这次题目主要是关于Java的类的使用和设计,学习了如何把一个大问题分成多个小问题,让多个对象来解决不同小问题最后把大问题解决。要想把问题很好地解决,就需要设计好各个类及类之间的关系,让类之间紧密配合把问题解决。
题目集4中的日期类聚合设计是DateUtil由Day聚合、Day由Month聚合、Month由Year聚合,题目集5中的是DateUtil由Day、Month、Year一起聚合。题目集4的这种设计将各各个类形成小聚合,因为只聚合了一个类所以DateUtil不用写太多方法,而题目集5中的DateUtil更麻烦,因为要控制三个类所以方法很多。题目集4层层相扣逻辑清晰很好看,但不容易想到,一般容易想到题目集5的写法。题目集4的类独立性不强,因为它每个类都由别的类聚合而成,不可以把一个类单独拿出来用。而题目集5就可以把Day、Month、Year单独拿出来,复用性强。
import java.util.Scanner; class Day{ int day; Day(int d){ this.day = d; } } class Month{ int month; private final int[] DAY_OF_MONTH = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; Month(int m){ this.month = m; } int getDayOfMonth(Year year) { int days = DAY_OF_MONTH[month - 1]; if (month == 2 && year.isLeapYear()) { days = 29; } return days; } } class Year{ int year; Year(int y){ this.year = y; } public boolean isLeapYear(){ return (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0; } } class DateUtil2{ Year y; Month m; Day d; DateUtil2(int year,int month,int day){ y = new Year(year); m = new Month(month); d = new Day(day); } public String getNextDay(int n){ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { d.day++; if (d.day > m.getDayOfMonth(y)) { d.day = 1; m.month++; if (m.month > 12) { m.month = 1; y.year++; } } } return y.year + "-" + m.month + "-" + d.day; } public String getPreviousNDay(int n){ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { d.day--; while (d.day < 1) { m.month--; if (m.month < 1) { m.month = 12; y.year--; } d.day += m.getDayOfMonth(y); } } return y.year + "-" + m.month + "-" + d.day; } public boolean checkInputValidity()//检测输入的年、月、日是否合法 { if (y.year < 1900 || y.year > 2050) return false; if (m.month < 1 || m.month > 12) return false; if(d.day > m.getDayOfMonth(y) ) return false; return d.day >= 1 && d.day <= 31; } public boolean compareDates(DateUtil2 date)//比较当前日期与date的大小(先后) { if (this.y.year > date.y.year) return true; if (this.y.year == date.y.year) { if (this.m.month > date.m.month) return true; if (this.m.month == date.m.month) { if (this.d.day >= date.d.day) return true; } } return false; } public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil2 date)//求当前日期与date之间相差的天数 { DateUtil2 dateUtil1 = this; // 小 DateUtil2 dateUtil2 = date; // 大 int[] mon = {0, 31, 59, 90, 120, 151, 181, 212, 243, 273, 304, 334}; if (this.compareDates(date)) { dateUtil1 = date; dateUtil2 = this; } int days; int leapYearNum = 0; for (int i = dateUtil1.y.year; i < dateUtil2.y.year; i++) { if ((i % 4 == 0 && i % 100 != 0) || i % 400 == 0) { leapYearNum++; } } days = 365 * (dateUtil2.y.year - dateUtil1.y.year) + leapYearNum; int d1 = mon[dateUtil1.m.month - 1] + dateUtil1.d.day + (dateUtil1.m.month > 2 && dateUtil1.y.isLeapYear() ? 1 : 0); int d2 = mon[dateUtil2.m.month - 1] + dateUtil2.d.day + (dateUtil2.m.month > 2 && dateUtil2.y.isLeapYear() ? 