前言:
继上篇blog所写的几种日期的求法,这次是把那几种聚合起来,即日期类的聚合设计。除下这类,一种是图形继承设计的3种变化,还有一种是3次对正则表达式的应用。当然,作为一个菜鸟,还是无法写成大佬的blog那种完美无瑕,我也尽我所能写出我所能写的最好的blog,这里给大家分享分享,希望看到我这篇blog的朋友,取其精魄,去其糟糠,也不做多废话,开始进入正文。题量说多也不多,毕竟是有一些是在原先的基础上变化的。
目录:
一. 题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-5)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较
参考题目7-2的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
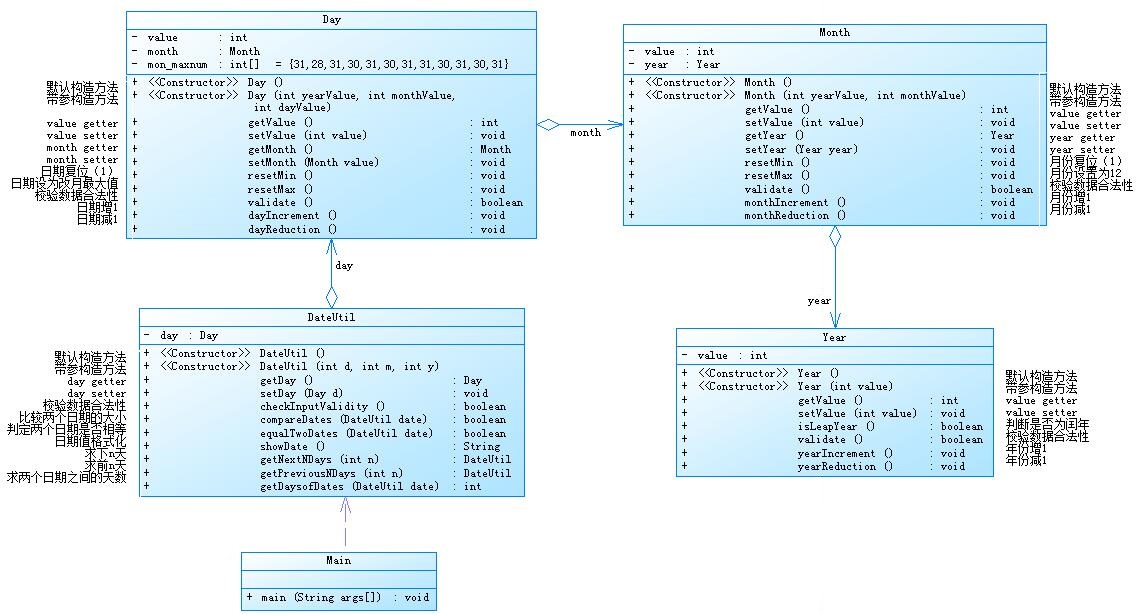
应用程序共测试三个功能:
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
Wrong Formatyear-month-dayyear-month-day天数值在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2312在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 1935 2 17 125340在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1591-12-17在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1999 3 28 6543在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2017-2-24在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2000 5 12 30在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format参考题目7-3的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
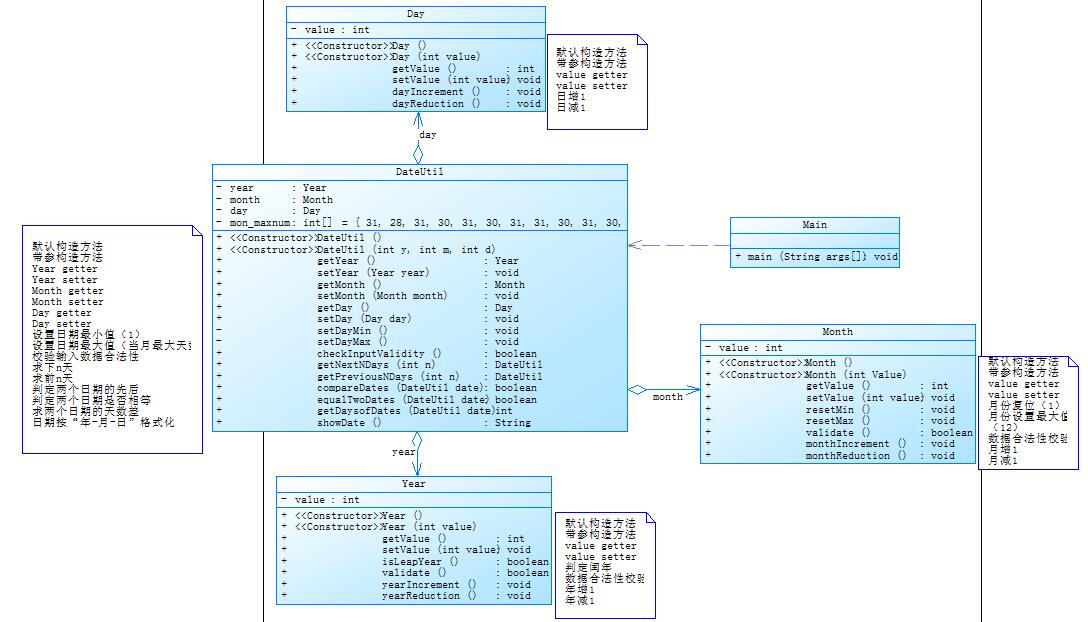
应用程序共测试三个功能:
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
Wrong Formatyear1-month1-day1 next n days is:year2-month2-day2year1-month1-day1 previous n days is:year2-month2-day2The days between year1-month1-day1 and year2-month2-day2 are:值在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
The days between 2014-2-14 and 2020-6-14 are:2312在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 1834 2 17 7821在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1834-2-17 previous 7821 days is:1812-9-19在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1999 3 28 6543在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1999-3-28 next 6543 days is:2017-2-24在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2000 5 12 30在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Formatpublic class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); int c=input.nextInt(); DateUtil dateUtil=new DateUtil(); switch (c){ case 1:{ dateUtil.year= input.nextInt(); dateUtil.month= input.nextInt(); dateUtil.day= input.nextInt(); dateUtil.setter(dateUtil.year, dateUtil.month, dateUtil.day); int n= input.nextInt(); if(dateUtil.checkInputValidity(dateUtil.year, dateUtil.month, dateUtil.day)){ dateUtil.getNextNDays(n); System.out.println(dateUtil.year+"-"+ dateUtil.month+"-"+ dateUtil.day); } break; } case 2: case 3: default: System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } }
聚合二Main类:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) { // 测试下n天 } else if (choice == 2) { // 求前n天 } else if (choice == 3) { //求两个日期相差的天数 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"+fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } }
