ltv 如果某时间不完成,会影响后续其它活动的开始)
lte 如果某时间不开始,则自身的剩余时间会不够用,影响后面顶点状态的完成时间点(从而推迟工期)
etv[n] 等于Vn的etv值 加上其后弧权值的和,可能存在多条路径,取最大值
ete 等于 etv[n] 因为etv事件的结束,也是以其后弧活动的开始
ltv[n] 等于Vn的ltv 减去 其前弧的权值,可能存在多条路径,取最小值(也就是以后面最大权值的弧为活动依据,否则会延期工程)
lte 等于 Vn的ltv 减去其前弧的权值(用此值和ete比较,如果相等则说明没有空闲,在工程的关键路径上), 只计算一次
图来自《大话数据结构》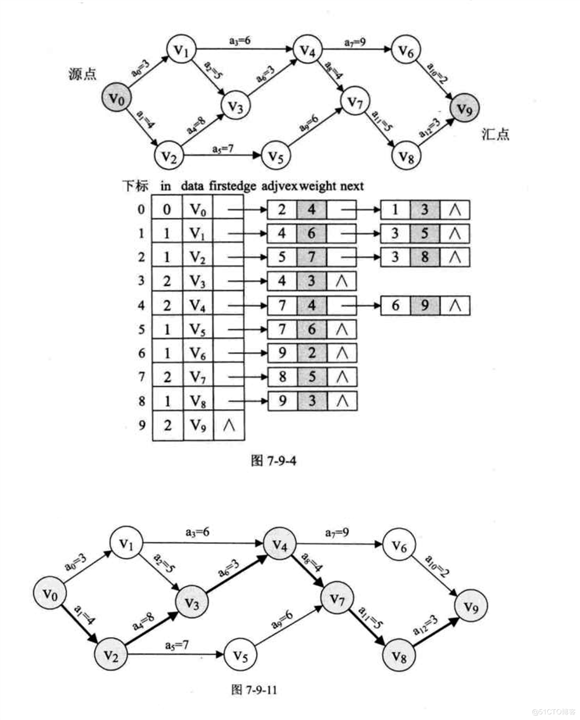
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/*
* 实现《大话数据结构》p287图7-9-11 关键路径
*/
#define MAXVEX 32
// 边表节点类型
typedef struct EdgeNode {
int adjVex;
int weight; // 弧的权值
struct EdgeNode *next;
}EdgeNode, *PE;
// 顶点表节点类型
typedef struct VertexNode {
int in; // 入度
int data; // 顶点的数据,简单用数字标识
PE firstEdge;
}VertexNode, *PV, AdjList[MAXVEX];
// 定义图
typedef struct {
AdjList adjList;
int numVertex, numEdge; // 未使用numEdge
}GraphAdjList, *PG;
// 全局变量
int ete, lte, *etv, *ltv;
int top2; // stack2的栈顶指针
int *stack2; // 复用拓扑排序的代码,把打印顶点改为入栈操作
void create(PG);
void topological(GraphAdjList);
void display(GraphAdjList);
void criticalPath(GraphAdjList);
void criticalPath(GraphAdjList graph)
{
int i, gettop, k;
PE e;
// 初始化ltv
ltv = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*graph.numVertex);
for (i=0; i<graph.numVertex; i++) {
ltv[i] = etv[graph.numVertex-1]; // ltv默认等于etv的最大值,即v9的etv
}
// 开始遍历, 计算ltv
while (top2 != 0) {
// 出栈,先输出的是V9顶点
gettop = stack2[top2--];
// 遍历出栈顶点的边表节点(V9的无边表节点,所以不会的进行此循环)
for (e = graph.adjList[gettop].firstEdge; e; e = e->next) {
// 保存节点下标
k = e->adjVex;
if (ltv[k] - e->weight < ltv[gettop]) // 取最小
ltv[gettop] = ltv[k] - e->weight;
}
}
// 比较ete lte找到关键路径
printf("关键路径为:\n");
for (i=0; i<graph.numVertex; i++) {
ete = etv[i]; // 直接赋值
for (e = graph.adjList[i].firstEdge; e; e=e->next) {
k = e->adjVex;
lte = ltv[k] - e->weight;
if (ete == lte) {
printf("<%d, %d>len[%d] -> ", i, k, e->weight); // 简单一些下村即顶点名
}
}
}
putchar(‘\n‘);
}
void display(GraphAdjList graph)
{
int i, k;
PE e;
for (i=0; i<graph.numVertex; ++i) {
printf("v%d, in %d, arcs:", graph.adjList[i].data, graph.adjList[i].in);
e = graph.adjList[i].firstEdge;
while (e) {
k = e->adjVex;
printf("->%d", graph.adjList[k].data);
e = e->next;
}
putchar(‘\n‘);
}
}
void topological(GraphAdjList graph)
{
int i;
int *stack; // 存放入度非0的顶点下标
int top; // 栈顶指针下标
int gettop; // 取栈顶
int count; // 打印顶点(入度为0)计算器
PE e;
count = 0;
top = 0; // 0为表示栈为空
stack = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * graph.numVertex);
// 先扫一遍,初始化栈
for (i=0; i<graph.numVertex; i++) {
if (graph.adjList[i].in == 0)
stack[++top] = i;
}
// 添加etv stack2初始化
top2 = 0;
stack2 = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * graph.numVertex);
etv = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * graph.numVertex);
for (i=0; i<graph.numVertex; i++) {
etv[i] = 0;
}
// 如果存在入度为0的顶点,则开始处理
printf("拓扑序列:\n");
while (top) {
gettop = stack[top--]; // 出栈,同时更新栈顶指针
printf("%d ", graph.adjList[gettop].data); // 打印顶点
// 添加stack2入栈
stack2[++top2] = gettop;
count++;
// 删除顶点相关的弧(操作为弧头顶点入度减1,如果减到0则弧头顶点入栈)
e = graph.adjList[gettop].firstEdge;
while (e) {
i = e->adjVex;
if (! --graph.adjList[i].in)
stack[++top] = i;
// 添加计算etv逻辑
