卷积神经网络(cnn):
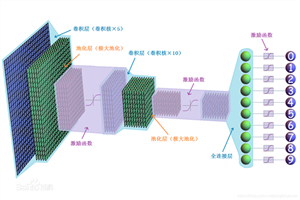
卷积:
卷积在pytorch中有两种方式,一种是torch.nn.Conv2d(),一种是torch.nn.functional.conv2d()。
1.输入:
首先需要输入一个torch.autograd.Variable()的类型
输入参数:(batch,channel,H,W)
(1).batch是输入的一批数据的数目
(2).通道数,一般彩色图是3,灰度图是1,而卷积网络过程中的通道数比较大,会出现几十到几百的通道数
(3).H和w是输入图片的高度和宽度
如一个batch是32的图片,每张图片是3通道,高和宽是50和100,那么输入的大小就是(32,3,50,100)。
2.内置参数:
torch.nn.Conv2d(
in_channels, #输入的通道数
out_channels, #输出的通道数(注:卷积核数,几个卷积核就通道(输出几张图片))
kernel_size, #卷积核大小
stride=1, #卷积核移动步长
padding=0, #补0的多少
dilation=1, #kernel间距
groups=1, #卷积核个数
bias=True )
3.卷积后尺寸计算:
N = (W ? F + 2P )/S+1
输出图片:N×N
池化:
1.作用:
一般较多使用最大池化,还有平均池化等。
torch.nn.max_pool():一般定义池化核大小(2,2)在2×2矩阵内 取最大值,一般具有缩小图片大小作用(1/2)
2.内置参数
torch.nn.max_pool(
kernel_size, #池化核大小
stride=None, #步长
padding=0, #补0
dialtion=1,
return_indices=False,
ceil_model=False )
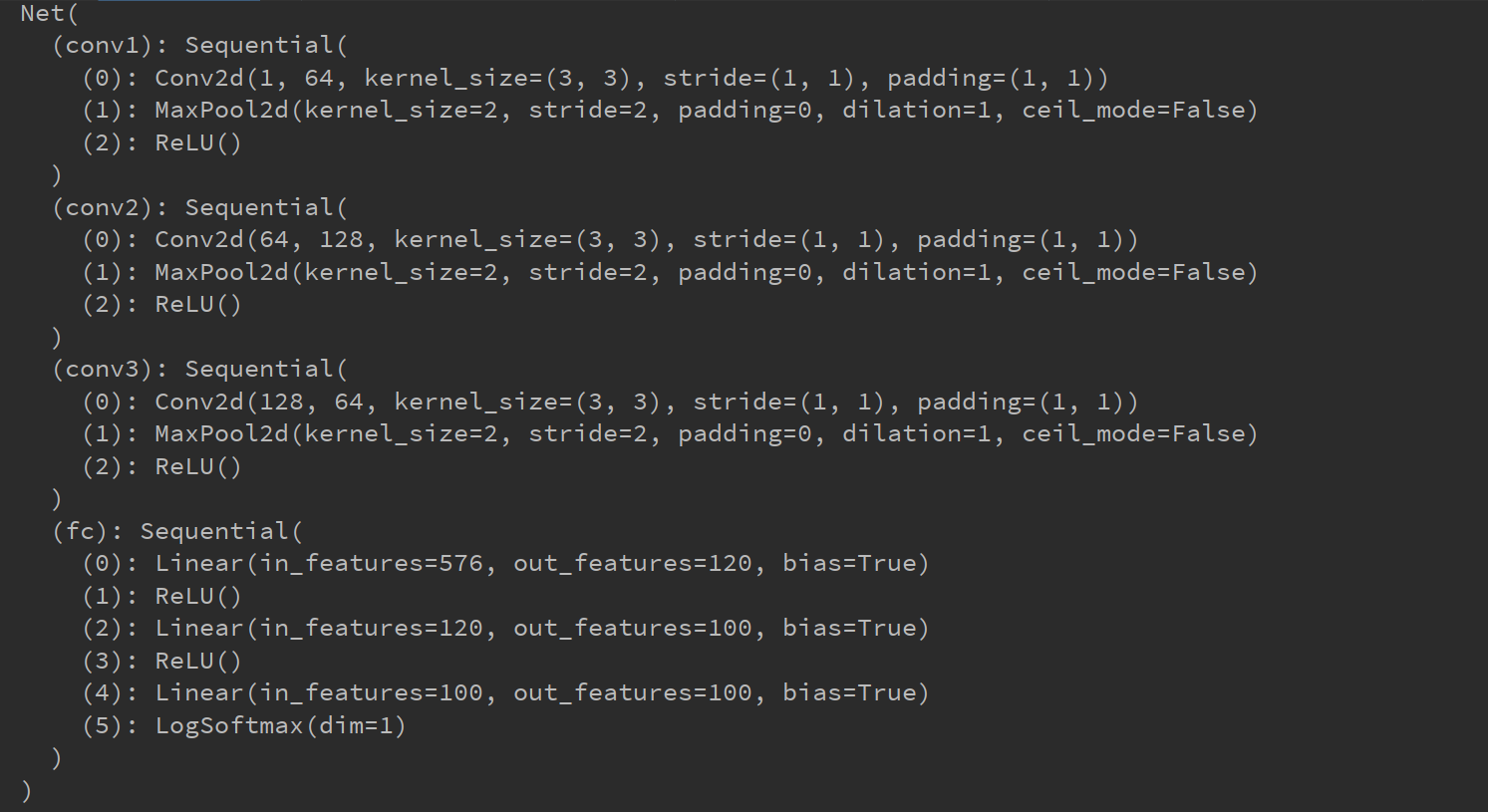
import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset from torch.utils.data import DataLoader class Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(Net, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1), torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # 池化 2*2取最大 缩小一半 64*28*28--->64*14*14 torch.nn.ReLU() ) self.conv2 = nn.Sequential( torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1), torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), torch.nn.ReLU() ) self.conv3 = nn.Sequential( torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1), torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), torch.nn.ReLU() ) self.fc = torch.nn.Sequential( torch.nn.Linear(64*3*3, 120), torch.nn.ReLU(), torch.nn.Linear(120, 100), torch.nn.ReLU(), torch.nn.Linear(100, 100), torch.nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1) ) def forward(self, inputs): # 向前传播函数 out = self.conv1(inputs) out = self.conv2(out) out = self.conv3(out) out = out.view(-1, 64*3*3) # 展开 拉成一维 输入到全连接层 out = self.fc(out) return out net = Net() print(net) # rand()均匀分布, 