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) //比较当前日期与date的大小(先后) { if (this.year > date.year) return true; if (this.year == date.year) { if (this.month > date.month) return true; if (this.month == date.month) { if (this.day >= date.day) return true; } } return false; } public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) //判断两个日期是否相等 { if (date != null) { if (year == date.year && month == date.month && day == date.day) { return true; } } return false; } private static final int[] mon = {0, 31, 59, 90, 120, 151, 181, 212, 243, 273, 304, 334}; public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) //求当前日期与date之间相差的天数 { DateUtil dateUtil1 = this; // 小 DateUtil dateUtil2 = date; // 大 if (this.compareDates(date)) { dateUtil1 = date; dateUtil2 = this; } int days; int leapYearNum = 0; for (int i = dateUtil1.getYear(); i < dateUtil2.getYear(); i++) { if (isLeapYear(i)) { leapYearNum++; } } days = 365 * (dateUtil2.getYear() - dateUtil1.getYear()) + leapYearNum; int d1 = mon[dateUtil1.getMonth() - 1] + dateUtil1.getDay() + (dateUtil1.getMonth() > 2 && isLeapYear(dateUtil1.getYear()) ? 1 : 0); int d2 = mon[dateUtil2.getMonth() - 1] + dateUtil2.getDay() + (dateUtil2.getMonth() > 2 && isLeapYear(dateUtil2.getYear()) ? 1 : 0); return days - d1 + d2; }
二·题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等)
编写程序,实现图形类的继承,并定义相应类对象并进行测试。
public double getArea();//求图形面积public double getVolume();//求球体积public double getVolume();//求立方体体积Constructing 类名主方法内,主要实现四个功能(1-4): 从键盘输入1,则定义圆类,从键盘输入圆的半径后,主要输出圆的面积; 从键盘输入2,则定义矩形类,从键盘输入矩形的宽和长后,主要输出矩形的面积; 从键盘输入3,则定义球类,从键盘输入球的半径后,主要输出球的表面积和体积; 从键盘输入4,则定义立方体类,从键盘输入立方体的宽、长和高度后,主要输出立方体的表面积和体积;
假如数据输入非法(包括圆、矩形、球及立方体对象的属性不大于0和输入选择值非1-4),系统输出Wrong Format
共四种合法输入
按照以上需求提示依次输出
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1.0在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Constructing Shape
Constructing Circle
Circle‘s area:3.14在这里给出一组输入。例如:
4 3.6 2.1 0.01211在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Constructing Shape
Constructing Rectangle
Constructing Box
Box‘s surface area:15.26
Box‘s volume:0.09在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 -2.3 5.110在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format思路与应用:
这道题目就是一个简单的继承题目,用Main当主类,创建图形Shape对象,Shape有Circle(圆)和Rectangle(矩形)两个子类,这两个子类分别又有个具体的对象子类Ball(球)和Box(立方体)类。且要求构造一个对象就要输出构造的类型,这就需要在每一个构造方法里添加一个输出自己类名的方法。在Circle和Rectangle类里需要有求面积的方法,Box和Ball除了求表面积外还需要添加求体积的方法。顺着这个思路,代码也有了雏形,下面就是以继承为主的代码。这里用到一个代码Math.PI,这个代码就是数学里面的π,也就是3.1415926。
import java.util.Scanner; class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int inType; Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); inType = scanner.nextInt(); switch (inType) { case 1: //圆类,输入半径,输出面积 double r = scanner.nextDouble(); //半径r if (r < 0.0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Circle circle = new Circle(); //circle:圆 circle.setRadius(r); System.out.println(String.format("Circle‘s