// 因为etv初始状态都是0,所以会依次更新顶点的etv值
if (etv[gettop] + e->weight > etv[i])
etv[i] = etv[gettop] + e->weight;
e = e->next;
}
}
putchar(‘\n‘);
if (count == graph.numVertex)
printf("拓扑排序成功, 无环\n");
else
printf("拓扑排序失败, 有环\n");
}
void create(PG g)
{
int i;
PE e;
g->numVertex = 10;
for (i=0; i<g->numVertex; i++) {
g->adjList[i].data = i; // i即为顶点名Vi
g->adjList[i].firstEdge = NULL;
}
// 填充邻接表(添加时顺序保持与书中7-9-4一致《大话数据结构》)
// v0
g->adjList[0].in = 0;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 2;
e->weight = 4;
e->next = g->adjList[0].firstEdge;
g->adjList[0].firstEdge = e;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 1;
e->weight = 3;
e->next = g->adjList[0].firstEdge;
g->adjList[0].firstEdge = e;
// v1
g->adjList[1].in = 1;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 4;
e->weight = 6;
e->next = g->adjList[1].firstEdge;
g->adjList[1].firstEdge = e;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 3;
e->weight = 5;
e->next = g->adjList[1].firstEdge;
g->adjList[1].firstEdge = e;
// v2
g->adjList[2].in = 1;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 5;
e->weight = 7;
e->next = g->adjList[2].firstEdge;
g->adjList[2].firstEdge = e;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 3;
e->weight = 8;
e->next = g->adjList[2].firstEdge;
g->adjList[2].firstEdge = e;
// v3
g->adjList[3].in = 2;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 4;
e->weight = 3;
e->next = g->adjList[3].firstEdge;
g->adjList[3].firstEdge = e;
// v4
g->adjList[4].in = 2;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 7;
e->weight = 4;
e->next = g->adjList[4].firstEdge;
g->adjList[4].firstEdge = e;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 6;
e->weight = 9;
e->next = g->adjList[4].firstEdge;
g->adjList[4].firstEdge = e;
// v5
g->adjList[5].in = 1;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 7;
e->weight = 6;
e->next = g->adjList[5].firstEdge;
g->adjList[5].firstEdge = e;
// v6
g->adjList[6].in = 1;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 9;
e->weight = 2;
e->next = g->adjList[6].firstEdge;
g->adjList[6].firstEdge = e;
// v7
g->adjList[7].in = 2;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 8;
e->weight = 5;
e->next = g->adjList[7].firstEdge;
g->adjList[7].firstEdge = e;
// v8
g->adjList[8].in = 1;
e = (PE)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjVex = 9;
e->weight = 3;
e->next = g->adjList[8].firstEdge;
g->adjList[8].firstEdge = e;
// v9
g->adjList[9].in = 2;
}
int main(void)
{
GraphAdjList graph;
create(&graph);
display(graph);
topological(graph);
criticalPath(graph);
return 0;
}
output
[root@8be225462e66 c]# gcc criticalPath.c && ./a.out
v0, in 0, arcs:->1->2
v1, in 1, arcs:->3->4
v2, in 1, arcs:->3->5
v3, in 2, arcs:->4
v4, in 2, arcs:->6->7
v5, in 1, arcs:->7
v6, in 1, arcs:->9
v7, in 2, arcs:->8
v8, in 1, arcs:->9
v9, in 2, arcs:
拓扑序列:
0 2 5 1 3 4 7 8 6 9
拓扑排序成功, 无环
关键路径为:
<0, 2>len[4] -> <2, 3>len[8] -> <3, 4>len[3] -> <4, 7>len[4] -> <7, 8>len[5] -> <8, 9>len[3] ->
[root@8be225462e66 c]#原文:https://blog.51cto.com/sndapk/2720758