

有一个现成的准确度的meter就是 m e t r i c s . A c c u r a c y ( ) metrics.Accuracy()metrics.Accuracy()。
如果只是简单的求一个平均值的话,有一个更加通用的meter就是 m e t r i c s . M e a n ( ) metrics.Mean()metrics.Mean()。
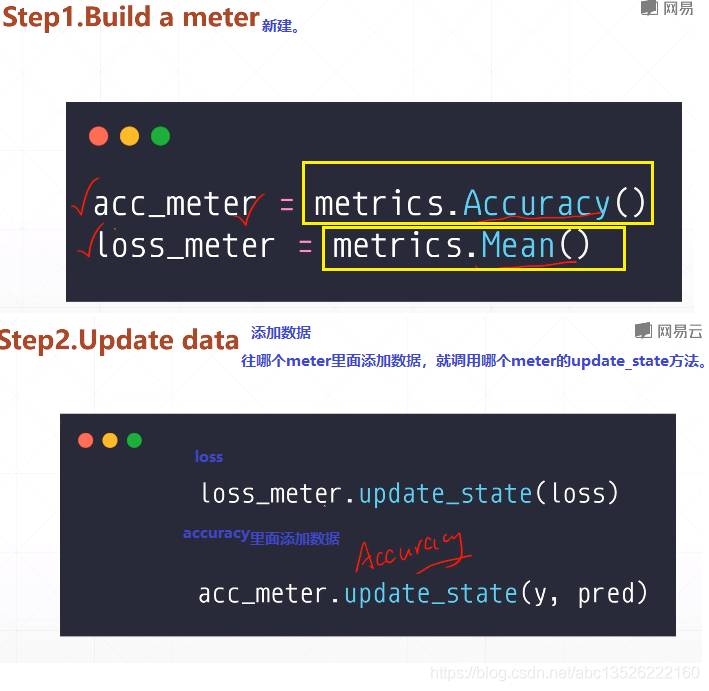
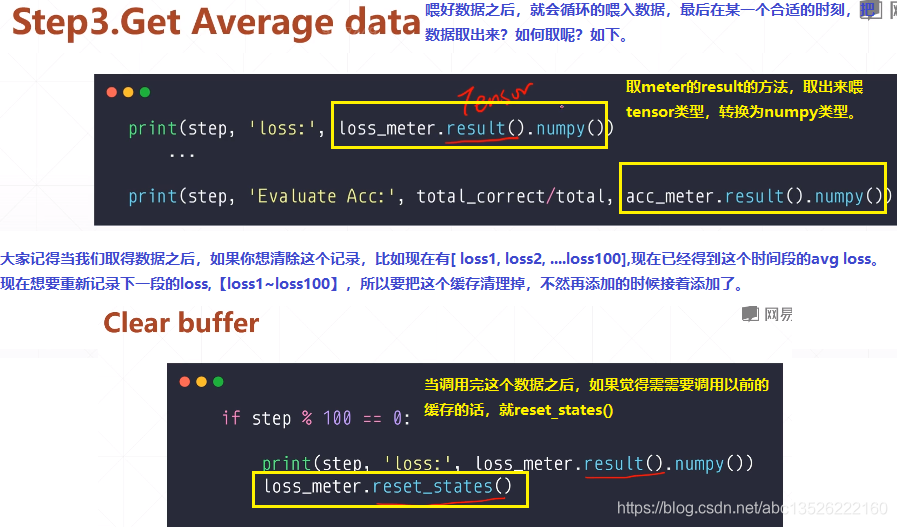
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, optimizers, Sequential, metrics def preprocess(x, y): x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255. y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32) return x, y batchsz = 128 (x, y), (x_val, y_val) = datasets.mnist.load_data() print(‘datasets:‘, x.shape, y.shape, x.min(), x.max()) db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x, y)) db = db.map(preprocess).shuffle(60000).batch(batchsz).repeat(10) ds_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_val, y_val)) ds_val = ds_val.map(preprocess).batch(batchsz) network = Sequential([layers.Dense(256, activation=‘relu‘), layers.Dense(128, activation=‘relu‘), layers.Dense(64, activation=‘relu‘), layers.Dense(32, activation=‘relu‘), layers.Dense(10)]) network.build(input_shape=(None, 28 * 28)) network.summary() optimizer = optimizers.Adam(lr=0.01) # 第一步: 这里要对loss和accuracy做一个跟踪。所以这里建立了2个metrics # 一个是accuracy的metrics,一个是求loss均值的metrics. acc_meter = metrics.Accuracy() loss_meter = metrics.Mean() for step, (x, y) in enumerate(db): with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784] x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28 * 28)) # [b, 784] => [b, 10] out = network(x) # [b] => [b, 10] y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10) # [b] loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_onehot, out, from_logits=True)) # 第二步: 每次loss计算完之后会更新一次metrics列表,这样loss会非常的准确。 loss_meter.update_state(loss) grads = tape.gradient(loss, network.trainable_variables) optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, network.trainable_variables)) if step % 100 == 0: # 第三步: 测试的时候把loss的result打印出来。 print(step, ‘loss:‘, loss_meter.result().numpy()) # 第四步: 把当前的loss buffer缓存清理掉。======这样每隔100次打印出来的loss是前100次的平均loss,而不是第100次了。 # 数值会看起来非常的稳定。 loss_meter.reset_states() # evaluate 测试的时候。我们来看acc metrics if step % 500 == 0: total, total_correct = 0., 0 # 首先: acc_meter缓存清0。 acc_meter.reset_states() for step, (x, y) in enumerate(ds_val): # [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784] x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28 * 28)) # [b, 784] => [b, 10] out = network(x) # [b, 10] => [b] pred = tf.argmax(out, axis=1) pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32) # bool type correct = tf.equal(pred, y) # bool tensor => int tensor => numpy total_correct += tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct, dtype=tf.int32)).numpy() total += x.shape[0] # 然后: acc_meter的值更新缓存到列表。 acc_meter.update_state(y, pred) print(step, ‘Evaluate Acc:‘, total_correct / total, acc_meter.result().numpy())
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangxianrong/p/14691288.html