/*
* 一、异常体系结构
* ------ java.lang.Error:一般不编写针对性的代码进行处理
* ------ java.lang.Exception:可以进行异常的处理
* ----编译时异常(checked)
* ----IOException
* ----FileNotFoundException
* ----ClassNotFoundException
* ----运行时异常(unchecked,RuntimeException)
* ----NullPointerException
* ----ArrayIndexOutOfBonudsException
* ----ClassCastException
* ----NumberFormatException
* ----InputMismatchException
* ----ArithmaticException
* 面试题:常见异常有哪些?
*/
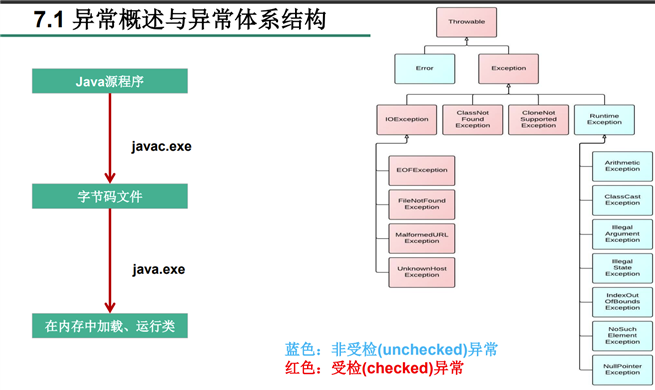
javac.exe命令时,可能出现的异常java.exe命令时,出现的异常 //********************以下是编译时异常****************
//javac.exe时就会报错 因而叫编译时异常
@Test
public void test7() throws IOException {
File f = new File("hello.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
int data = fis.read();
while(data!=-1) {
System.out.println((char)data);
data=fis.read();
}
fis.close();
}
//****************以下是运行时异常************************
//javac.exe时不会报错
// ArithmaticException
@Test
public void test6() {
System.out.println(2/0);
}
//InputMismatchException
@Test
public void test5() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int score = in.nextInt();
System.out.println(score);
}
//NumberFormatException
@Test
public void tets4() {
String str = "abc";
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
}
// ClassCastException
@Test
public void test3() {
Object date = new Date();
String str = (String)date;
}
//ArrayIndexOutOfBonudsException
@Test
public void test2() {
String str = "abc";
System.out.println(str.charAt(3));
}
//NullPointerException
@Test
public void test1() {
int[] arr = null;
System.out.println(arr[3]);
}
/*
* 一、异常的处理:抓抛模型
*
* 过程一:“抛”
* 程序在正常执行过程中,一旦出现异常,就会在异常代码处,就会在异常代码处生成一个对应异常类的对象。
* 并将此对象抛出。一旦抛出对象以后,其后的代码就不再执行
*
* 关于异常对象的产生:① 系统自动生成的异常对象 ② 手动的生成一个对象,并抛出(throw)
*
* 过程二:“抓”
* 可以理解为异常的处理方式
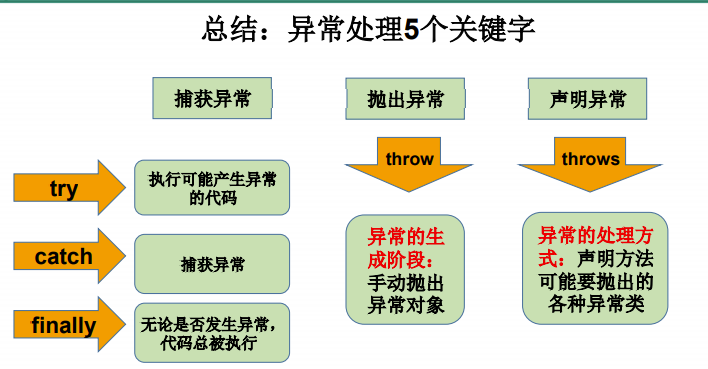
* ① try-catch-finally
* ② throws
*
* 体会1:使用try-catch-finally处理编译异常,使得程序在编译时就不再报错,但是运行时仍可能报错
* 相当于我们使用try-catch-finally将一个编译时可能出现的异常,延迟到运行时出现。
* 体会2:开发中,由于运行时异常比较常见,所以我们就通常就不针对运行时异常编写try-catch-finally来处理(处理了也一样有红字)
* 针对编译时异常,我们一定要考虑异常的处理(不然连编译都过不了)
*/
/* 二、try-catch-finally的使用
* try{
* //可能出现异常的代码
* }catch(异常类型1 变量名1){
* //处理异常的方式1
* }catch(异常类型2 变量名2){
* //处理异常的方式2
* }finally{
* 一定会执行的代码
* }
*
* 说明:
* 1. finally是可选的
* 2. 使用try将可能出现异常的代码包装起来,在执行过程中,一旦出现异常,就会生成一个对应异常类的对象,根据此对象的类型,去catch中进行匹配
* 3. 一旦try中的异常对象匹配到某一个catch时,就进入catch中的异常处理,一旦处理完成,就跳出try-catch结构,继续执行后面的代码(在没有finally的情况下)
* 4. catch中的异常,如果没有子父类关系,谁在上谁在下都可以
* 如果有字符类关系,则子类在上父类在下
* 5. 常用异常对象的处理方式
* ① String getMessage()
* ② printStackTrace()
* 6. try-catch-finally可以相互嵌套
*/
/* 体会1:使用try-catch-finally处理编译异常,使得程序在编译时就不再报错,但是运行时仍可能报错
* 相当于我们使用try-catch-finally将一个编译时可能出现的异常,延迟到运行时出现。
* 体会2:开发中,由于运行时异常比较常见,所以我们就通常就不针对运行时异常编写try-catch-finally来处理(处理了也一样有红字)
* 针对编译时异常,我们一定要考虑异常的处理(不然连编译都过不了)
*/
接2
/* 说明:
* 1. finally是可选的
* 2. 使用try将可能出现异常的代码包装起来,在执行过程中,一旦出现异常,就会生成一个对应异常类的对象,根据此对象的类型,去catch中进行匹配
* 3. 一旦try中的异常对象匹配到某一个catch时,就进入catch中的异常处理,一旦处理完成,就跳出try-catch结构,继续执行后面的代码(在没有finally的情况下)
* 4. catch中的异常,如果没有子父类关系,谁在上谁在下都可以,如果有字符类关系,则子类在上父类在下。
* 5. 像数据库连接,输入输出流。网络编程等Socket等资源,JVM是不能自动回收的,我们需要自己手动的进行资源的释放,此时资源的释放,就需要声明在finally中
*/
2.3 面试题
finally、final、finalize的区别?
