hello,大家好。又到了分享学习经验的时刻,我有经验,您有酒吗?
总的来说,这三次题目集的综合难度保持在一个比较高的水准。
题目集4的第一题,和题目集5的第四,五题,对于我这个小菜鸡而言,难度系数不是一般的高,所以呢,我把题目发在这里,如果大神有什么见解,千万别藏着掖着。我有什么错误的话,还请您指正。别让我误人子弟。
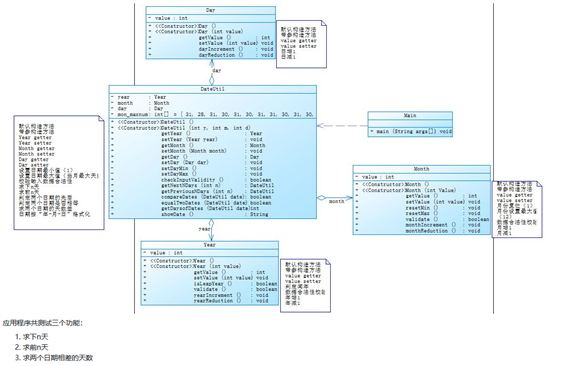
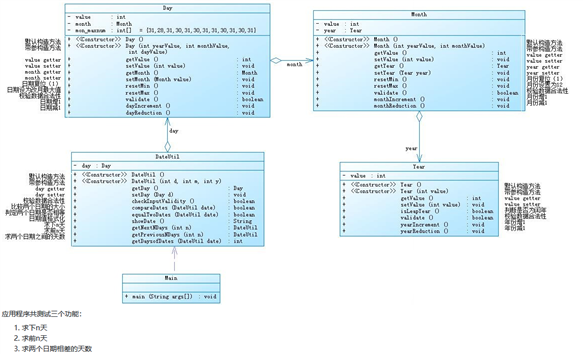
这两道题实现的功能基本是一样的,但是呢聚合不一样
DateUntil这个类可以进行比较,一个是将月份,年份,天数,的setter和getter写到了DateUntil这个类中,另一个是将这些setter和getter分别写在相应的月份类,年份类,以及天数类下面
我认为二者并没有绝对的谁好谁坏,相比较我更习惯于第一种,第一种是代码更加简化,思路更加清楚,可以准确的看到方法到底是为谁服务的,并且阅读性可能会更好一点,降低耦合性。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println(fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
这是我的主类,


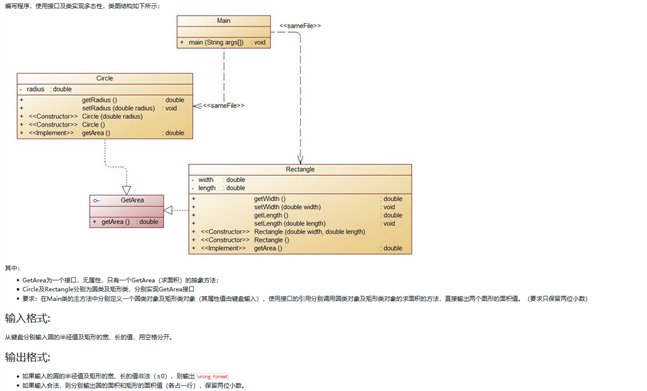
比较一下三道题图像技术设计思路和技术运用(继承 封装 多态和接口)
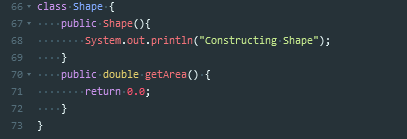
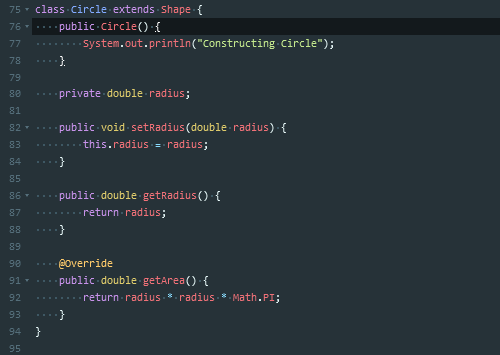
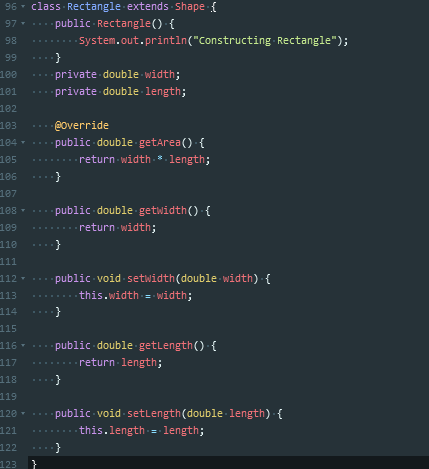
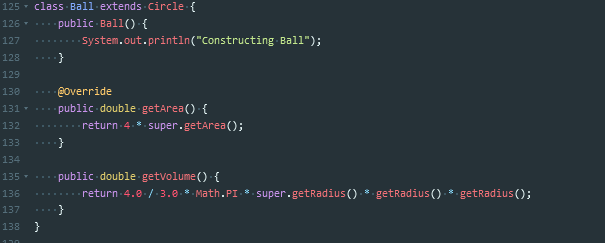
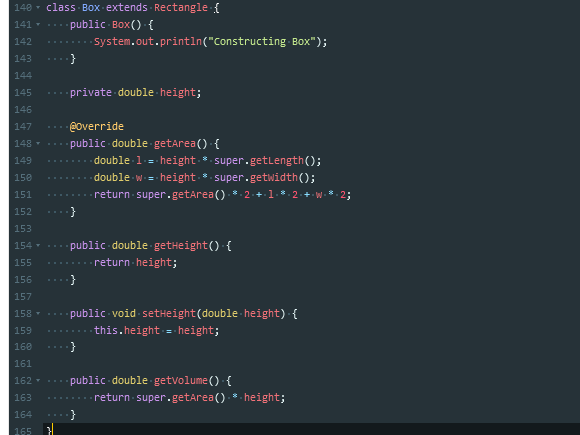
这个题主要用到了继承这种方法
继承的主要作用在于,在已有基础上继续进行功能的扩充
在Java中,继承用extends关键字来实现
当发生了类继承关系之后,子类可以直接继承父类的操作,可以实现代码的重用,子类最低也维持和父类相同的功能。
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in =new Scanner(System.in);
int a,b,c;
double sumArea=0.0;
a=in.nextInt();
b=in.nextInt();
c=in.nextInt();
int d=a+b+c;
if(a<0||b<0||c<0){
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
Circle[] circles=new Circle[a];
Rectangle[] rectangles=new Rectangle[b];
Triangle[] triangles=new Triangle[c];
for (int i=0;i<a;i++){
double radius=in.nextDouble();
circles[i]=new Circle(radius);
// System.out.println(circle[i].radius);
}
for (int i=0;i<b;i++){
double w=in.nextDouble();
double l=in.nextDouble();
rectangles[i]=new Rectangle(w,l);
}
for (int i=0;i<c;i++){
double side1=in.nextDouble();
double side2=in.nextDouble();
double side3=in.nextDouble();
