并行与并发:

方式一:继承Thread类,重写run方法
package com.example.demo;
?
public class test_thread extends Thread {
?
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if(i % 2 == 0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程"+i);
}
else if(i==20){
try {
sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
?
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
?
test_thread t1 = new test_thread();
test_thread2 t2 = new test_thread2();
t1.start();
t2.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if(i % 2 == 0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"main线程"+i);
}
?
}
}
}
?
?
class test_thread2 extends Thread {
?
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程" + i);
} else if (i == 20) {
try {
sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
?
启动方式,子类.start()
方式二:实现Runable接口,重写run方法
package com.example.demo;
?
class test_thread4 implements Runnable{
private static int ticket = 100;
如果thread.run()的话,那么输出结果就会变成是main线程执行,因为thread.run只是变成main线程里面调用方法,而不是启动别的线程。
注意事项:
为什么一定要对象.start()实现多线程呢? 先说说结论:首先通过对象.run()方法可以执行方法,但是不是使用的多线程的方式,就是一个普通的方法(main线程调用的方法),要想实现多线程的方式,一定需要通过对象.start()方法。
现在,让我们来看下源码,就一目了然啦。
start方法的源码:
public synchronized void start() {
/**
* This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added
* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.
*
* A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".
*/
// 没有初始化,抛出异常
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
* so that it can be added to the group‘s list of threads
* and the group‘s unstarted count can be decremented. */
group.add(this);
// 是否启动的标识符
boolean started = false;
try {
// start0() 是启动多线程的关键
// 这里会创建一个新的线程,是一个 native 方法
// 执行完成之后,新的线程已经在运行了
start0();
// 主线程执行
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
run方法的源码:就是普通的调用我们重写的run方法
?
真正实现多线程的方法就是start0,看看源码:
private native void start0();
start0 被标记成 native ,也就是本地方法,并不需要我们去实现或者了解,为什么 start0() 会标记成 native?
start()方法里面调用了start0(),该线程并不一定会立即执行,只是线程变成了可运行状态,等cpu执行调度程序,由CPU统一调度
Java是跨平台的,可以在不同的系统上运行,不同的系统可能cpu也不同,所以执行start0()方法交给JVM来实现,自然就标记了Native方法。
真正实现多线程的是start()中的start0()方法,run方法是普通的方法。
为什么使用实现Runable方法多于继承Thread方法呢,因为Java只支持单继承,如果子类继承了Thread的话,那么就不能继承别的类了,可扩展性不高,所以实现多线程方法用实现Runable接口比较多。
实现的方式更适合用来处理多线程共享数据,例如
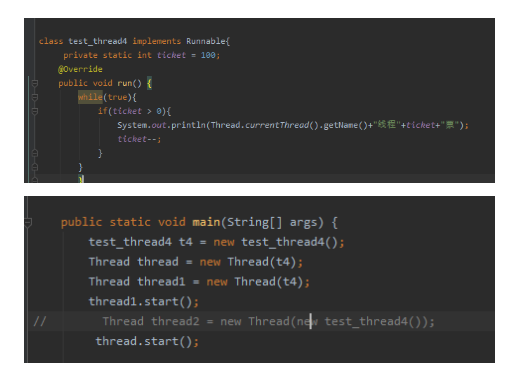
子类只new一次,我们可以创建多个Thread类,将子类对象作为参数传递到Thread类的构造器中,创建Thread类的对象。ticket变量可以被多线程共享,前提是子类对象当作参数传到Thread类的构造器中。
说明:高优先级的线程要抢占低优先级线程cpu的执行权,但是从概率来讲,并不是意味着高优先级执行完才到低优先级来
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/wly2zZ/p/14779042.html