本文是基于jdk8_271版本进行分析的。
ArrayList是Java集合中出场率最多的一个类。底层是基于数组实现,根据元素的增加而动态扩容。如果在创建ArrayList时没有指定Object[]数组的长度,它默认创建一个长度为10的数组。它的线程是不安全的。
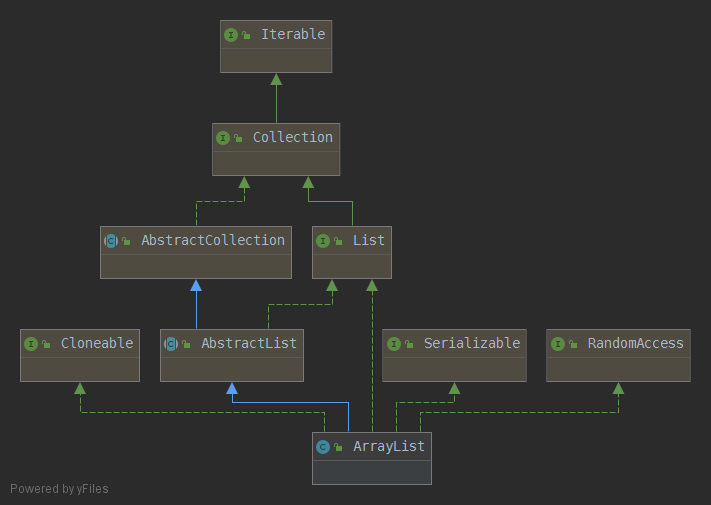
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
1 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; 2 3 /** 4 * Shared empty array instance used for empty instances. 5 */ 6 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; 7 8 /** 9 * Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We 10 * distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when 11 * first element is added. 12 */ 13 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
1 transient Object[] elementData; //存放数组元素,transient表示该字段不进行序列化操作 2 private int size; //数组中实际存放元素的个数
1 //无参构造 2 public ArrayList() { 3 this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 4 } 5 6 //带参构造,指定初始化数组长度 7 public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { 8 if (initialCapacity > 0) { 9 this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; 10 } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { 11 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 12 } else { 13 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity); 14 } 15 } 16 17 //带参构造,传入一个集合元素 18 public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { 19 elementData = c.toArray(); 20 if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { 21 //如果c.toArray返回的不是Object[]类型的数组,转换成Object[]类型 22 if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) 23 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); 24 } else { 25 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 26 } 27 } 28
1 /** 2 * 计算最小的容量大小 3 */ 4 private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { 5 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { 6 // elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,这种情况是无参构造创建的ArrayList对象,还未进行其他操作。如果给定需要的容量值小于默认值会初始化默认容量大小 7 return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); 8 } 9 return minCapacity; 10 } 11 12 /** 13 * 确保容量。如果容量不足会进行扩容处理 14 */ 15 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { 16 ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); 17 } 18 19 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { 20 modCount++; 21 22 // overflow-conscious code 23 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) 24 // 如果计算的最小容量值大于当前数组的长度,表示需要进行扩容 25 grow(minCapacity); 26 } 27 28 /** 29 * 数组最大容量。2147483647-8=2147483639 30 */ 31 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; 32 33 /** 34 * 真正扩容方法 35 */ 36 private void grow(int minCapacity) { 37 // overflow-conscious code 38 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; 39 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); 40 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) 41 newCapacity = minCapacity; 42 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) 43 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); 44 // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: 45 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); 46 } 47 48 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { 49 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow 50 throw new OutOfMemoryError(); 51 return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? 52 Integer.MAX_VALUE : 53 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; 54 }
注意:在进行添加操作之前,都会先进行判断数组是否需要扩容;入参如果涉及索引,还会判断索引是否越界。
1 public boolean add(E e) { 2 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! 3 elementData[size++] = e; 4 return true; 5 } 6 public void add(int index, E element) { 7 rangeCheckForAdd(index); 8 9 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! 10 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,size - index); 11 elementData[index] = element; 12 size++; 13 } 14 15 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { 16 Object[] a = c.toArray(); 17 int numNew = a.length; 18 ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount 19 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); 20 size += numNew; 21 return numNew != 0; 22 } 23 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { 24 rangeCheckForAdd(index); 25 26 Object[] a = c.toArray(); 27 int numNew = a.length; 28 ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount 29 30 int numMoved = size - index; 31 if (numMoved > 0) 32 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, 33 numMoved); 34 35 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); 36 size += numNew; 37 return numNew != 0; 38 }
1 public E remove(int index) { 2 rangeCheck(index); 3 4 modCount++; 5 E oldValue = elementData(index); 6 7 int numMoved = size - index - 1; 8 if (numMoved > 0) 9 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, 10 numMoved); 11 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work 12 13 return oldValue; 14 } 15 public boolean remove(Object o) { 16 if (o == null) { 17 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 18 if (elementData[index] == null) { 19 fastRemove(index); 20 return true; 21 } 22 } else { 23 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 24 if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { 25 fastRemove(index); 26 return true; 27 } 28 } 29 return false; 30 } 31 32 private void fastRemove(int index) { 33 modCount++; 34 int numMoved = size - index - 1; 35 if (numMoved > 0) 36 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, 37 numMoved); 38 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work 39 } 40 41 public void clear() { 42 modCount++; 43 44 // clear to let GC do its work 45 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 46 elementData[i] = null; 47 48 size = 0; 49 } 50 51 protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { 52 modCount++; 53 int numMoved = size - toIndex; 54 System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex, 55 numMoved); 56 57 // clear to let GC do its work 58 int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex); 59 for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) { 60 elementData[i] = null; 61 } 62 size = newSize; 63 } 64 65 //从此列表中删除指定集合c中包含的所有元素 66 public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { 67 Objects.requireNonNull(c); 68 return batchRemove(c, false); 69 } 70 //此列表中仅保留包含在指定集合中的元素 71 public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) { 72 Objects.requireNonNull(c); 73 return batchRemove(c, true); 74 } 75 //ArrayList的批量删除算法 76 private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { 77 final Object[] elementData = this.elementData; 78 int r = 0, w = 0; 79 boolean modified = false; 80 try { 81 for (; r < size; r++) 82 if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) 83 elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; 84 } finally { 85 // Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, 86 // even if c.contains() throws. 87 if (r != size) { 88 System.arraycopy(elementData, r, 89 elementData, w, 90 size - r); 91 w += size - r; 92 } 93 if (w != size) { 94 // clear to let GC do its work 95 for (int i = w; i < size; i++) 96 elementData[i] = null; 97 modCount += size - w; 98 size = w; 99 modified = true; 100 } 101 } 102 return modified; 103 }
1 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) 2 throws java.io.IOException{ 3 // Write out element count, and any hidden stuff 4 int expectedModCount = modCount; 5 s.defaultWriteObject(); 6 7 // Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone() 8 s.writeInt(size); 9 10 // Write out all elements in the proper order. 11 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { 12 s.writeObject(elementData[i]); 13 } 14 15 if (modCount != expectedModCount) { 16 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 17 } 18 } 19 20 private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) 21 throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { 22 elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 23 24 // Read in size, and any hidden stuff 25 s.defaultReadObject(); 26 27 // Read in capacity 28 s.readInt(); // ignored 29 30 if (size > 0) { 31 // be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity 32 ensureCapacityInternal(size); 33 34 Object[] a = elementData; 35 // Read in all elements in the proper order. 36 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { 37 a[i] = s.readObject(); 38 } 39 } 40 }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Y2EX/p/14784959.html