triangles[i]=new Triangle(side1,side2,side3);
}
for (int i=0;i<a;i++){
if(!circles[i].validate()){
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
for (int i=0;i<b;i++){
if(!rectangles[i].validate()){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
for (int i=0;i<c;i++){
if(!triangles[i].validate()){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
System.out.print("Original area:\n");
double [] o=new double[d];
for (int i=0;i<a;i++){
if(a==0){
break;
}
System.out.printf("%.2f ",circles[i].getarea());
o[i]=circles[i].getarea();
sumArea+=circles[i].getarea();
}
// System.out.printf("\n");
for (int i=0;i<b;i++){
if(b==0){
break;
}
System.out.printf("%.2f ",rectangles[i].getarea());
o[a+i]=rectangles[i].getarea();
sumArea+=rectangles[i].getarea();
}
// System.out.println("\n");
for (int i=0;i<c;i++){
if(c==0){
break;
}
System.out.printf("%.2f ",triangles[i].getarea());
// System.out.println(triangles[i].getarea());
o[a+b+i]=triangles[i].getarea();
sumArea+=triangles[i].getarea();
}
System.out.print("\n");
System.out.printf("Sum of area:%.2f",sumArea);
System.out.print("\nSorted area:\n");
Arrays.sort(o);
for (double i :o){
System.out.printf("%.2f ",i);
}
System.out.print("\n");
System.out.printf("Sum of area:%.2f",sumArea);
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
double radius;
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getarea(){
return Math.PI*radius*radius;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Circle{" +
"radius=" + radius +
‘}‘;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(radius>0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
Circle(double radius){
this.radius=radius;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