类似
thows和throw、
Collection和Collections、
String和StringBuffer和StringBuilder、
Array List和LinkedList、
HashMap和LinkedHashMap、
重写和重载
/*
* 异常处理方式之二:throws+异常类型
* 1. throws+异常类型 写在方法的声明处。指明在此方法执行时,可能会抛出的异常类型
* 一旦方法体被执行时,出现异常,仍会在代码处生成一个异常类的对象,此对象满足throws后的异常类型时,就会抛出
* 抛出后后续代码不再执行
*/
/* 2. try-catch-finally:真正的将异常给处理掉了
* throws只是将异常抛给了方法的调用者,并没有真正的将异常处理掉
*/
·1. 使用说明
package com.shc.java1;
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
try {
s.regist(-10010);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
// e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println(s);
}
}
class Student{
private int id;
public void regist(int id) throws Exception {
if(id>0) {
this.id = id;
}else {
// System.out.println("输入数据非法");
// throw new RuntimeException("输入非法"); 运行时异常 不需要做处理
// throw new Exception("输入非法"); //编译时异常 需要显示处理
throw new MyException("不能输入负数");
//必须抛出异常类的东西
// throw new String("hh");
//No exception of type String can be thrown; an exception type must be a subclass of Throwable
}
}
}
package com.shc.java1;
/*
* 如何自定义异常类
* 1. 继承于Exception(需要显示处理) / RuntimeEception(不用显示处理)
* 2. 提供全局常量:serialVersionUID(序列号)
* 3. 提供重载的构造器
*/
public class MyException extends RuntimeException{
//序列号
static final long serialVersionUID = -7034897190745766939L;
public MyException() {}
public MyException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
package com.shc.exer1;
import org.junit.Test;
/*
* 编写应用程序EcmDef.java,接收命令行的两个参数,要求不能输入负数,计算
两数相除。
对 数 据 类 型 不 一 致 (NumberFormatException) 、 缺 少 命 令 行 参 数
(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException、除0(ArithmeticException)及输入负数(EcDef 自定义的异常)进行异常处理。
?提示:
(1)在主类(EcmDef)中定义异常方法(ecm)完成两数相除功能。
(2)在main()方法中使用异常处理语句进行异常处理。
(3)在程序中,自定义对应输入负数的异常类(EcDef)。
(4)运行时接受参数 java EcmDef 20 10 //args[0]=“20” args[1]=“10”
(5)Interger类的static方法parseInt(String s)将s转换成对应的int值。
如:int a=Interger.parseInt(“314”); //a=314
//关键点:
// 1. 如何从命令行输入参数?
* Run as -- configuration(配置) -- arguments --- 输入参数
* 2. 如何将输入的字符串转化为数字?
* 一个字符串的一个一个的转化为数字:int i = Integer.parseInt(字符串);
* 注意字符串中不能有字母 NumberFormatException
* 还可能发生的运行时异常:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
* 除0:ArithmeticException
* 3. 自定义异常:输入负数(EcDef 自定义的异常) throw的是编译时异常
*/
public class EcmDef {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
//这里可能会有运行时异常
//对 数 据 类 型 不 一 致 (NumberFormatException) 、 缺 少 命 令 行 参 数(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException)、除0(ArithmeticException)
int i = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);//parse:分析
int j = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int res = ecm(i,j);
System.out.println(res);
}catch(EcDef e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}catch(NumberFormatException e) {
//NumberFormatException 企图将非数字字符转化为数字
// e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("数据类型不一致");
}catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("缺少命令行参数");
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("除0");
}finally {
}
}
public static int ecm(int i,int j) throws EcDef {
if(i<0||j<0) {
throw new EcDef("分子或者分母为负数");
}
return i/j;
}
@Test
public void test1() {
int a = Integer.parseInt("123a");
System.out.println(a);
}
}
package com.shc.exer1;
//自定义异常类
public class EcDef extends Exception{
//序列号
static final long serialVersionUID = -3387516993124229948L;
public EcDef() {}
public EcDef(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/4-Prestar/p/14773013.html