1 : 0); return days - d1 + d2; } } public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year; int month; int day; int n; DateUtil2 r,r2; switch(input.nextInt()){ case 1: year = input.nextInt(); month = input.nextInt(); day = input.nextInt(); n = input.nextInt(); r= new DateUtil2(year,month,day); if(r.checkInputValidity()){ System.out.println(r.getNextDay(n)); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); break; case 2: year = input.nextInt(); month = input.nextInt(); day = input.nextInt(); n = input.nextInt(); r = new DateUtil2(year,month,day); if(r.checkInputValidity()){ System.out.println(r.getPreviousNDay(n)); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); break; case 3: year = input.nextInt(); month = input.nextInt(); day = input.nextInt(); r = new DateUtil2(year,month,day); year = input.nextInt(); month = input.nextInt(); day = input.nextInt(); r2 = new DateUtil2(year,month,day); if(r.checkInputValidity() && r2.checkInputValidity()){ System.out.println(r.getDaysofDates(r2)); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); break; default: System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } }
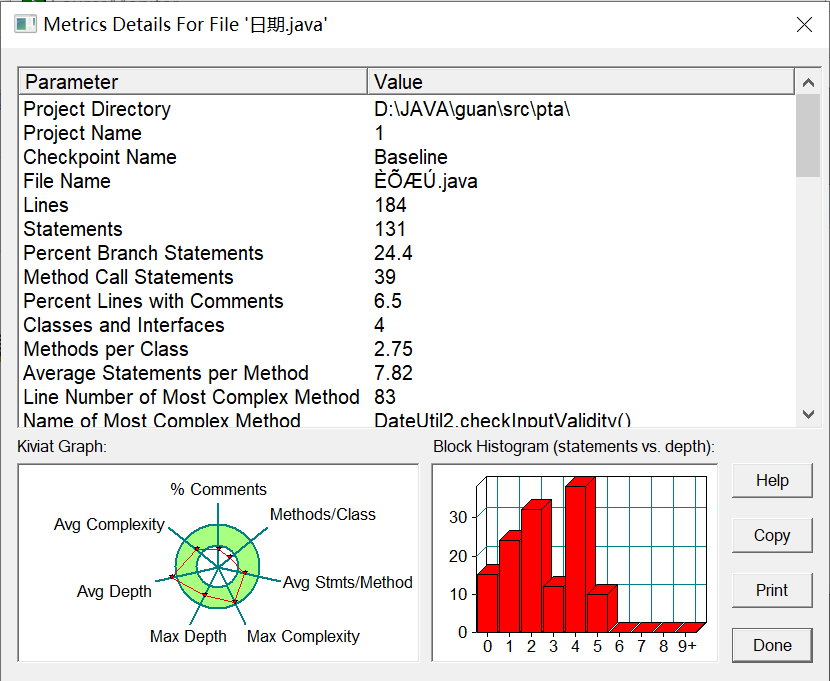
7-5 将Shape定义为抽象类并声明多个抽象函数,子类继承它后重写抽象方法。
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner; abstract class Shape{ abstract double getArea(); abstract boolean validata(); abstract String toStrings(); } class Circle extends Shape{ private double radius; Circle(double r){ this.radius = r; } @Override double getArea(){ return Math.PI*radius*radius; } @Override boolean validata(){ return radius > 0; } @Override String toStrings(){ return ""; } } class Rectangle extends Shape{ private double width; private double length; Rectangle(double a,double b){ this.length = a; this.width = b; } @Override double getArea(){ return width*length; } @Override boolean validata(){ return width > 0 && length > 0; } @Override String toStrings(){ return ""; } } class Triangle extends Shape{ private double side1; private double side2; private double side3; Triangle(double a,double b,double c){ this.side1 = a; this.side2 = b; this.side3 = c; } @Override double getArea(){ double s = (side1+side2+side3)/2.0; return Math.sqrt(s*(s-side1)*(s-side2)*(s-side3)); } @Override boolean validata(){ return side1+side2>side3&&side2+side3>side1&&side3+side1>side2; } @Override String toStrings(){ return ""; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int a,b,c; a = in.nextInt(); b = in.nextInt(); c = in.nextInt(); double[] f = null; if(a<0||b<0||c<0){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else{ f = new double[a+b+c]; for(int i = 0;i < a;i++){ Shape circle = new Circle(in.nextDouble()); if(!circle.validata()){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else{ f[i] = circle.getArea(); } } for(int i = 0;i < b;i++){ Shape rectangle = new Rectangle(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); if(!rectangle.validata()){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else{ f[i+a] = rectangle.getArea(); } } for(int i = 0;i < c;i++){ Shape triangle = new Triangle(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); if(!triangle.validata()){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else{ f[i+a+b] = triangle.getArea(); } } } System.out.println("Original area:"); for(double fe:f){ System.out.print(String.format("%.2f",fe)+" "); } double sum = 0; for(double fe:f){ sum = sum + fe; } System.out.println("\n"+"Sum of area:"+String.format("%.2f",sum)); Arrays.sort(f); System.out.println("Sorted area:"); for(double fe:f){ System.out.print(String.format("%.2f",fe)+" "); } System.out.println("\n"+"Sum of area:"+String.format("%.2f",sum)); } }
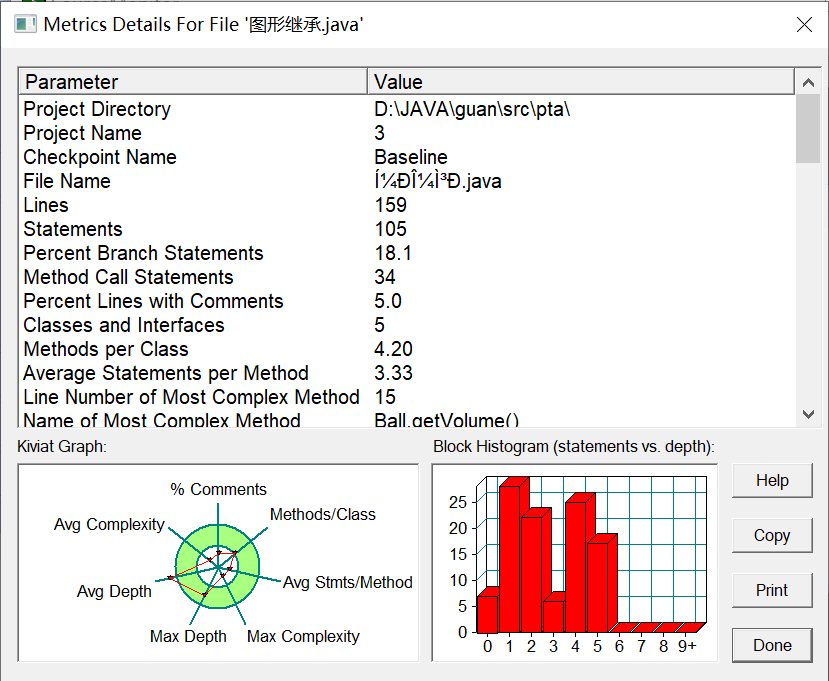
7-3 类Shape,无属性,有一个返回0.0的求图形面积的公有方法 public double getArea();//求图形面积 子类继承它并重写这个方法。
import java.util.Scanner; class Shape{ public double getArea() { return 0.0; } } class Circle extends Shape{ private double radius; double circlearea; Circle(){ } public double getradius() { return radius; } public void setradius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public Circle(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getArea(double radius) { circlearea = radius*radius*Math.PI; return circlearea; } } class Rectange extends Shape{ private double width; private double length; double rectangearea; Rectange(){ } public double getwidth() { return width; } public void setradius(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getlength() { return length; } public void setlength() { this.length = length; } public Rectange(double width,double length) { this.width = width; this.length = length; } public double getArea(double width,double length) { rectangearea=width*length; return rectangearea; } } class Ball extends Circle{ /* public Box(double width,double length) { super(width,length); } */ Ball(){ } public double getArea(double radius) { return 4.0*Math.PI*radius*radius; } public double getVolume(double radius) { return 4.0/3.0*Math.PI*radius*radius*radius; } } class Box extends Rectange{ /* public Box(double width,double length) { super(width,length); } */ double boxvolum; double boxarea; Box(){ } public double getArea(double width,double length,double height) { boxarea=2.0*(height*length+height*width+length*width); return boxarea; } public double getVolume(double width,double length,double height) { boxvolum=height*length*width; return boxvolum; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); Circle circle = new Circle(); Rectange rectange = new Rectange(); Ball ball = new Ball(); Box box = new Box(); int choose =input.nextInt(); switch(choose) { case 1:{ double r = input.nextDouble(); if(r>=0) { double circlearea = circle.getArea(r); System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); System.out.println("Circle‘s