double width;
double length;
Rectangle(double width,double length){
this.length=length;
this.width=width;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getarea() {
return width*length;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(width<0||length<0)
return false;
else
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Rectangle{" +
"width=" + width +
", length=" + length +
‘}‘;
}
}
abstract class Shape {
public abstract double getarea();
public abstract boolean validate();
public abstract String toString();
}
class Triangle extends Shape{
double side1=0;
double side2=0;
double side3=0;
Triangle(double side1,double side2,double side3){
this.side1=side1;
this.side2=side2;
this.side3=side3;
}
public void setSide1(double side1) {
this.side1 = side1;
}
public void setSide2(double side2) {
this.side2 = side2;
}
public void setSide3(double side3) {
this.side3 = side3;
}
public double getarea() {
double p;
p=(side1+side2+side3)/2.0;
double temp=Math.sqrt(p*(p-side1)*(p-side2)*(p-side3));
// S=Math.sqrt[p(p-a)(p-b)(p-c)]
return temp;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(side1<0||side2<0||side3<0)
return false;
else if(side1>0||side2>0||side3>0){
if((side1+side2)>side3&&(side2+side3)>side1&&(side3+side1)>side2)
return true;
else
return false;
}
else
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Triangle{" +
"side1=" + side1 +
", side2=" + side2 +
", side3=" + side3 +
‘}‘;
}
}
排序方法可以直接调用,比较省事。
在进行继承的时候,子类会继承父类的所有结构(包括私有属性、构造方法、普通方法)
显示继承:所有非私有操作属于显示继承(可以直接调用)。
隐式继承:所有私有操作属于隐式继承(不可以直接调用,需要通过其它形式调用(get或者set))。
实际在子类构造方法中,相当于隐含了一个语句super(),调用父类的无参构造。同时如果父类里没有提供无参构造,那么这个时候就必须使用super(参数)明确指明要调用的父类构造方法。
继承的主要作用是对类进行扩充以及代码的重用!
