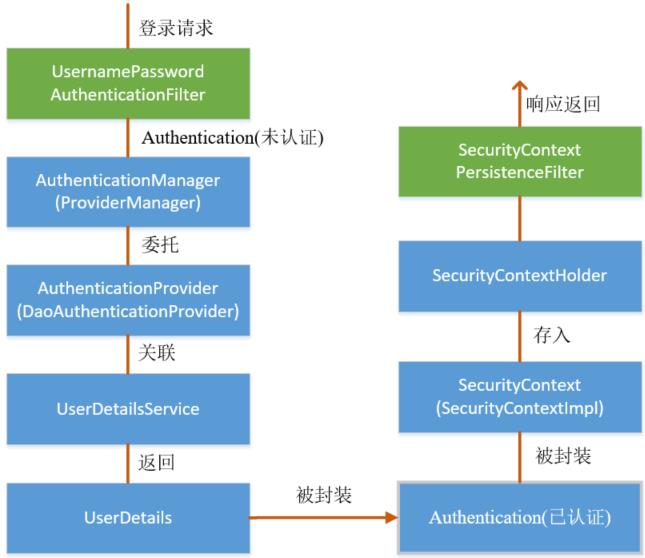
上一个部分通过源码的方式介绍了认证流程,下面介绍权限访问流程,主要是对ExceptionTranslationFilter过滤器和FilterSecurityInterceptor过滤器进行介绍。
该过滤器是用于处理异常的,不需要我们配置,对于前端提交的请求会直接放行,捕获后续抛出的异常并进行处理(例如:权限访问限制)。具体源码如下:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
logger.debug("Chain processed normally");
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace
Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
if (ase == null) {
ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(
AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
}
if (ase != null) {
if (response.isCommitted()) {
throw new ServletException("Unable to handle the Spring Security Exception because the response is already committed.", ex);
}
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase);
}
else {
// Rethrow ServletExceptions and RuntimeExceptions as-is
if (ex instanceof ServletException) {
throw (ServletException) ex;
}
else if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
// Wrap other Exceptions. This shouldn‘t actually happen
// as we‘ve already covered all the possibilities for doFilter
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
对于前端提交的请求会直接放行,不进行拦截
try {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
logger.debug("Chain processed normally");
}
捕获后续出现的异常进行处理
catch (Exception ex) {
// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace
Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
if (ase == null) {
ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(
AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
}
访问需要认证的资源,但当前请求未认证所抛出的异常
RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
访问权限受限的资源所抛出的异常
ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(
AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
FilterSecurityInterceptor是过滤器链的最后一个过滤器,该过滤器是过滤器链的最后一个过滤器,根据资源权限配置来判断当前请求是否有权限访问对应的资源。如果访问受限会抛出相关异常,最终所抛出的异常会由前一个过滤器ExceptionTranslationFilter进行捕获和处理。
具体源码如下:
/**
* Method that is actually called by the filter chain. Simply delegates to the
* {@link #invoke(FilterInvocation)} method.
*
* @param request the servlet request
* @param response the servlet response
* @param chain the filter chain
*
* @throws IOException if the filter chain fails
* @throws ServletException if the filter chain fails
*/
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
invoke(fi);
}
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
if ((fi.getRequest() != null)
&& (fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null)
&& observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don‘t re-do security checking
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
else {
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
if (fi.getRequest() != null && observeOncePerRequest) {
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}
根据资源权限配置来判断当前请求是否有权限访问对应的资源。如果不能访问,则抛出相应的异常
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
访问相关资源,通过 SpringMVc 的核心组件 DispatcherServlet 进行访问
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
需要注意,Spring Security的过滤器链是配置在SpringMVC 的核心组件DispatcherServlet 运行之前。也就是说,请求通过Spring Security的所有过滤器,不意味着能够正常访问资源,该请求还需要通过SpringMVC 的拦截器链。
一般认证成功后的用户信息是通过Session 在多个请求之间共享,那么Spring Security中是如何实现将已认证的用户信息对象Authentication 与Session 绑定的进行具体分析。
在前面讲解认证成功的处理方法successfulAuthentication() 时,有以下代码:
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication success. Updating SecurityContextHolder to contain: "
+ authResult);
}
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
查看SecurityContext 接口及其实现类SecurityContextImpl,该类其实就是对Authentication 的封装
/**
* Base implementation of {@link SecurityContext}.
* <p>
* Used by default by {@link SecurityContextHolder} strategies.
*
* @author Ben Alex
*/
public class SecurityContextImpl implements SecurityContext {
private static final long serialVersionUID = SpringSecurityCoreVersion.SERIAL_VERSION_UID;
// ~ Instance fields
// ================================================================================================
private Authentication authentication;
public SecurityContextImpl() {}
public SecurityContextImpl(Authentication authentication) {
this.authentication = authentication;
}
查看SecurityContextHolder类 , 该类其实是对ThreadLocal的封装 ,存储SecurityContext 对象
public class SecurityContextHolder {
// ~ Static fields/initializers
// =====================================================================================
public static final String MODE_THREADLOCAL = "MODE_THREADLOCAL";
public static final String MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL = "MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL";
public static final String MODE_GLOBAL = "MODE_GLOBAL";
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTY = "spring.security.strategy";
private static String strategyName = System.getProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY);
private static SecurityContextHolderStrategy strategy;
private static int initializeCount = 0;
默认使用MODE_THREADLOCAL模式
默认使用 ThreadLocalSecur1tyContextHolderStrategy 创建 strategy,其内部使用 ThreadLocal对SecurityContext进行存储
private static void initialize() {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(strategyName)) {
// Set default
strategyName = MODE_THREADLOCAL;
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(strategyName)) {
// Set default
strategyName = MODE_THREADLOCAL;
}
if (strategyName.equals(MODE_THREADLOCAL)) {
strategy = new ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy();
}
else if (strategyName.equals(MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL)) {
strategy = new InheritableThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy();
}
else if (strategyName.equals(MODE_GLOBAL)) {
strategy = new GlobalSecurityContextHolderStrategy();
}
else {
// Try to load a custom strategy
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(strategyName);
Constructor<?> customStrategy = clazz.getConstructor();
strategy = (SecurityContextHolderStrategy) customStrategy.newInstance();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
ReflectionUtils.handleReflectionException(ex);
}
}
initializeCount++;
}
需要注意,如果当前线程对应的 ThreadLocal
/**
* Obtain the current <code>SecurityContext</code>.