area:%.2f", circle.getArea())); } break; case 2: //矩形类,输入宽和长,输出面积 double width = scanner.nextDouble(); //宽 double length = scanner.nextDouble(); //长 if (width < 0.0 || length < 0.0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(); //rectangle:矩形 rectangle.setLength(length); rectangle.setWidth(width); System.out.println(String.format("Rectangle‘s area:%.2f", rectangle.getArea())); } break; case 3: //球类,输入半径,输出表面积和体积 double r2 = scanner.nextDouble(); //球半径r2 if (r2 < 0.0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Ball ball = new Ball(); //ball:球 ball.setRadius(r2); System.out.println(String.format("Ball‘s surface area:%.2f", ball.getArea())); System.out.println(String.format("Ball‘s volume:%.2f", ball.getVolume())); } break; case 4: //立方体类,输入宽,长,高,输出表面积和体积 double width2 = scanner.nextDouble(); //宽 double length2 = scanner.nextDouble(); //长 double height = scanner.nextDouble(); //高 if (width2 < 0.0 || length2 < 0.0 || height < 0.0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Box box = new Box(); //box:盒子,立方体 box.setHeight(height); box.setWidth(width2); box.setLength(length2); System.out.println(String.format("Box‘s surface area:%.2f", box.getArea())); System.out.println(String.format("Box‘s volume:%.2f", box.getVolume())); } break; default: System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } } class Shape //定义一个无自身属性,有一个返回值为0.0的求面积方法 { public Shape() { System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); } public double getArea() { return 0.0; } } class Circle extends Shape//继承自Shape 圆 { public Circle() //圆 { System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); } private double radius;//新定义一个半径 public void setRadius(double radius) {// 设置半径 this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() {// 获取半径 return radius; } public double getArea() { //求圆的面积:π*r*r return Math.PI*radius*radius; //Math.PI是π } } class Rectangle extends Shape //矩形 { public Rectangle() { System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); } private double width; private double length; public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } public double getArea() { //矩形的面积:a*b return width*length; } } class Ball extends Circle //球 { private double radius2; public Ball() { System.out.println("Constructing Ball"); } public void setRadius(double radius2) {// 设置半径 this.radius2 = radius2; } public double getRadius() {// 获取半径 return radius2; } public double getArea() { //球的表面积:4*π*r*r return 4.0*Math.PI*radius2*radius2; } public double getVolume() //球的体积:4/3 * π * r的立方 { double r2=getRadius(); return 4.0/3.0*r2*r2*r2*Math.PI; } } class Box extends Rectangle //立方体 { public Box() { System.out.println("Constructing Box"); } private double height; public double getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(double height) { this.height = height; } public double getVolume() //求立方体的体积a*b*c { return height*super.getArea(); } public double getArea() { //求立方体的表面积2*(a*b+a*c+b*c) double w2=getWidth(); double l2=getLength(); return 2*(w2*l2+w2*height+l2*height); } }