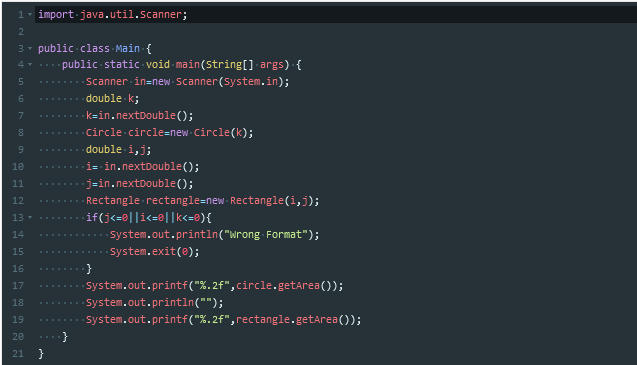
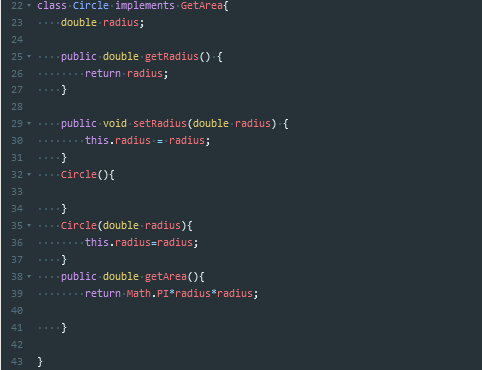
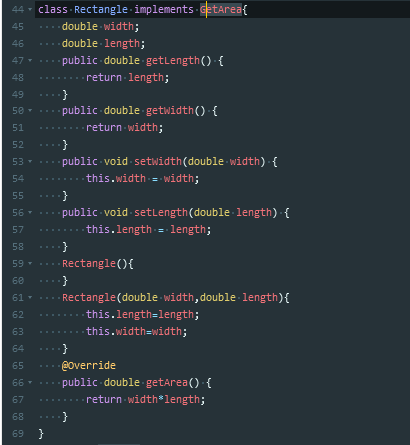
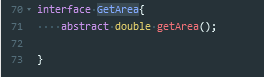
有借口,抽象方法
抽象方法只能存在于抽象类或者接口中,但抽象类中却能存在非抽象方法,即有方法体的方法。接口是百分之百的抽象类
因为Java不像C++一样支持多继承,所以Java可以通过实现接口来弥补这个局限
为了声明一个接口,我们使用interface这个关键字,在接口中的所有方法都必须只声明方法标识,而不要去声明具体的方法体,因为具体的方法体的实现是由继承该接口的类来去实现的,因此,接口并不用管具体的实现。接口中的属性默认为Public Static Final.一个类实现这个接口必须实现这个接口中定义的所有的抽象方法。



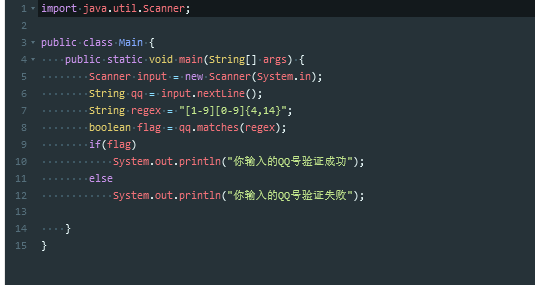
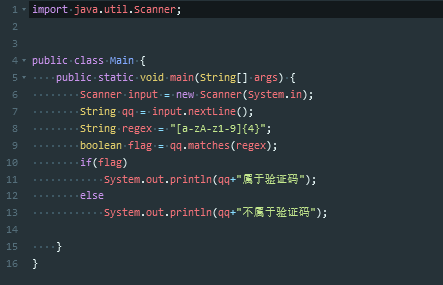
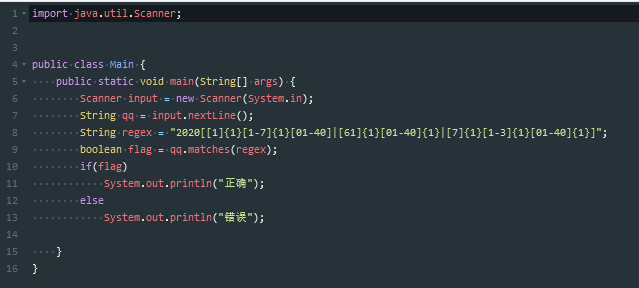
常用的正则

踩坑心得:
一个类实现这个接口必须实现这个接口中定义的所有的抽象方法。
要记住常用的正则
有时候会忘记创建一个新的对像
改进建议:
希望各位给点意见分析在上面
总结:
java目前教会我可以运用封装继承,还有接口,以及抽象类等
还了解了异常,以及自定义异常。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/168-24G252/p/14725800.html