*
* @return the security context (never <code>null</code>)
*/
public static SecurityContext getContext() {
return strategy.getContext();
}
设置当前线程对应的 ThreadLocal
/**
* Associates a new <code>SecurityContext</code> with the current thread of execution.
*
* @param context the new <code>SecurityContext</code> (may not be <code>null</code>)
*/
public static void setContext(SecurityContext context) {
strategy.setContext(context);
}
清空当前线程对应的 ThreadLocal
/**
* Explicitly clears the context value from the current thread.
*/
public static void clearContext() {
strategy.clearContext();
}
ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy
/**
* A <code>ThreadLocal</code>-based implementation of
* {@link SecurityContextHolderStrategy}.
*
* @author Ben Alex
*
* @see java.lang.ThreadLocal
* @see org.springframework.security.core.context.web.SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
*/
final class ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy implements
SecurityContextHolderStrategy {
// ~ Static fields/initializers
// =====================================================================================
private static final ThreadLocal<SecurityContext> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
使用 ThreadLocal对 SecurityContext 进行存储
private static final ThreadLocal<SecurityContext> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
需要注意,如果当前线程对应的 ThreadLocal
public SecurityContext getContext() {
SecurityContext ctx = contextHolder.get();
if (ctx == null) {
ctx = createEmptyContext();
contextHolder.set(ctx);
}
return ctx;
}
设置当前线程对应的 ThreadLocal
public void setContext(SecurityContext context) {
Assert.notNull(context, "Only non-null SecurityContext instances are permitted");
contextHolder.set(context);
}
清空当前线程对应的 ThreadLocal
public void clearContext() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
创建一个空的 SecurityContext 对象
public SecurityContext createEmptyContext() {
return new SecurityContextImpl();
}
前面提到过,在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器认证成功之后,会在认证成功的处理方法中将已认证的用户信息对象Authentication 封装进SecurityContext,并存入SecurityContextHolder。
之后,响应会通过SecurityContextPersistenceFilter过滤器,该过滤器的位置在所有过滤器的最前面,请求到来先进它,响应返回最后一个通过它,所以在该过滤器中处理已认证的用户信息对象Authentication 与Session 绑定。
认证成功的响应通过SecurityContextPersistenceFilter过滤器时,会从SecurityContextHolder 中取出封装了已认证用户信息对象Authentication 的SecurityContext,放进Session 中。当请求再次到来时,请求首先经过该过滤器,该过滤器会判断当前请求的Session 是否存有SecurityContext 对象,如果有则将该对象取出再次放入SecurityContextHolder 中,之后该请求所在的线程获得认证用户信息,后续的资源访问不需要进行身份认证;当响应再次返回时,该过滤器同样从SecurityContextHolder 取出SecurityContext 对象,放入Session 中。具体源码如下:
public class SecurityContextPersistenceFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
if (request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null) {
// ensure that filter is only applied once per request
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
request.setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
if (forceEagerSessionCreation) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
if (debug && session.isNew()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly created session: " + session.getId());
}
}
HttpRequestResponseHolder holder = new HttpRequestResponseHolder(request,
response);
SecurityContext contextBeforeChainExecution = repo.loadContext(holder);
try {
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(contextBeforeChainExecution);
chain.doFilter(holder.getRequest(), holder.getResponse());
}
finally {
SecurityContext contextAfterChainExecution = SecurityContextHolder
.getContext();
// Crucial removal of SecurityContextHolder contents - do this before anything
// else.
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
repo.saveContext(contextAfterChainExecution, holder.getRequest(),
holder.getResponse());
request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED);
if (debug) {
logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder now cleared, as request processing completed");
}
}
}
}
请求到来时,检查当前 Session 中是否存有SecurityContext 对象,如果有,从Session中取出该对象;如果没有,创建一个空的 SecurityContext对象
SecurityContext contextBeforeChainExecution = repo.loadContext(holder);
将上述获得 SecurityContext对象放入 SecurityContextHolder中
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(contextBeforeChainExecution);
进入下ー个过滤器
chain.doFilter(holder.getRequest(), holder.getResponse());
响应返回时,从 SecurityContextHolder 中取出 SecurityContext
SecurityContext contextAfterChainExecution = SecurityContextHolder
.getContext();
移除 SecurityContextHolder 中的SecurityContext 对象
// Crucial removal of SecurityContextHolder contents - do this before anything
// else.
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
将取出的 SecurityContext 对象放进 Session
repo.saveContext(contextAfterChainExecution, holder.getRequest(),
holder.getResponse());
request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED);
if (debug) {
logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder now cleared, as request processing completed");
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/iamfatotaku/p/14675149.html