上代码
const arr = [1,2,3,4,5] function t(num) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(()=>{ console.log(‘定时器‘, num) resolve() }, 1000) }) }
目前需求。想先forEach执行完毕之后再打印end
arr.forEach(async (i) =>{ await t(1) }) console.log(‘end‘)
测试发现是先打印end再执行forEach里面的async await
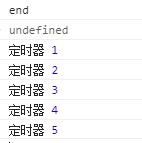 (打印结果)
(打印结果)
查阅资料(百度)后发现forEach里面是异步执行。所以在怎么用async await也无法按照预期执行
因为forEach是异步,那就把forEach改成for in
for(let i in arr){ await t(i) } console.log(‘end‘)
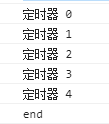 (打印结果 耗时5s)
(打印结果 耗时5s)
需求处理ok了。再到性能优化环节
因为for里面用await的会先执行完毕再走循环,因此会串行执行接口
就好比如我这里每个请求耗时1s。加起来走完请求就5s了,在用户体验上很不友好。
这个时候就需要用到Promise.all()+map()了。 Promise.all()是啥自行查阅资料!
await Promise.all(arr.map(async i=> await t(i))) console.log(‘end‘)
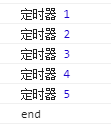 (打印结果 耗时1s)
(打印结果 耗时1s)
需求解决
解决forEach函数中异步调用及Promise.all()的基础使用
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/HDWdemo/p/14698151.html