数据集 假设100张 28*28 黑白照 x_train = torch.rand(size=(100, 1, 28, 28)) # x_train = torch.rand(100, 1, 28, 28) # 标签 y = torch.tensor([0, 1]*50) # 损失函数与优化器 loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 一般分类用此函数 optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.1) x = TensorDataset(x_train, y) xx = DataLoader(x, batch_size=100, shuffle=True) # 模型训练 for epoch in range(100): for (x1, y1) in xx: y_pred = net(x1) loss = loss_func(y_pred, y1) print(loss.item()) optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清0 loss.backward() # 反向 optimizer.step()
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # 池化 2*2取最大 缩小一半 64*28*28--->64*14*14
torch.nn.ReLU()
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
torch.nn.ReLU()
)
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
torch.nn.ReLU()
)
self.fc = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(64*3*3, 120),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(120, 100),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(100, 100),
torch.nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
)
def forward(self, inputs): # 向前传播函数
out = self.conv1(inputs)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = out.view(-1, 64*3*3) # 展开 拉成一维 输入到全连接层
out = self.fc(out)
return out
net = Net()
print(net)
# rand()均匀分布, 数据集 假设100张 28*28 黑白照
x_train = torch.rand(size=(100, 1, 28, 28))
# x_train = torch.rand(100, 1, 28, 28)
# 标签
y = torch.tensor([0, 1]*50)
# 损失函数与优化器
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 一般分类用此函数
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.1)
x = TensorDataset(x_train, y)
xx = DataLoader(x, batch_size=100, shuffle=True)
# 模型训练
for epoch in range(100):
for (x1, y1) in xx:
y_pred = net(x1)
loss = loss_func(y_pred, y1)
print(loss.item())
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清0
loss.backward() # 反向
optimizer.step()
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/ljh354114513/p/14769746.html