
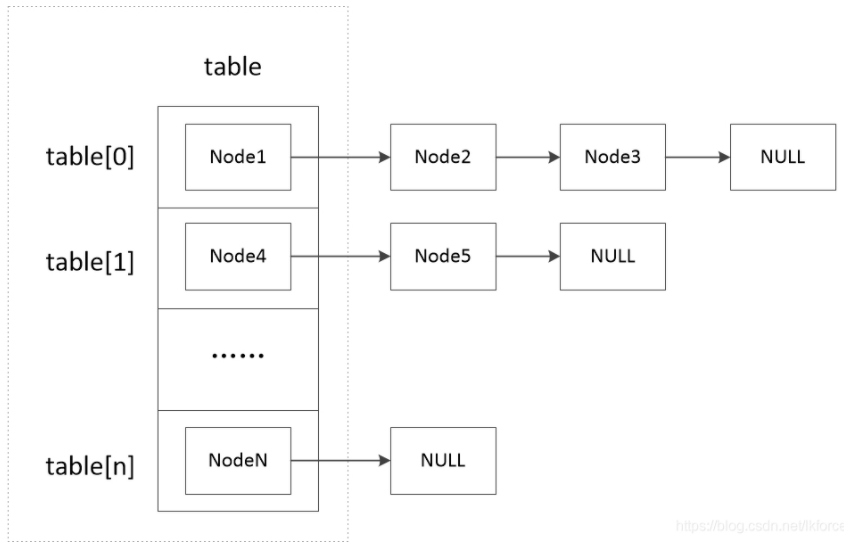
1 public V put(K key, V value) { 2 return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); 3 } 4 //散列算法计算key的hash值 5 static final int hash(Object key) { 6 int h; 7 return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); 8 } 9 10 final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, 11 boolean evict) { 12 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; 13 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) 14 n = (tab = resize()).length; 【注释1】 15 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) 【注释2】 16 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 17 else { 18 Node<K,V> e; K k; 19 if (p.hash == hash && 20 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 【注释3】 21 e = p; 22 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) 【注释4】 23 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); 24 else { 25 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { 26 if ((e = p.next) == null) { 27 p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 【注释6】 28 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st 29 treeifyBin(tab, hash); 【注释7】 30 break; 31 } 32 if (e.hash == hash && 33 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 34 break; 【注释5】 35 p = e; 36 } 37 } 38 if (e != null) { 【注释30】 39 V oldValue = e.value; 40 if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) 41 e.value = value; 42 afterNodeAccess(e); 43 return oldValue; 44 } 45 } 46 ++modCount; 47 if (++size > threshold) 【注释8】 48 resize(); 49 afterNodeInsertion(evict); 50 return null; 51 }
1 public V get(Object key) { 2 Node<K,V> e; 3 return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; 4 } 5 6 final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { 7 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; 8 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && 9 (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 10 if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node 11 ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 12 return first; 【注释1】 13 if ((e = first.next) != null) { 14 if (first instanceof TreeNode) 15 return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); 【注释2】 16 do { 【注释3】 17 if (e.hash == hash && 18 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 19 return e; 20 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 21 } 22 } 23 return null; 24 } 25 26 final TreeNode<K,V> getTreeNode(int h, Object k) { 27 return ((parent != null) ? root() : this).find(h, k, null); 28 }
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
文章定期同步更新于公众号【小大白日志】,欢迎关注公众号:

原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/afei1759/p/14792094.html