area:"+String.format("%.2f", circlearea)); break; }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); break; } } case 2:{ double a = input.nextDouble(); double b = input.nextDouble(); if(a>=0&&b>=0) { double rectangearea = rectange.getArea(a, b); System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); System.out.println("Rectangle‘s area:"+String.format("%.2f", rectangearea)); break; }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); break; } } case 3:{ double r = input.nextDouble(); if(r>=0) { double ballarea = ball.getArea(r); double ballvolume = ball.getVolume(r); System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); System.out.println("Constructing Ball"); System.out.println("Ball‘s surface area:"+String.format("%.2f",ballarea)); System.out.println("Ball‘s volume:"+String.format("%.2f", ballvolume)); break; }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); break; } } case 4:{ double a = input.nextDouble(); double b = input.nextDouble(); double c = input.nextDouble(); if(a>=0&&b>=0&&c>=0) { double boxvolum = box.getVolume(a,b,c); double boxarea = box.getArea(a,b,c); System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); System.out.println("Constructing Box"); System.out.println("Box‘s surface area:"+String.format("%.2f", boxarea)); System.out.println("Box‘s volume:"+String.format("%.2f", boxvolum)); break; }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); break; } } default: System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } }
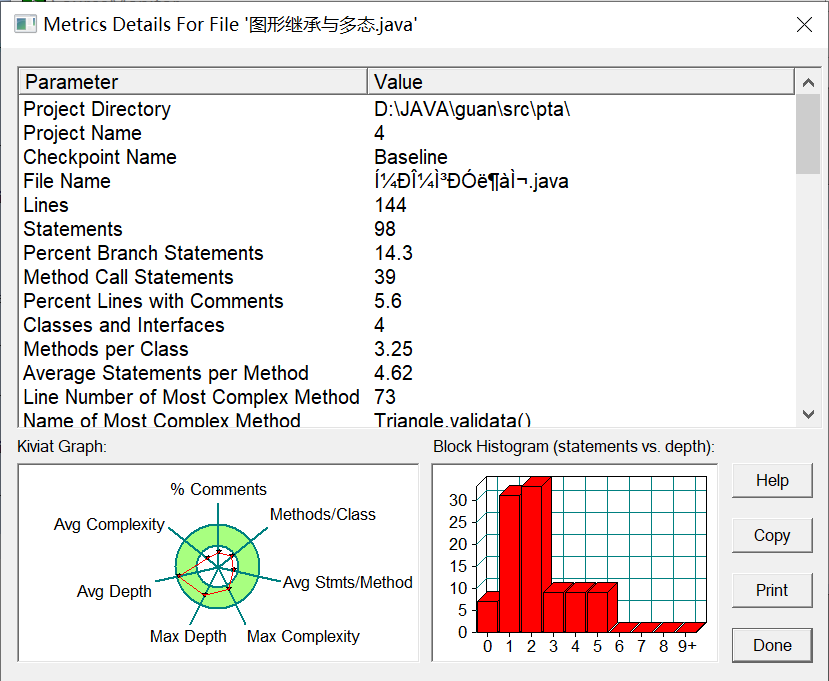
7-6 GetArea为一个接口,无属性,只有一个GetArea(求面积)的抽象方法,子类实现这个接口后重写GetArea(和7-3很像)。
import java.util.Scanner; /** * * @author 管希雄 */ interface GetArea { double getArea(); } class Circle implements GetArea{ private double radius; Circle(double r){ this.radius = r; } @Override public double getArea(){ return Math.PI*radius*radius; } } class Rectangle implements GetArea{ private double width; private double length; Rectangle(double a,double b){ this.length = a; this.width = b; } @Override public double getArea(){ return width*length; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); double r = in.nextDouble(); double w = in.nextDouble(); double l = in.nextDouble(); if(r<=0||w<=0||l<=0){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else{ Circle y = new Circle(r); Rectangle f = new Rectangle(w,l); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f",y.getArea())); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f",f.getArea())); } } }
正则表达式(regular expression)描述了一种字符串匹配的模式(pattern),可以用来检查一个串是否含有某种子串、将匹配的子串替换或者从某个串中取出符合某个条件的子串等。
使用了ArrayList集合储存关键字,使用contains()法判断输入是否是关键字
"\"在表达式中有特殊意义,需要在它前面添加 "\" 才能当作普通文本字符来使用。
无
合理的运用抽象类和接口可以使我们编写代码更有条理,实现代码复用。在这次作业中使用抽象类和接口看起来显得多此一举,这种小题目里确实是多此一举,但这只是让我们了解它们是什么、如何使用它们、它们有什么用。经过这次学习,我感受到了它们的作用,浅显理解它们存在的意义,以后仍需深入研究。
使用正则表达式可以用于匹配我们想要的字符串格式。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Gxx-x/p/14709424.html