编写程序,使用接口及类实现多态性,类图结构如下所示:
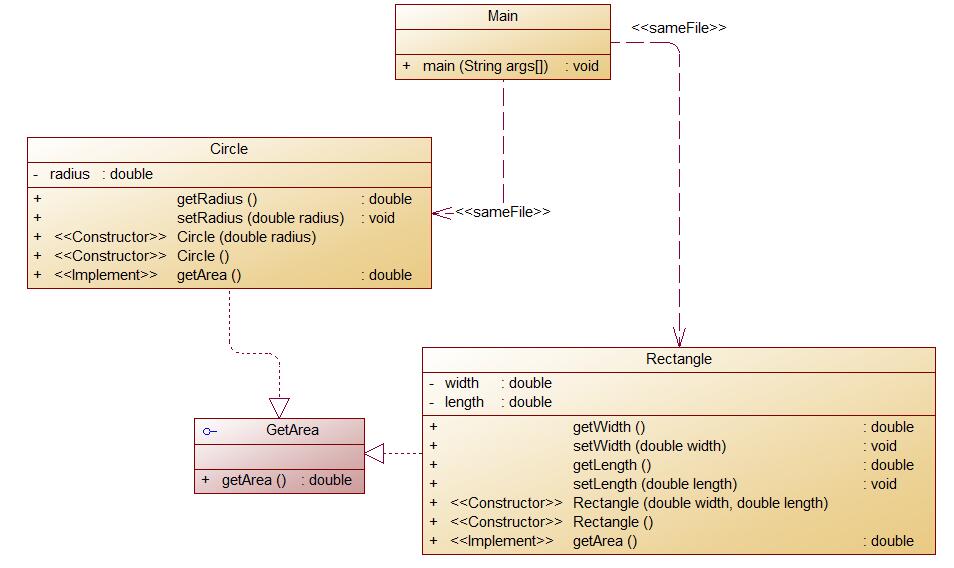
其中:
从键盘分别输入圆的半径值及矩形的宽、长的值,用空格分开。
Wrong Format在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 3.6 2.45在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
12.57
8.82在这里给出一组输入。例如:
9 0.5 -7.03在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Formatimport java.util.Scanner; class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); double r = scanner.nextDouble(); //半径r double width = scanner.nextDouble(); //宽 double length = scanner.nextDouble(); //长 if (r < 0.0||width <= 0.0 || length <= 0.0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Circle circle = new Circle(); //circle:圆 circle.setRadius(r); Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(); //rectangle:矩形 rectangle.setLength(length); rectangle.setWidth(width); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", circle.getArea())); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", rectangle.getArea())); } } } class Shape //定义一个无自身属性,有一个返回值为0.0的求面积方法 { public double getArea() { return 0.0; } } class Circle extends Shape//继承自Shape 圆 { private double radius;//新定义一个半径 public void setRadius(double radius) {// 设置半径 this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() {// 获取半径 return radius; } public double getArea() { //求圆的面积:π*r*r return Math.PI*radius*radius; //Math.PI是π } } class Rectangle extends Shape //矩形 { private double width; private double length; public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } public double getArea() { //矩形的面积:a*b return width*length; } }
三·对题目集6中3次用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结(7.1QQ号校验 7.3验证码校验 7.4学号校验)
QQ号要求:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner a = new Scanner(System.in); String qq = a.nextLine(); String b = "[1-9][0-9]{4,14}"; //{4,14}表示有4到14个[0-9] boolean t = qq.matches(b); //boolean是java中的布尔型(逻辑型)数据类型,在java中boolean值只能是true和false if(t) System.out.println("你输入的QQ号验证成功"); else System.out.println("你输入的QQ号验证失败"); } }
验证码要求:
String b = "[a-z]|[A-Z]|[0-9]{4}";
学号要求:
总结:
正则表达式看起来是不是很简单啊,是的,就是很简单,但又不是很简单,正则表达式就我做的这3道题来说,我个人感觉有点难的,因为不熟悉,它灵活多变。
QQ号,第一个不能为0,所以用[1-9]表示数字1到数字9之间任意一个数字;[0-9]{4,14}表示有4到14个数字,这个数字又是在0~9之间任意取的一个。//这里就用到了中括号[ ]和大括号{ },还有括号里面的“-”和“,”,这两种符号代表的又不一样。
验证码,[a-z] | [A-Z] | [0-9]表示这字母a到z或者大写字母A到Z或者数字0到9期间任取一个字符,这里又用到了“|”这个符号,这个符号表示“或”的意思。
学号,学号这题我就做错了几次,一开始是写了(2020(11|12|13|14|15|16|17|61|71|72|73|81|82)[0-9]{2})的,后来发现情况不对,这样学号40号以后的也会算进去,最后两位我又改成了[0-3][0-9],但是又没有了40号,要是能加上40号我就完成了,最后我想到了“&&”符号,这个符号的意思就是“和”。
所以正则表达式看起来很简单,但是要考虑的东西有点多,容易多加东西进去,所以要记清楚各种符号表达的意思,要理解。
四·题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的分析总结
编写程序统计一个输入的Java源码中关键字(区分大小写)出现的次数。说明如下:
输入Java源码字符串,可以一行或多行,以exit行作为结束标志
Wrong Format数量\t关键字在这里给出一组输入。例如:
//Test public method
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
exit在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1 float
3 if
2 int
2 new
2 public
3 this
2 throwjava的53个关键字:"abstract","assert","boolean","break","byte","case","catch", "char","class","const","continue","default","do","double","else", "enum","extends","false","final","finally","float", "for","goto","if","implements","import","instanceof", "int","interface","long","native","new","null","package", "private","protected","public","return","short","static", "strictfp","super","switch","synchronized","this","throw", "throws","transient","true","try","void","volatile","while"
import java.util.*; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); String a; StringBuilder n=new StringBuilder(); Map<String, Integer> map=new HashMap<String, Integer>(); //关键字 String []key= { "abstract","assert","boolean","break","byte","case","catch", "char","class","const","continue","default","do","double","else", "enum","extends","false","final","finally","float", "for","goto","if","implements","import","instanceof", "int","interface","long","native","new","null","package", "private","protected","public","return","short","static", "strictfp","super","switch","synchronized","this","throw", "throws","transient","true","try","void","volatile","while"}; int j=0; for(int i=0;;i++) { a=input.nextLine(); if(a.equals("exit")) //没有统计数据,,输出为空。 break; if(a.matches("(.*)//(.*)")) //注释不统计 {String b[]=a.split("//"); n.append(b[0]+" "); } else {n.append(a+" "); } } int count=0; String s=n.toString(); Pattern p=Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\""); Matcher m=p.matcher(s); while(m.find()){ //字符串内关键字测试 s=s.replace(m.group()," "); p=Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\""); m=p.matcher(s); } p=Pattern.compile("/\\**(.*?)/"); m=p.matcher(s); while(m.find()){ //两种注释测试 s=s.replace(m.group()," "); m=p.matcher(s); } if(s.isEmpty()) //未输入源码 {System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } s= s.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z]", " "); String []s1=s.split("[ ‘ ‘]"); for(int i=0;i<s1.length;i++) { for( j=0;j<key.length;j++) //查出出现的关键字 if(s1[i].equals(key[j])) { map.put(key[j], 0); } } for( int i = 0;i<s1.length;i++) { for( j=0;j<key.length;j++) //统计关键字出现的次数 if(s1[i].equals(key[j])) { count=map.get(key[j]); map.put(key[j], count+1); } } Set set=map.keySet(); Object[] arr=set.toArray(); Arrays.sort(arr); for(Object k:arr){ System.out.println(map.get(k)+"\t"+k); } } }
总结:
这次的blog题目集总结归纳,总体来说,完成的还是可以的。在PTA上完成了习题后,过了几天,我又忘记了很多东西,经过这次总结归纳,我又想起了一部分知识,首先就是正则表达式,还是要多练多记,加以巩固;其次就是类图,类图还是有地方看不懂,接下来还是要重点去复习一下类图的关系,继承和多态也是要复习的。
实验这种东西,能够反映出哪里没掌握,哪里出错。还是要多练习了,但是如果知识不牢固,没学好,那实验做起来还是好难的啊。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhang1018/p/14725757.html